(Press-News.org) The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) is opening 12 postdoctoral positions for international researchers, with a specific focus on American scholars working in socially significant fields. These prestigious fellowships come with substantial funding (€2.5 million) as part of the European Marie Skłodowska-Curie (MSCA) program. Additionally, as part of the Brains for Brussels initiative, VUB aims to actively attract American professors looking to relocate. In collaboration with its Francophone sister university ULB, VUB is also providing 18 apartments for international researchers seeking temporary residence at the Brussels Institute for Advanced Studies.
VUB's initiative is a response to the alarming political interference in academic research by the Trump administration in the U.S. The university is taking a firm stand against these developments. "Our university is freeing up funds and establishing a dedicated contact point for American researchers who want to continue their work in Brussels," says VUB Rector Jan Danckaert. "U.S. universities and their scholars are the biggest victims of this political and ideological interference. They are seeing millions in research funding disappear for ideological reasons. European universities are also being affected. The Vrije Universiteit Brussel has already experienced this firsthand, becoming one of the first Flemish institutions impacted by the Trump administration. Recently, two research projects we had approved in collaboration with U.S. partners were canceled due to 'changed policy priorities.' One project focused on Youth and Disinformation, while the other explored the Transatlantic Dialogue between the U.S. and Europe."
"As a European pioneer in climate research, in-vitro fertilization (IVF), artificial intelligence (AI), and geopolitical security, VUB offers an excellent environment where top American researchers can work freely," Rector Danckaert emphasizes. "Our university is committed to actively supporting free academic inquiry. VUB was founded in 1834 precisely to safeguard academic freedom, free from interference by church or state. We see it as our duty to assist our American colleagues."
Following the terrorist attacks of March 22, 2016, in Brussels, then-President Trump famously referred to the Belgian capital, specifically the Brussels district of Sint-Jans-Molenbeek, as a "hellhole," a remark that sparked strong emotional reactions across Europe. This makes VUB's initiative even more symbolically significant.
To assist American researchers, VUB is launching a revamped website featuring its academic job openings (academicpositions.com/employer/vrije-universiteit-brussel). Additionally, VUB has set up a dedicated contact point (research.welcome@vub.be) where U.S. researchers can find information about research programs, visa applications, and life and work in Brussels.
END
Free University Brussels (VUB) opens its doors to censored American researchers
University allocates funding and contact point for U.S. scholars looking to relocate to Brussels
2025-03-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
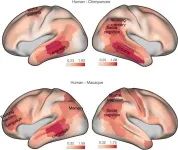
Neuroanatomy that sets humans apart from other primates
2025-03-17
Researchers have widely accepted that what sets humans apart from nonhuman primates are prefrontal cortex–driven behaviors such as decision-making, reasoning, planning, and attention. In a new JNeurosci paper, research led by Rogier Mars, at University of Oxford, and Katherine Bryant, at Aix-Marseille University, provides a better picture of the cortical evolution that distinguishes human brains from other primates.
The researchers compared cortical organization not only between humans and macaques, which is a standard for human and nonhuman primate ...
Stress and sex influence traumatic brain injury outcomes
2025-03-17
How stress impacts behavioral outcomes of traumatic brain injury (TBI) represents a major gap in knowledge. This oversight is especially felt by those in the military due to the high prevalence of TBI and the abundance of stress that they endure. In a study funded by the US Department of Defense, researchers led by Pamela VandeVord at Virginia Tech discovered that prior stress exposure influences TBI outcomes in a sex-dependent manner.
In their eNeuro paper, VandeVord and colleagues used an unpredictable stress paradigm ...
Study: suppressing key protein may unlock immunotherapy for Glioblastoma
2025-03-17
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL MARCH 17, 2025, AT NOON EDT) – Glioblastoma has remained one of the toughest cancers to treat, resisting even the latest advances in immunotherapy. But new research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, suggests a way forward: suppressing a protein called ZNF638 triggers an antiviral immune response, making immune checkpoint inhibitors more effective. The discovery not only offers a potential new treatment strategy but also identifies ...
Early surgical intervention in children with sleep-disordered breathing reduces need for doctor visits, prescriptions
2025-03-17
In a randomized trial, Mass General Brigham researchers found the surgical removal of tonsils and adenoids was effective for children with snoring and mild sleep apnea
An estimated 6 to 17 percent of children have sleep-disordered breathing, ranging from snoring to sleep apnea, which can cause behavioral, neurocognitive, cardiovascular, and cardiometabolic issues. A new study from Mass General Brigham researchers reveals that adenotonsillectomy—the surgical removal of tonsils and adenoids—is an effective early intervention for these children. Their results are published in JAMA Pediatrics.
“To ...
Statin use and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease
2025-03-17
About The Study: This cohort study found that statin use was associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation in patients with chronic liver disease. These findings provide support for the potential role of statins in prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver disease progression.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Jonggi Choi, MD, PhD, (j.choi@amc.seoul.kr) and Raymond T. Chung, MD, (chung.raymond@mgh.harvard.edu).
To ...
Gender-affirming hormone therapy and depressive symptoms among transgender adults
2025-03-17
About The Study: In this longitudinal observational cohort study, gender-affirming hormone therapy was associated with lower rates of moderate-to-severe depressive symptoms, highlighting the importance of gender-affirming primary care models for transgender, nonbinary, and gender diverse patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sari L. Reisner, ScD, MA, email sreisner@umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.0955)
Editor’s ...
Surgery in kids with mild sleep-disordered breathing tied to fewer doctor visits, meds
2025-03-17
What: Surgical removal of enlarged tonsils and adenoids in children with mild sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) appears to significantly reduce the frequency of medical office visits and prescription medicine use in this group, according to a clinical study supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The findings, published in JAMA Pediatrics, show that the surgery, called adenotonsillectomy, was tied to a 32% reduction in medical visits and a 48% reduction in prescription use among children with a mild form of the condition.
SDB refers to breathing disturbances during sleep ...
Magnetic microalgae on a mission to become robots
2025-03-17
Stuttgart – A team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) in Stuttgart developed a biohybrid micro swimmer covered with magnetic material, whose swimming ability is largely unaffected by the coating. The team from the Physical Intelligence Department at MPI-IS published their work in the journal Matter, which covers a wide range of materials science research.
In nature, the ten-micron small, single-cell microalgae are fantastic swimmers, propelled by their two whip-like ...
Impact journals to participate at the AACR Annual Meeting 2025
2025-03-17
Impact Journals is proud to participate in the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025, taking place April 25-30 in Chicago, Illinois.
BUFFALO, NY- March 17, 2025 – Impact Journals is pleased to announce its participation as an exhibitor at the upcoming American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025. The meeting is scheduled for April 25-30, 2025, at the McCormick Place Convention Center in Chicago, Illinois.
The 2025 AACR Annual Meeting theme, “Unifying Cancer Science and Medicine: A Continuum of Innovation ...
Webb telescope captures its first direct images of carbon dioxide outside solar system
2025-03-17
The James Webb Space Telescope has captured its first direct images of carbon dioxide in a planet outside the solar system in HR 8799, a multiplanet system 130 light-years away that has long been a key target for planet formation studies.
The observations provide strong evidence that the system’s four giant planets formed in much the same way as Jupiter and Saturn, by slowly building solid cores. They also confirm Webb can do more than infer atmospheric composition from starlight measurements—it can directly analyze the chemistry ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
[Press-News.org] Free University Brussels (VUB) opens its doors to censored American researchersUniversity allocates funding and contact point for U.S. scholars looking to relocate to Brussels