(Press-News.org) The oxytocin system – which helps release breast milk and strengthens the bond between mother and baby – may be affected during breastfeeding in mothers experiencing postnatal depression, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The new research, published in Psychoneuroendocrinology, investigated the link between maternal mood and the oxytocin pathway during breastfeeding, in mothers with and without symptoms of postnatal depression.
Oxytocin is a hormone that is released in both the brain and body. It plays a central role in childbirth and breastfeeding, and is involved in social relationships, especially intimacy, and the attachment process during infancy.
In breastfeeding, oxytocin triggers the ‘let-down’ reflex that releases the mother’s milk and is stimulated in both mothers and their baby by skin-to-skin touch.
Oxytocin release also interacts with specific brain regions to reduce stress and stimulate reward associated with this, facilitating mother-infant bonding and early infant development.
Mothers experiencing postnatal depression report increased stress during breastfeeding and early weaning. Although the social context related to a mother’s depression likely contributes to this, it has not been known whether the oxytocin system may also be affected.
In the UK, postnatal depression affects more than one in every 10 women within a year of giving birth, symptoms include persistent low mood, feeling agitated or irritable, and trouble sleeping,
For the new study, 62 new mothers aged between 23 and 44 years old, who had an infant between three and nine months old, were each given a nasal spray prior to breastfeeding, containing either oxytocin or a placebo.
Breast milk samples were collected during breastfeeding and analysed for oxytocin. The team found that oxytocin levels in breast milk were not affected by mothers’ mood at baseline.
However, while oxytocin was seen to increase in the breast milk of women without postnatal depression after using a nasal spray containing the hormone, this effect was reduced in mothers experiencing postnatal depression.
Lead author, Dr Kate Lindley Baron-Cohen (UCL Psychology & Language Sciences) said: “Our findings indicate that the oxytocin system is affected by postnatal depression in new mothers in the context of breastfeeding. Since higher levels of oxytocin in mothers are associated with positive outcomes in a child’s social development and in their mental health, these results point to a possible pathway through which infants of mothers experiencing postnatal depression may be at greater risk of later mental health vulnerabilities.”
These findings indicate a new direction for research, to further explore how oxytocin is affected in postnatal depression, and what the most effective treatment could be to support mothers who would like to breastfeed but are experiencing challenges.
The research was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research ARC North Thames, the Lord Leonard and Lady Estelle Wolfson Foundation, Wellcome, the University of York, the Fund for Psychoanalytic Research through the American Psychoanalytic Association, the International Psychoanalytical Association, the Michael Samuel Charitable Trust, the Denman Charitable Trust, and the Galvani Foundation.
END
Oxytocin system of breastfeeding affected in mothers with postnatal depression
2025-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
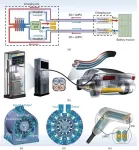
Liquid metal-enabled synergetic cooling and charging: a leap forward for electric vehicles
2025-03-14
A recent study published in Engineering presents a novel approach to address the challenges of high-power direct current fast charging (DC-HPC) in electric vehicles (EVs). The research, led by a team from China Agricultural University, focuses on developing a synergetic cooling and charging strategy using a gallium-based liquid metal flexible charging connector (LMFCC).
As the demand for EVs grows, DC-HPC technology, especially for megawatt-level charging currents (≥1000 A), is crucial for reducing charging time. However, it brings the ...
Defensive firearm use is far less common than exposure to gun violence
2025-03-14
Those with access to firearms rarely use their weapon to defend themselves, and instead are far more likely to be exposed to gun violence in other ways, according to a Rutgers Health study.
An overwhelming majority of firearm users, or about 92%, indicated they never have used their weapons to defend themselves, with less than 1% say they did in the previous year, a new study by the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center found.
“Adults with firearm access are far more likely to be exposed to gun violence than they are to defend themselves with their firearms,” ...
Lifetime and past-year defensive gun use
2025-03-14
About The Study: In this survey of adults with firearm access, defensive gun use (DGU) was rare relative to gun violence exposure. Perceived threats may not necessitate DGU, and given the association between DGU and gun violence exposure, the consequences of DGU may be substantial. Narratives centering DGU as a consideration in firearm policies may misstate the risk profile of firearm access.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Michael D. Anestis, PhD, email mda141@sph.rutgers.edu.
To access the ...
Lifetime health effects and cost-effectiveness of tirzepatide and semaglutide in US adults
2025-03-14
About The Study: This economic evaluation found that although tirzepatide and semaglutide offered substantial long-term health benefits, they were not cost-effective at current net prices. Efforts to reduce the net prices of new anti-obesity medications are essential to ensure equitable access to highly effective anti-obesity medications.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jennifer H. Hwang, DO, email jennifer.hwang2@bsd.uchicago.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.5586)
Editor’s ...
New members of the CDKL family of genes linked to neurodevelopmental disorders
2025-03-14
CDKL5, one of the five members of the CDKL family of genes, is important for proper neurodevelopment and associated with seizures. However, the role the other four members of this family play in health and disease is unknown.
A team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital has deepened our understanding of two other members of the CDKL family, CDKL2 and CDKL1. The labs of Drs. Oguz Kanca and Hugo Bellen show that ...
Advancements in organ preservation: paving the way for better transplantation outcomes
2025-03-14
A review article published in Engineering delves into the crucial field of organ preservation, exploring its history, current techniques, and future prospects. The shortage of donor organs remains a significant global challenge, with only about 10% of the global demand for organ transplantation being met, as stated by the World Health Organization. This shortage is further exacerbated by the limitations of current organ preservation methods.
Currently, the main clinical methods for organ preservation are static cold storage (SCS) and machine perfusion (MP). SCS, which involves storing organs in a preservation solution at low temperatures (usually 4 °C), is simple and ...
Pitt study makes new insights into the origins of ovarian cancer
2025-03-14
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have identified a novel trigger of a deadly form of ovarian cancer: a subset of progenitor cells that reside in fallopian tube supportive tissue, or stroma.
The discovery of these high-risk cells, described in a new study published today in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, could pave the way for better approaches to prevent and detect high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC), the most common form of ovarian cancer, which kills more than 12,000 women in the U.S. each year.
“Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecologic cancer in the Western world, but we currently ...
Topical steroid withdrawal diagnostic criteria defined by NIH researchers
2025-03-14
WHAT:
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have determined that dermatitis resulting from topical steroid withdrawal (TSW) is distinct from eczema and is caused by an excess of an essential chemical compound in the body. Scientists from NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) identified treatments that could be studied in clinical trials for the condition based on their potential to lower levels of the chemical compound—called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a form of ...
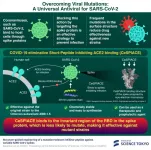
CeSPIACE: A broad-spectrum peptide inhibitor against variable SARS-CoV-2 spikes
2025-03-14
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, infects cells by binding its spike protein to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors. Blocking this interaction with inhibitors could prevent infection. Since these inhibitors act directly on the virus without affecting human cells, they may be safer than some existing treatments. However, mutations in the spike protein can alter its structure, reducing the effectiveness of these inhibitors.
In a significant breakthrough, a research team led by Professor Yoshinori Fujiyoshi ...
Understanding the origin of magnetic moment enhancement in novel alloys
2025-03-14
Magnetic materials have become indispensable to various technologies that support our modern society, such as data storage devices, electric motors, and magnetic sensors. High-magnetization ferromagnets are especially important for the development of next-generation spintronics, sensors, and high-density data storage technologies. Among these materials, the iron-cobalt (Fe-Co) alloy is widely used due to its strong magnetic properties. However, there is a limit to how much their performance can be improved, necessitating a new approach.
Some of the earlier studies have shown that epitaxially grown films made up of Fe-Co alloys doped with heavier elements exhibit remarkably high ...