(Press-News.org) The American College of Cardiology (ACC) has issued its first Concise Clinical Guidance (CCG) to create more streamlined and efficient processes to implement best practices in patient care. This CCG focuses on evaluating and managing cardiogenic shock (CS), addressing important questions around clinical decision-making and providing actionable guidance for health care providers.
“ACC has a long history of developing clinical policy to complement clinical practice guidelines and to inform clinicians about areas where evidence is new and evolving or where randomized data is more limited. Despite this, numerous gaps persist in the evaluation and management of CS,” said Shashank S. Sinha, MD, MSc, FACC, writing committee chair and advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Inova Fairfax Medical Campus. Dr Sinha serves as Director, Cardiogenic Shock Program, Inova Health System; Medical Director of the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit, Cardiology; and Director of the Cardiovascular Critical Care Research Program. “Concise Clinical Guidance represents a key component of solution sets. They are highly focused, limited in scope, and aim to illustrate clinical decision-making processes using figures, tables, and checklists. They address patient populations who share certain characteristics, such as critically ill conditions like CS.”
CS is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the body’s organs, resulting in hypotension (low blood pressure) and multi-organ damage or failure. CS has a high in-hospital mortality rate, ranging from 30 to 50%, and is one of the most common causes of cardiac intensive care admission.
The CCG addresses the importance of early recognition of CS for improving patient outcomes, providing comprehensive recommendations for its initial assessment, introducing a new mnemonic, SUSPECT CS, which includes laboratory markers along with clinical assessment for congestion—such as pulmonary edema, jugular venous distension and peripheral edema—and hypoperfusion.
“These markers should include a complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel, cardiac biomarkers including troponin and natriuretic peptides, lactic acid and arterial or venous blood gas,” Sinha said. “Once CS is suspected, a 12-lead electrocardiogram, chest radiography—and a transthoracic echocardiogram and/or point-of-care ultrasound, if available—should be completed as soon as possible.”
Other recommendations outlined in the CCG include invasive hemodynamic monitoring via pulmonary artery catheter for both the diagnosis and management of CS. It provides guidance on the medical management of CS with a focus on maintaining tissue perfusion to preserve organ performance. It also provides guidance on what to do when end-organ perfusion cannot be maintained with pharmacological interventions alone with escalation to temporary mechanical circulatory support.
For the first time, the CCG provides a one hour and 24-hour roadmap for clinicians on the evaluation and management of CS. In addition, it provides recommendations for the pharmacological and temporary mechanical circulatory support treatment for CS, highlights the need for ongoing patient monitoring, reassessment and follow-up, and provides guidance for the decision-making around a patient’s candidacy for advanced therapies, heart recovery or transfers to advanced heart failure centers. It also underscores the importance of interdisciplinary, team-based collaboration for the care of patients with CS.
“Community-based centers with limited resources should identify an on-site clinician to serve as their ‘shock champion’ as well as a center providing advanced heart failure therapies to partner with on complex CS cases,” Sinha said. “These partnerships are a key ingredient to successful strategies for managing this complex syndrome.”
The 2025 Concise Clinical Guidance: An ACC Expert Consensus Statement on the Evaluation and Management of Cardiogenic Shock will be published in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A session at the ACC’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25), taking place March 29 – 31 in Chicago, will introduce CCGs as a new clinical policy format for the ACC and will formally present this document as the first publication to use the format. The session, ACC’s Solutions Sets: Real-Time Support for the Frontline Cardiovascular Clinician, will take place on Monday, March 31 at 11:30 a.m. CT / 12:30 p.m. ET.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org.
The ACC’s JACC Journals rank among the top cardiovascular journals in the world for scientific impact. The flagship journal, the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) — and specialty journals consisting of JACC: Advances, JACC: Asia, JACC: Basic to Translational Science, JACC: CardioOncology, JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, JACC: Case Reports, JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology and JACC: Heart Failure — pride themselves on publishing the top peer-reviewed research on all aspects of cardiovascular disease. Learn more at JACC.org.
###
END
A new analysis led by surgeons at UCLA Health finds that psychological prehabilitation can significantly enhance recovery after surgery. The research, led by Anne E. Hall in the lab of Dr. Justine Lee analyzed data from 20 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) conducted between 2004 and 2024, involving a total of 2,376 patients. It is published in the Annals of Surgery
What is Psychological Prehabilitation? Prehabilitation is a proactive approach aimed at improving surgical outcomes through preventive measures. Traditionally, ...
Trial of strength at the cellular level: cells are in constant competition with each other and so eliminate diseased or unwanted cells. Cell competition is therefore a central principle for maintaining the health of tissues and organs. Researchers have investigated the success factors of superior cells and discovered a previously unknown winning strategy in mechanical cell competition. They identified a variety in the ability of cells to exert mechanical forces onto other cells as the decisive regulator. With their results ...
Milan, Italy – March 2025 – The Italian Association of Science Writers, SWIM, has announced an extension of the application deadline for the 2025 SWIM Award. Candidates now have until March 31, 2025, at 23:59 CET to submit their applications for the prestigious award, which has been recognizing excellence and innovation in science journalism in Italy since 2021.
The SWIM Award highlights the critical role of science journalists in fostering public understanding and dialogue on scientific issues. The competition also serves as the Italian selection process for the European ...
On first inspection, the Cuban blue-headed quail dove doesn’t look like much: drab brown feathers, a slender beak, a pronounced strut in their walk typical of most other doves. You’d be forgiven for overlooking it in favor of Cuba’s prismatic parrots. But looks aren’t everything. For decades, this unassuming bird has perplexed biologists, who have no idea where it came from, how it got to the island or what it’s related to.
Now, for the first time, scientists have sequenced DNA from the blue-headed quail dove with the goal of finally getting to the bottom of things. Instead, they’re even more perplexed now than when they started.
“This ...
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) is opening 12 postdoctoral positions for international researchers, with a specific focus on American scholars working in socially significant fields. These prestigious fellowships come with substantial funding (€2.5 million) as part of the European Marie Skłodowska-Curie (MSCA) program. Additionally, as part of the Brains for Brussels initiative, VUB aims to actively attract American professors looking to relocate. In collaboration with its Francophone sister university ULB, VUB is also providing 18 apartments for international ...
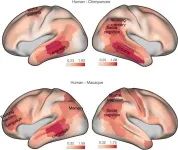
Researchers have widely accepted that what sets humans apart from nonhuman primates are prefrontal cortex–driven behaviors such as decision-making, reasoning, planning, and attention. In a new JNeurosci paper, research led by Rogier Mars, at University of Oxford, and Katherine Bryant, at Aix-Marseille University, provides a better picture of the cortical evolution that distinguishes human brains from other primates.
The researchers compared cortical organization not only between humans and macaques, which is a standard for human and nonhuman primate ...
How stress impacts behavioral outcomes of traumatic brain injury (TBI) represents a major gap in knowledge. This oversight is especially felt by those in the military due to the high prevalence of TBI and the abundance of stress that they endure. In a study funded by the US Department of Defense, researchers led by Pamela VandeVord at Virginia Tech discovered that prior stress exposure influences TBI outcomes in a sex-dependent manner.
In their eNeuro paper, VandeVord and colleagues used an unpredictable stress paradigm ...
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL MARCH 17, 2025, AT NOON EDT) – Glioblastoma has remained one of the toughest cancers to treat, resisting even the latest advances in immunotherapy. But new research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, suggests a way forward: suppressing a protein called ZNF638 triggers an antiviral immune response, making immune checkpoint inhibitors more effective. The discovery not only offers a potential new treatment strategy but also identifies ...
In a randomized trial, Mass General Brigham researchers found the surgical removal of tonsils and adenoids was effective for children with snoring and mild sleep apnea
An estimated 6 to 17 percent of children have sleep-disordered breathing, ranging from snoring to sleep apnea, which can cause behavioral, neurocognitive, cardiovascular, and cardiometabolic issues. A new study from Mass General Brigham researchers reveals that adenotonsillectomy—the surgical removal of tonsils and adenoids—is an effective early intervention for these children. Their results are published in JAMA Pediatrics.
“To ...
About The Study: This cohort study found that statin use was associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation in patients with chronic liver disease. These findings provide support for the potential role of statins in prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver disease progression.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Jonggi Choi, MD, PhD, (j.choi@amc.seoul.kr) and Raymond T. Chung, MD, (chung.raymond@mgh.harvard.edu).
To ...