CNIC scientists discover a type of immune cell that produces defensive "shields" in the skin
CNIC scientists have discovered a specialized population of skin neutrophils that produce extracellular matrix, strengthening the skin’s defensive function against infection
2025-03-19
(Press-News.org)
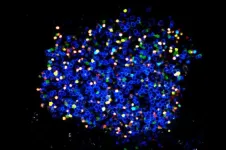
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Dr. Andrés Hidalgo has discovered a specialized population of neutrophils in the skin that produce extracellular matrix, helping to maintain the skin’s resistance and integrity. The study, published in Nature, demonstrates that the immune system not only targets pathogens, but also physically strengthens the skin to prevent them entering the body.
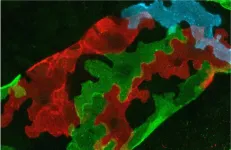
Neutrophils are an important type of circulating immune cell. The specialized neutrophils described in the new study populate the skin, where they produce collagen and other matrix proteins that strengthen the skin barrier. The discovery broadens understanding of the immune system and may lead to new strategies for treating skin diseases, inflammation, diabetes, and age-related conditions.
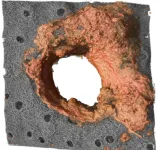
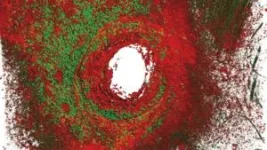
Although neutrophils are best known for their microbicidal properties, the new study reveals an unexpected role for these cells in the generation and remodeling of the subepidermal extracellular matrix. Hidalgo explains that, “The extracellular matrix is critical for maintaining the structure and function of the skin and other tissues, acting as a barrier to the entry of microorganisms and toxins.”
First author Tommaso Vicanolo adds that the study, “demonstrates that these neutrophils help to maintain skin integrity under normal conditions and are activated in response to injury to generate protective structures around wounds that prevent the entry of bacteria and toxins.”
The study further shows that this structural function of skin neutrophils is regulated by the TGF-β signaling pathway. By genetically deleting this pathway in mice, the authors showed that the deposition of extracellular matrix was diminished, resulting in skin that was more fragile and permeable. Hidalgo notes that, “This suggests that the interaction between the immune system and the body’s structural components is much more direct than previously believed.”
Another fascinating result emerging from the study is that the activity of these skin neutrophils follows a day-night pattern, adjusting the production of extracellular matrix according to the body’s circadian cycle. As a result, the skin of mice is more resistant at night than during the day, thanks to the nocturnal peak in neutrophil activity. Hidalgo underlines that, “This finding opens new avenues for investigating how internal body rhythms influence tissue defence, regeneration and repair.”
For Hidalgo, now at Yale University School of Medicine, the discovery of matrix-producing neutrophils not only broadens knowledge about innate immunity, but also suggests new treatment strategies for skin diseases and immunological disorders. He explains, “These findings will help develop treatments to strengthen the skin barrier in patients with inflammatory diseases or immunological alterations, including patients with diabetes and older adults.”
The authors conclude that this advance—the fruit of collaboration between various CNIC groups and laboratories in Germany, the United States, Singapore, and China, “signals a change in the way we view the immune system’s protective role in the body.”
Dr. Hidalgo is currently investigating the possible implications of the study findings for fibrotic processes and cancer.
The study was supported by funding from Fundación “la Caixa”, the Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the Swiss National Science Foundation.
The CNIC is an affiliate center of the Carlos III Health Institute (ISCIII), an executive agency of the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities. Directed by Dr. Valentín Fuster, the CNIC is dedicated to cardiovascular research and the translation of the knowledge gained into real benefits for patients. The CNIC has been recognized by the Spanish government as a Severo Ochoa center of excellence (award CEX2020-001041-S, funded by MICIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033). The center is financed through a pioneering public-private partnership between the government (through the ISCIII) and the Pro-CNIC Foundation, which brings together 11 of the most important Spanish private companies.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-19
A new study explains how a parakeet’s brain helps it to mimic human words.
By recording for the first time the brain activity of parakeets as they made sounds, a research team at NYU Grossman School of Medicine found that their brains generate patterns seen before only in humans as they speak.
Published online March 19 in the journal Nature, the study mapped the activity of a group of nerve cells in the bird’s brain called the central nucleus of the anterior arcopallium (AAC), which is known to strongly influence the muscles in its vocal ...
2025-03-19
By revealing for the first time what happens in the brain when an animal makes a mistake, Johns Hopkins University researchers are shedding light on the holy grail of neuroscience: the mechanics of how we learn.
The team pinpointed the exact moment mice learned a new skill by observing the activity of individual neurons, confirming earlier work that suggested animals are fast learners that purposely test the boundaries of new knowledge.
The federally funded work, which upends assumptions about the speed of learning and the role of the sensory cortex, and which the researchers believe will hold true across animal ...
2025-03-19
For the first time, scientists have witnessed the very moment DNA begins to unravel, revealing a necessary molecular event for DNA to be the molecule that codes all life. A new study from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), published in Nature, captures the moment DNA begins to unwind, allowing for all the events that follow in DNA replication. This direct observation sheds light on the fundamental mechanisms that allow cells to faithfully duplicate their genetic material, a cornerstone for growth and reproduction.
Using cryo-electron microscopy and deep learning to observe the helicase ...
2025-03-19
For the first time, scientists have systematically analysed somatic mutations in stomach lining tissue to unpick mutational processes, some of which can lead to cancer. The team also uncovered hints of a potential new cause of stomach cancer that needs further research.
Researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, the University of Hong Kong, and their collaborators sequenced the whole genomes of normal stomach lining samples from people with and without gastric cancer.
The team ...
2025-03-19
The cells that make up the walls of the finest of all lymphatic vessels have a lobate, oak leaf-like shape that makes them particularly resilient to changes in fluid volume. A similar cell shape also supports mechanical stability in plants. This has been shown by researchers from Uppsala University in a new article published in the journal Nature.
The lymphatic system consists of a network of lymph vessels that maintains the body’s fluid balance and supports the immune system. The finest of all these lymphatic vessels are called lymph capillaries. They have walls that are made up of just a single layer of lymphatic endothelial ...
2025-03-19
A vaccine's ability to generate long-lasting, high-affinity antibodies hinges on a delicate balance. Upon exposure to a vaccine or pathogen, B cells scramble to refine their defenses, rapidly mutating in hopes of generating the most effective antibodies. But each round of this process is a roll of the genetic dice—every mutation has the potential to improve affinity; far more often, however, it degrades or destroys a functional antibody. How do high-affinity B cells ever beat the odds?
New research now suggests that B cells avoid gambling away good mutations by strategically banking successful ones. As described in Nature, ...
2025-03-19
New geological data has given more insight into the rate and magnitude of global sea level rise following the last ice age, about 11,700 years ago. This information is of great importance to understand the impact global warming has had on the ice caps and on sea level rise. The findings have been published in the scientific journal Nature by researchers from Deltares, Utrecht University, TNO Netherlands Geological Service, Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ), University of Leeds, University of Sheffield, University of Amsterdam, LIAG and BGR.
Better ...
2025-03-19
Germinal centers are high-speed evolution machines. Tiny clusters in the lymph nodes, germinal centers refine antibodies through mutation and expansion until they produce high-affinity B cells adapted to keep different pathogens in check. But rapid evolution should come at a cost. Most mutations are deleterious, so constant mutation during every cell division, coupled with unchecked proliferation, should be a recipe for disaster. How B cells somehow rapidly mutate and improve all at once was a long-standing mystery.
Now, advanced imaging techniques reveal the ...
2025-03-19
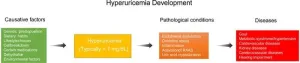
Hyperuricemia (HU) is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated uric acid (UA) levels in the bloodstream, commonly diagnosed when UA levels exceed 420 µmol/L (7 mg/dL) in men and 350 µmol/L (6 mg/dL) in women. Unlike other mammals, humans lack uricase, an enzyme that breaks down UA into a more soluble form, making them more susceptible to HU. The condition is influenced by genetic, dietary, and environmental factors, with contributors including purine-rich foods, metabolic dysfunctions, obesity, and ...
2025-03-19
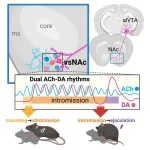
To uncover what drives sexual behavior in animals, researchers studied the brain activity of male mice throughout the series of actions involved in sex leading up to ejaculation. Their results, publishing in the Cell Press journal Neuron on March 19, show that the intricate dance in the brain area responsible for pleasure between two chemicals—dopamine and acetylcholine—controls the progression of sexual behavior. These findings could inspire treatments for disorders like premature ejaculation.
“Sexual behavior is a complex sequence of events,” says senior author Qinghua Liu of the National ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] CNIC scientists discover a type of immune cell that produces defensive "shields" in the skin
CNIC scientists have discovered a specialized population of skin neutrophils that produce extracellular matrix, strengthening the skin’s defensive function against infection