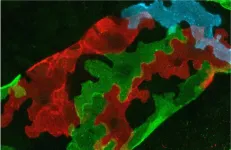
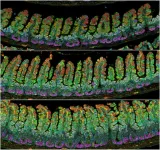
(Press-News.org) The cells that make up the walls of the finest of all lymphatic vessels have a lobate, oak leaf-like shape that makes them particularly resilient to changes in fluid volume. A similar cell shape also supports mechanical stability in plants. This has been shown by researchers from Uppsala University in a new article published in the journal Nature.
The lymphatic system consists of a network of lymph vessels that maintains the body’s fluid balance and supports the immune system. The finest of all these lymphatic vessels are called lymph capillaries. They have walls that are made up of just a single layer of lymphatic endothelial cells that are permeable to fluids, cells and large molecules from surrounding tissues for transport to other parts of the body. These vessels need to be able to let fluid through efficiently while also being resilient to sudden changes in fluid volume in the surrounding tissue, such as in the case of swelling, without rupturing.
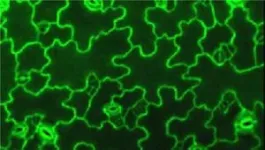
Stretched cells took on a lobate shape
In the current study, the researchers investigated how the thin layer of lymphatic endothelial cells can withstand changes in vessel calibre when the capillary takes up fluid. This turned out to be due to the cells’ capacity to continuously change their peculiar shape.
“It has been known for a long time that capillary lymphatic endothelial cells have a lobate shape, rather like oak leaves or jigsaw puzzle pieces. However, the reason for this unique morphology was not known, and it had never previously been successfully replicated in cultured cells. In our study, we exposed a thin layer of cultured lymphatic endothelial cells to repeated multidirectional stretching and found that the cells began to acquire a lobate appearance. There was also a greater overlap between the cells, which meant that each cell’s contact surface with their neighbouring cells increased,” says Taija Makinen, professor at Uppsala University, who led the study.
Similar to the cells in plant leaves
Lobate shapes can also be found in a completely different type of cell – those on the surfaces of plant leaves. There, their role is to withstand turgor pressure, i.e. the fluid pressure required for plants to grow and hold themselves upright.
“The lobate shape of the plant cells is controlled by a specific signalling pathway and a corresponding pathway is also present in lymphatic endothelial cells. When we tested blocking this signalling pathway in cultured cells, the stretch-induced overlap between the cells was reduced,” says Taija Mäkinen and continues:
“In mice that lack one of the signalling molecules in the pathway, not only was the shape of the lymphatic endothelial cells altered but the integrity and function of the lymphatic capillaries was also impaired. This indicates that the lymphatic capillaries need this overlap for the vessel to be able to expand without rupturing when the fluid pressure rises,” says Taija Mäkinen.
The lobate appearance of both plant cells and mammalian lymphatic endothelial cells stands out as a distinctive feature among the diversity of cell shapes that have been observed in nature. The researchers have interpreted the results from their study as this shape being due to their specialised function: to be able to withstand changes in fluid volumes. This reveals a biological design principle that exists in very diverse species to increase structural stability.”
Contact
Taija Mäkinen, Professor at the Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University.
+46 18 471 41 51, +46 70 425 03 60, taija.makinen@igp.uu.se
END
Unique cell shape keeps lymphatic vessels and plant leaves stable
2025-03-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New understanding of B cell mutation strategies could have implications for vaccines
2025-03-19
A vaccine's ability to generate long-lasting, high-affinity antibodies hinges on a delicate balance. Upon exposure to a vaccine or pathogen, B cells scramble to refine their defenses, rapidly mutating in hopes of generating the most effective antibodies. But each round of this process is a roll of the genetic dice—every mutation has the potential to improve affinity; far more often, however, it degrades or destroys a functional antibody. How do high-affinity B cells ever beat the odds?
New research now suggests that B cells avoid gambling away good mutations by strategically banking successful ones. As described in Nature, ...
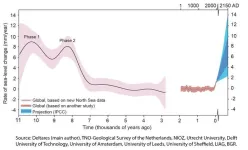
Sea level rise after the last ice age: More knowledge
2025-03-19
New geological data has given more insight into the rate and magnitude of global sea level rise following the last ice age, about 11,700 years ago. This information is of great importance to understand the impact global warming has had on the ice caps and on sea level rise. The findings have been published in the scientific journal Nature by researchers from Deltares, Utrecht University, TNO Netherlands Geological Service, Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ), University of Leeds, University of Sheffield, University of Amsterdam, LIAG and BGR.
Better ...
New mechanism behind adaptive immunity revealed. It could impact how we design vaccines.
2025-03-19
Germinal centers are high-speed evolution machines. Tiny clusters in the lymph nodes, germinal centers refine antibodies through mutation and expansion until they produce high-affinity B cells adapted to keep different pathogens in check. But rapid evolution should come at a cost. Most mutations are deleterious, so constant mutation during every cell division, coupled with unchecked proliferation, should be a recipe for disaster. How B cells somehow rapidly mutate and improve all at once was a long-standing mystery.
Now, advanced imaging techniques reveal the ...
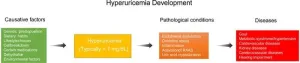
Hyperuricemia: Current state and prospects
2025-03-19
Hyperuricemia (HU) is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated uric acid (UA) levels in the bloodstream, commonly diagnosed when UA levels exceed 420 µmol/L (7 mg/dL) in men and 350 µmol/L (6 mg/dL) in women. Unlike other mammals, humans lack uricase, an enzyme that breaks down UA into a more soluble form, making them more susceptible to HU. The condition is influenced by genetic, dietary, and environmental factors, with contributors including purine-rich foods, metabolic dysfunctions, obesity, and ...
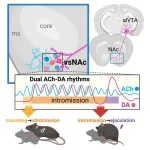
What happens in the male mouse brain during sex
2025-03-19
To uncover what drives sexual behavior in animals, researchers studied the brain activity of male mice throughout the series of actions involved in sex leading up to ejaculation. Their results, publishing in the Cell Press journal Neuron on March 19, show that the intricate dance in the brain area responsible for pleasure between two chemicals—dopamine and acetylcholine—controls the progression of sexual behavior. These findings could inspire treatments for disorders like premature ejaculation.
“Sexual behavior is a complex sequence of events,” says senior author Qinghua Liu of the National ...
Prescription stimulant use, misuse, and use disorder among US adults ages 18 to 64
2025-03-19
About The Study: Although access to prescription stimulants is essential to addressing important clinical needs of patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), this study found that among U.S. adults ages 18 to 64 using prescription stimulants, one-fourth reported misuse, and nearly one-tenth had prescription stimulant use disorder. The findings may suggest potential progress in addressing the mental health care gap for middle-aged women and the need for evidence-based clinical guidance and training on benefits ...
Suicide and self-harm events with GLP-1 receptor agonists in adults with diabetes or obesity
2025-03-19
About The Study: There is unlikely to be an increase in the very low incidence of suicide-related adverse events among individuals receiving glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) within the context of randomized clinical trials. While these findings may further ease concerns about these adverse effects, continued monitoring is warranted to identify particular patients who may be at risk as extended use of GLP-1 RAs expands.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sean P. Heffron, MD, MS, MSc, email sean.heffron@nyulangone.org.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Pregnancy irreversibly remodels the mouse intestine
2025-03-19
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that the small intestine grows in response to pregnancy in mice. This partially irreversible change may help mice support a pregnancy and prepare for a second.
The organs of many female animals are remodelled by reproduction, but the underlying mechanisms behind the response of the gut to pregnancy have only recently begun to be investigated. For example, scientists previously identified that the fruit fly gut expands during reproduction.
In research published today in Cell, the same team found that pregnant mice had a longer small intestine from just seven days ...
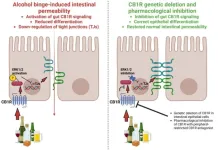
Blocking gut cannabinoids may prevent leaky gut
2025-03-19
Heavy alcohol consumption is a leading cause of gastrointestinal diseases, with binge drinking linked to increased intestinal permeability—a condition commonly known as "leaky gut." Despite the significant health impact of alcohol-associated gastrointestinal disorders, effective pharmacological treatments remain limited. A new study published in eGastroenterology explores the role of gut cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) in alcohol binge-induced intestinal permeability and reveals how its inhibition can help protect the gut barrier.
The research, conducted by scientists from the National Institute ...
Plant patch can detect stress signals in real time
2025-03-19
Environmental conditions can cause damaging stress to plants, posing challenges for home gardeners and farmers. Therefore, early detection — before leaves visibly discolor, wilt or wither — is crucial. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sensors have created a wearable patch for plants that quickly senses stress and relays the information to a grower. The electrochemical sensor attaches directly to live plant leaves and monitors hydrogen peroxide, a key distress signal.
Pests, drought, extreme temperatures and infections all cause stress ...