South Africa and China establish record-breaking 12,900 km ultra-secure quantum satellite link
This milestone marks the first-ever quantum satellite communication link established in the Southern Hemisphere.
2025-03-19
(Press-News.org)
Scientists from South Africa and China have successfully established the world’s longest intercontinental ultra-secure quantum satellite link, spanning 12,900 km. Using the Chinese quantum microsatellite Jinan-1, launched into low Earth orbit, this milestone marks the first-ever quantum satellite communication link established in the Southern Hemisphere.
In this demonstration, quantum keys were generated in real-time through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), enabling the secure encryption of images transmitted between ground stations in China and South Africa via one-time pad encryption—considered unbreakable. The results from this pioneering experiment from a collaborative research initiative between scientists from Stellenbosch University (South Africa) and the University of Science and Technology of China were published in Nature today
Stellenbosch’s ideal environmental conditions—clear skies and low humidity—allowed the local ground station to achieve an exceptional key generation rate of 1.07 million secure bits during a single satellite pass.
Quantum communication leverages fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, guaranteeing highly secure information transfer. Quantum Key Distribution, a critical component, employs single photons to encode and transmit secure keys. Because single photons cannot be intercepted, copied, or measured without altering their quantum states, this technology provides unparalleled security, even against powerful adversaries.
China is currently at the forefront of quantum communication technology, guided by renowned quantum physicist Prof Jian-Wei Pan. The country’s extensive quantum infrastructure includes a 2,000 km terrestrial fibre-based quantum network connecting 32 trusted nodes across major cities, from Beijing to Shanghai. Prof Juan Yin was instrumental in developing China’s first quantum satellite, Micius, previously demonstrated groundbreaking satellite-based quantum links, including a notable 7,600 km intercontinental link between China and Austria in 2017. For this South Africa-China collaboration, Prof Juan Yin again led the Chinese research team.
The South African research team at Stellenbosch University’s Department of Physics was led by Dr Yaseera Ismail, the lead experimentalist responsible for successfully establishing the quantum satellite link. Prof Francesco Petruccione, Professor of Quantum Computing in the School of Data Science and Computational Thinking and Director of the National Institute for Theoretical and Computational Sciences (NITheCS) at Stellenbosch University, pioneered quantum communication in South Africa, notably developing one of the world’s first fibre-optic quantum communication networks in Durban. This landmark achievement also supports the forthcoming launch of the Stellenbosch Centre for Quantum Science and Technology, which aims to strengthen South Africa’s leading role in quantum research and innovation.
Reflecting on this achievement, Dr Yaseera Ismail emphasised the importance of collaboration: “International and national collaborations are essential to drive cutting-edge research and push scientific boundaries. Implementing the first quantum satellite link in the Southern Hemisphere is an outstanding achievement for South Africa, demonstrating the significant potential to develop a thriving quantum ecosystem.”
Prof Francesco Petruccione added: "This successful demonstration of quantum satellite technology firmly positions South Africa as a significant player in the rapidly evolving global quantum technology ecosystem. Collaborations such as this accelerate scientific breakthroughs, build local expertise, and enable translating advanced quantum research into tangible technological solutions.”
Prof Sibusiso Moyo, Deputy Vice-Chancellor for Research, Innovation and Postgraduate Studies at SU, said: "This breakthrough underscores the importance of supporting and investing in the basic sciences such as quantum computing. We are proud that our researchers are pushing the frontiers of science. This work is in line with SU’s Vision 2040, to be Africa’s leading research-intensive university recognised for its excellence and advancing knowledge in service of society. Congratulations to both teams.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-19
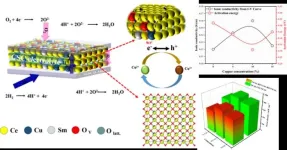
A joint research team from Southeast University and Shenzhen University has developed a novel function of semiconductor-ionic conductor (SIC) using a Cu-Sm co-doping ceria (SCDC). By enhancing ionic and electronic conductivity in the same time, the team is able to achieve superionic transport property and excellent fuel cell performance using the SIC electrolyte. It changes traditional pure ionic electrolyte to SIC with strong electron-ion coupling synergistic effect to obtain exceptional ionic conductivity and fuel cell performance. This study leads to a new way to develop advanced electrolytes and fuel cells in energy conversion technologies.
Ceramic ...
2025-03-19
NEW YORK, March 19, 2025 – Imagine a world where your phone stays cool no matter how long you use it, and it’s also equipped with tiny sensors that can identify dangerous chemicals or pollutants with unparalleled sensitivity and precision. Newly published research in the journal Nature demonstrates a new way of generating long-wave infrared and terahertz waves, which is an important step toward creating materials that can help realize these technological advances. The work, led by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) paves the way for cheaper, smaller long-wave infrared light sources and more efficient device cooling.
Phonon-polaritons ...
2025-03-19
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Dr. Andrés Hidalgo has discovered a specialized population of neutrophils in the skin that produce extracellular matrix, helping to maintain the skin’s resistance and integrity. The study, published in Nature, demonstrates that the immune system not only targets pathogens, but also physically strengthens the skin to prevent them entering the body.
Neutrophils are an important type of circulating immune cell. The specialized neutrophils described ...
2025-03-19
A new study explains how a parakeet’s brain helps it to mimic human words.
By recording for the first time the brain activity of parakeets as they made sounds, a research team at NYU Grossman School of Medicine found that their brains generate patterns seen before only in humans as they speak.
Published online March 19 in the journal Nature, the study mapped the activity of a group of nerve cells in the bird’s brain called the central nucleus of the anterior arcopallium (AAC), which is known to strongly influence the muscles in its vocal ...
2025-03-19
By revealing for the first time what happens in the brain when an animal makes a mistake, Johns Hopkins University researchers are shedding light on the holy grail of neuroscience: the mechanics of how we learn.
The team pinpointed the exact moment mice learned a new skill by observing the activity of individual neurons, confirming earlier work that suggested animals are fast learners that purposely test the boundaries of new knowledge.
The federally funded work, which upends assumptions about the speed of learning and the role of the sensory cortex, and which the researchers believe will hold true across animal ...
2025-03-19
For the first time, scientists have witnessed the very moment DNA begins to unravel, revealing a necessary molecular event for DNA to be the molecule that codes all life. A new study from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), published in Nature, captures the moment DNA begins to unwind, allowing for all the events that follow in DNA replication. This direct observation sheds light on the fundamental mechanisms that allow cells to faithfully duplicate their genetic material, a cornerstone for growth and reproduction.
Using cryo-electron microscopy and deep learning to observe the helicase ...
2025-03-19
For the first time, scientists have systematically analysed somatic mutations in stomach lining tissue to unpick mutational processes, some of which can lead to cancer. The team also uncovered hints of a potential new cause of stomach cancer that needs further research.
Researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the University of Hong Kong, and their collaborators sequenced the whole genomes of normal stomach lining samples from people with and without gastric cancer.
The team ...
2025-03-19
The cells that make up the walls of the finest of all lymphatic vessels have a lobate, oak leaf-like shape that makes them particularly resilient to changes in fluid volume. A similar cell shape also supports mechanical stability in plants. This has been shown by researchers from Uppsala University in a new article published in the journal Nature.
The lymphatic system consists of a network of lymph vessels that maintains the body’s fluid balance and supports the immune system. The finest of all these lymphatic vessels are called lymph capillaries. They have walls that are made up of just a single layer of lymphatic endothelial ...
2025-03-19
A vaccine's ability to generate long-lasting, high-affinity antibodies hinges on a delicate balance. Upon exposure to a vaccine or pathogen, B cells scramble to refine their defenses, rapidly mutating in hopes of generating the most effective antibodies. But each round of this process is a roll of the genetic dice—every mutation has the potential to improve affinity; far more often, however, it degrades or destroys a functional antibody. How do high-affinity B cells ever beat the odds?
New research now suggests that B cells avoid gambling away good mutations by strategically banking successful ones. As described in Nature, ...
2025-03-19
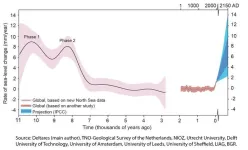
New geological data has given more insight into the rate and magnitude of global sea level rise following the last ice age, about 11,700 years ago. This information is of great importance to understand the impact global warming has had on the ice caps and on sea level rise. The findings have been published in the scientific journal Nature by researchers from Deltares, Utrecht University, TNO Netherlands Geological Service, Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ), University of Leeds, University of Sheffield, University of Amsterdam, LIAG and BGR.
Better ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] South Africa and China establish record-breaking 12,900 km ultra-secure quantum satellite link
This milestone marks the first-ever quantum satellite communication link established in the Southern Hemisphere.