(Press-News.org) A liquid robot capable of transforming, separating, and fusing freely like living cells has been developed.
Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that a joint research team led by Professor Ho-Young Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Jeong-Yun Sun from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Keunhwan Park from the Department of Mechanical, Smart, and Industrial Engineering at Gachon University has successfully developed a next-generation soft robot based on liquid.
This research was published in the world-renowned journal Science Advances on March 21.
Biological cells possess the ability to deform freely divide, fuse, and capture foreign substances. Research efforts have long been dedicated to replicating these unique capabilities in artificial systems. However, traditional solid-based robots have faced limitations in effectively mimicking the flexibility and functionality of living cells.
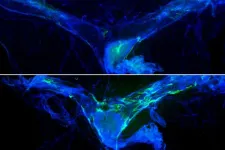
To overcome these challenges, the joint research team successfully developed a particle-armored liquid robot, encased in unusually dense hydrophobic (water-repelling) particles. This novel next-generation soft robot benefits from both the exceptional deformability of liquid and the structural stability of solid. As a result, it can withstand extreme compression or high-impact drops, recovering its original shape like a droplet without breaking.
Leveraging these strengths, the joint research team demonstrated various functions of the liquid robot. Similar to the liquid robot T-1000 from the 1991 movie Terminator 2, this innovative robot can pass through metal bars, capture and transport foreign substances, and merge with other liquid robots. Additionally, it can move freely across both surfaces of water and solid ground. The research team experimentally proved that the liquid robot could continuously perform these tasks and developed a technique to control its movement at desired speeds using ultrasound.
Thus, the newly developed liquid robot is expected to be utilized in biomedical and soft robotics applications, such as targeted drug delivery and therapeutic interventions inside the human body. Furthermore, due to its ability to pass through extremely narrow spaces, it could be deployed in large numbers inside complex machinery, between obstacles in rugged terrain, and in disaster zones to conduct exploration, cleaning, chemical-based obstacle removal, and nutrient supply operations.
Hyobin Jeon, the first author of the paper, stated, “When we first started developing the liquid robot, we initially considered encapsulating a spherical droplet with particles, just as adopted in making conventional liquid marbles. However, by shifting our perspective, we came up with the idea of coating an ice cube with particles and then melting it, which significantly enhanced the stability of our robots.”
Professor Ho-Young Kim, the corresponding author, remarked, “Building upon our current findings, we are now working on technologies that will allow the liquid robot to change shape freely using sound waves or electric fields.” Co-corresponding author Professor Jeong-Yun Sun added, “We plan to enhance the material functionality of the liquid robot to enable broader industrial applications in the future.”
□ Introduction to the SNU College of Engineering
Seoul National University (SNU) founded in 1946 is the first national university in South Korea. The College of Engineering at SNU has worked tirelessly to achieve its goal of ‘fostering leaders for global industry and society.’ In 12 departments, 323 internationally recognized full-time professors lead the development of cutting-edge technology in South Korea and serving as a driving force for international development.
END
SNU-GU researchers jointly develop a liquid robot capable of transformation, separation, and fusion like living cells
- Liquid structures protected by unusually dense particle layers enable separation, fusion, and foreign substance capture / - Expected applications in extreme environment exploration and biomedical soft robotics
2025-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate warming and heatwaves accelerate global lake deoxygenation, study reveals
2025-03-21
Freshwater ecosystems require adequate oxygen levels to sustain aerobic life and maintain healthy biological communities. However, both long-term climate warming and the increasing frequency and intensity of short-term heatwaves are significantly reducing surface dissolved oxygen (DO) levels in lakes worldwide, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
Led by Prof. SHI Kun and Prof. ZHANG Yunlin from the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the Nanjing University and the UK’s ...
Unlocking dopamine’s hidden role: Protective modification of Tau revealed
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 19, 2025: The research group led by Prof. Wang Chu from the College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering at Peking University published a research article entitled “Quantitative Chemoproteomics Reveals Dopamine’s Protective Modification of Tau” in Nature Chemical Biology (DOI:10.1038/s41589-025-01849-9). Using a novel quantitative chemoproteomic strategy, the team uncovered a protective role of dopamine (DA) in regulating the function of the microtubule-associated protein Tau. This discovery deepens our understanding of dopamine’s physiological and pathological roles in the human brain.
Why it matters:
1. Dopamine, ...
New drug therapy combination shows promise for advanced melanoma patients
2025-03-21
A federally funded research team led by Sheri Holmen, PhD, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor in the Department of Surgery at the University of Utah (the U), is testing a new combination drug therapy that could both treat and prevent melanoma metastasis, or spreading from its original site, to the brain.
“Once melanoma has spread to the brain, it’s very hard to treat. Metastasis to the brain is one of the main causes of death from melanoma,” says Holmen. “We wanted to find a solution to an unmet clinical need for those patients who had no other treatment options ...
Nature’s warriors: How rice plants detect and defend against viral invaders
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 20, 2025: A groundbreaking study led by Li Yi, professor at the School of Life Sciences, was published in Nature on March 12, titled “Perception of viral infections and initiation of antiviral defence in rice”, uncovering a molecular mechanism by which rice cells perceive viral infections and initiate antiviral response, which significantly contributes to understanding of virus-host interactions for further disease resistance breeding.
Why it matters:
Viruses affecting rice, a staple food for more than half of the world population, pose ...
How the brain responds to prices: Scientists discover neural marker for price perception
2025-03-21
Russian scientists have discovered how the brain makes purchasing decisions. Using electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), researchers found that the brain responds almost instantly when a product's price deviates from expectations. This response engages brain regions involved in evaluating rewards and learning from past decisions. Thus, perceiving a product's value is not merely a conscious choice but also a function of automatic cognitive mechanisms. The results have been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Every day, people are faced with prices of food, technology, and services. Sometimes, a product seems overpriced, ...
Boosting brain’s waste removal system improves memory in old mice
2025-03-21
As aging bodies decline, the brain loses the ability to cleanse itself of waste, a scenario that scientists think could be contributing to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, among others. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have found a way around that problem by targeting the network of vessels that drain waste from the brain. Rejuvenating those vessels, they have shown, improves memory in old mice.
The study, published online March 21 in the journal Cell, lays the groundwork to develop therapies for age-related cognitive decline that overcome ...
New study sheds light on risks from residential heat and energy burdens in Miami
2025-03-21
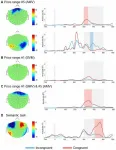
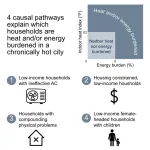
A new study on indoor extreme heat connects these two burdens to reveal how the co-occurrence of escalating energy bills and dangerously hot homes in Miami-Dade County exacerbates health and well-being risks for vulnerable households across months of the year.
“Our findings help us understand which types of households are struggling with high indoor heat and high energy bills in a place like Miami, which is hot for many months of the year,” said Lynée Turek-Hankins, the lead author of the study that was conducted during her doctoral studies at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Abess Center for Ecosystem ...
Racial and ethnic inequalities in actual vs nearest delivery hospitals
2025-03-21
About The Study: This cohort study found that American Indian and Black individuals delivered at lower-quality hospitals than white individuals. The disparity in care between Black and white birthing individuals would have been reduced if individuals had delivered at their nearest hospital.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nansi S. Boghossian, PhD, email nboghoss@email.sc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1404)
Editor’s ...
State earned income tax credits and firearm suicides
2025-03-21
About The Study: In this cohort study, the presence and generosity of state refundable earned income tax credits were associated with a decrease in firearm suicide rates, supporting the growing body of literature highlighting the importance of antipoverty policies for reducing firearm suicide.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole Asa, MPH, email nasa3@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1398)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
VR study reveals how pain and fear weaken sense of body ownership
2025-03-21
A study from Hiroshima University found that when people were told to imagine their virtual bodies in pain, their brains resisted the illusion of ownership. Their findings could provide insights into why some people may struggle with feeling connected to their own bodies, particularly in contexts involving depersonalization or negative physical states.
The sense of body ownership—the feeling that our body belongs to us—is crucial in distinguishing ourselves from objects and responding to threats. Researchers study it using techniques like the rubber hand illusion (RHI) and full-body illusion (FBI), in which an individual is somehow ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
[Press-News.org] SNU-GU researchers jointly develop a liquid robot capable of transformation, separation, and fusion like living cells- Liquid structures protected by unusually dense particle layers enable separation, fusion, and foreign substance capture / - Expected applications in extreme environment exploration and biomedical soft robotics