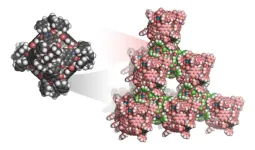
(Press-News.org) Researchers from Kyoto University have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in materials science by developing the world's first three-dimensional van der Waals open frameworks (WaaFs). This innovation challenges the conventional belief that van der Waals interactions are too weak for open framework materials, demonstrating their potential for stable and highly porous materials.
Published in Nature Chemistry, the study presents a strategy using octahedral metal-organic polyhedra (MOPs) as building blocks to construct WaaFs. These frameworks exhibit high thermal stability, exceptional porosity, and reversible assembly, opening new avenues for applications in gas storage, separation, and catalysis. WaaFs utilize van der Waals interactions, which were previously considered too weak, to form robust three-dimensional frameworks. These structures maintain their integrity at temperatures up to 593 K and achieve surface areas exceeding 2,000 m²/g, making them highly stable and efficient for various industrial applications. Moreover, WaaFs can be disassembled and reassembled in solution, allowing for scalable production and recyclability, a feature that enhances their practicality. Given their tunable porosity and chemical stability, WaaFs hold significant promise for gas storage, carbon capture, water harvesting, and catalytic applications.
Professor Shuhei Furukawa of Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) emphasized the broader impact of this breakthrough, stating, "Our research challenges the long-standing assumption that van der Waals forces are too weak to construct stable frameworks. Through careful supramolecular design, we have demonstrated that these interactions can be harnessed to create robust and highly porous materials with practical applications."
Mr. Shun Tokuda, lead researcher of the study, added, "This discovery redefines the design principles of porous materials, showcasing a new approach to material engineering that enables both scalability and recyclability. WaaFs offer an innovative solution for gas separation, storage, and beyond."
###
Paper:
“Three-dimensional van der Waals open frameworks”
Nature Chemistry|https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-025-01777-0
About Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS):
At iCeMS, our mission is to explore the secrets of life by creating compounds to control cells, and further down the road to create life-inspired materials.
https://www.icems.kyoto-u.ac.jp/
For more information, contact:
Izumi Mindy Takamiya
cd@mail2.adm.kyoto-u.ac.jp
END
Revolutionary van der Waals open frameworks: a new era in porous materials
Van der Waals forces, once deemed too weak for structural integrity, have been shown to create stable, highly porous frameworks with exceptional thermal resilience and reversible assembly, paving the way for scalable and recyclable materials
2025-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
“Significant proportion” of world’s rural population missing from global estimates, says study
2025-03-18
Global population datasets, crucial for decision-making by governments and institutions, may underestimate rural populations by as much as 53% to 84%, reveals an Aalto University study.
Governments, international bodies and researchers rely on global population data for resource allocation and infrastructure planning to disease epidemiology and disaster risk management. In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Aalto University in Finland show the profound and systematic extent to which these datasets underestimate ...
Genetic study reveals hidden chapter in human evolution
2025-03-18
Modern humans descended from not one, but at least two ancestral populations that drifted apart and later reconnected, long before modern humans spread across the globe.
Using advanced analysis based on full genome sequences, researchers from the University of Cambridge have found evidence that modern humans are the result of a genetic mixing event between two ancient populations that diverged around 1.5 million years ago. About 300,000 years ago, these groups came back together, with one group contributing 80% of the genetic makeup of modern humans and the other contributing 20%.
For the last two decades, the prevailing view in human evolutionary genetics has been that Homo sapiens first ...
New AI tool visualizes a cell’s ‘social network’ to help treat cancer
2025-03-18
A first-of-its-kind artificial intelligence (AI)-based neural network can rapidly analyse and interpret millions of cells from a patient sample, predicting molecular changes in the tissue. It can potentially pinpoint where personalised treatments could be most effective for conditions such as cancer.
NicheCompass leverages the power of generative AI to create a visual database combining spatial genomic data on cell types, where they are found, and how they communicate. Created by researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the Institute of AI for Health ...
New ‘shy’ fungus found in old-growth forest
2025-03-18
Although fungi of the genus Piloderma are common, scientists have now discovered five previously unknown species. One of these is one of the most widely distributed species in Northern Europe, while another is found only in old-growth forests. The discoveries, published in Fungal Biology, show that diversity in this genus is much greater than previously thought and that some of its species are at risk of disappearing as old-growth forest is logged.
Many of the fungi of the genus Piloderma are among the most common fungal species ...
Some nicotine pouch flavors much more addictive than others
2025-03-18
A new paper in Nicotine & Tobacco Research, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that different nicotine pouches, which have become very popular in recent years, particularly among young people, may influence user preferences very differently. An investigation using rats finds some flavors lead to much more nicotine consumption than others.
According to the World Health Organization, tobacco use remains a major global health threat, with 1.3 billion tobacco users, and 8 million tobacco-related deaths annually. ...
Low doses of antibiotic work just as well as higher ones to treat rare type of chronic hair loss
2025-03-18
Small amounts of a common antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drug can curb symptoms where a misplaced immune reaction (e.g., autoimmunity) can cause permanent hair loss, a new study shows. This regimen may also come with fewer side effects than higher doses of the medication.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the study explored lymphocytic scarring alopecia, a rare skin condition in which the body’s immune cells damage hair follicles, leading to hair loss and scarring. Physicians typically treat this chronic disorder with relatively high doses of the antibiotic doxycycline, often ...
Social media pressures could make friendship a full-time job
2025-03-18
Friendships are critical parts of our lives. Staying in touch with friends online is crucially important, especially for teenagers. Fostering friendships online, however, takes time and might require near constant availability, which can cause digital stress that can arise when expectations on social media are not met. This in turn, can lead to conflicts among friends.
New research published in Frontiers in Digital Health by scientists in Italy highlights how social media expectations within friend groups and digital stress shape adolescent friendships and conflicts over time.
“We show that adolescents’ perceptions of social media norms and perceptions of unique features ...
CD2AP and Alzheimer’s disease: A key regulator of neurodegeneration and potential therapeutic target
2025-03-18
XIAMEN, China, 18 March 2025 – A groundbreaking peer-reviewed Thought Leaders Invited Review article in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press, New York) explores how CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) contributes to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), one of the most devastating neurodegenerative disorders affecting millions worldwide. CD2AP, initially identified for its role in cellular transport and cytoskeletal architecture, has now emerged as a crucial factor in AD pathology.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have established CD2AP as a major genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease ...
Maternal infection disrupts newborn brain development: A link to neurodevelopmental disorders
2025-03-18
BRATISLAVA, Slovakia, 18 March 2025 – A pioneering peer-reviewed research study published in Brain Medicine provides compelling evidence that maternal infections during pregnancy can have lasting effects on offspring brain function. Researchers from the Slovak Academy of Sciences investigated the impact of maternal immune activation (MIA) on hippocampal pyramidal neurons in newborn rat offspring and found that prenatal inflammation significantly impairs neuronal excitability. These changes in brain function may underlie the increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders associated with maternal infections.
“Maternal ...
inait announces collaboration with Microsoft to deploy novel AI based on digital brains across industries
2025-03-18
Zürich/Lausanne, Switzerland – 18 March 2025 – inait today announced a collaboration with Microsoft to accelerate the development and commercialization of inait’s innovative AI technology, using its unique digital brain AI platform. The collaboration will focus on joint product development, go-to-market strategies, and co-selling initiatives, initially targeting the finance and robotics sectors.
inait's AI technology, born from decades of neuroscience research offers a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence. Its “brain programming language” and ability to learn from experience and understand cause and effect delivers cognitive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Revolutionary van der Waals open frameworks: a new era in porous materialsVan der Waals forces, once deemed too weak for structural integrity, have been shown to create stable, highly porous frameworks with exceptional thermal resilience and reversible assembly, paving the way for scalable and recyclable materials