(Press-News.org) Des Plaines, IL — Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM), has published its March issue dedicated to the topic of errors in emergency care, with a strong emphasis on diagnostic error. This special issue, supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), brings together leading scholars and clinicians to discuss aspects of errors relevant to emergency care and propose actionable solutions.
Following the landmark 2015 National Academies report, “Improving Diagnosis in Healthcare,” national awareness of diagnostic errors has increased significantly. Errors—ranging from missed, incorrect, or delayed diagnoses—are recognized as universal issues across all medical specialties, with emergency medicine being particularly vulnerable due to its high-pressure, resource-limited environment.
This special issue of AEM features a comprehensive examination of many of these challenges, publishing 10 original reports, three special contributions, one systematic review, two research letters, four commentaries, and one reflection. Topics are organized according to themes, such as the role of cognitive processing in doctors and nurses, flawed communication, potential errors of omission, specific conditions, and a special contribution on the potential role of artificial intelligence to reduce error.
According to AEM Editor-in-Chief Jeffrey A. Kline, MD, the contributions to this special issue offer valuable insights, with a key takeaway: the need to move beyond blame and individual fault. “Instead, we must recognize errors as complex, often arising from a convergence of factors—including gaps in knowledge and communication, inadequate awareness, and various system-based challenges,” he said.
The AEM special issue was made possible through the leadership of Dr. Kline and the commitment and expertise of its guest editors: Richard T. Griffey, MD; Brandon C. Maughan, MD, MHS, MSHP; and Margaret E. Samuels-Kalow, MD, MPhil, MSHP. Their guidance, along with the contributions of top researchers in the field, has resulted in an issue that aims to help move the specialty of emergency care forward in a positive manner.
###
ABOUT ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
Academic Emergency Medicine, the monthly journal of Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, features the best in peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research relevant to the practice and investigation of emergency care. The above issue is published open access and can be downloaded by following https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/toc/15532712/2025/32/3. Journalists wishing to interview authors may contact Melissa Matusek at mmatusek@saem.org.
ABOUT THE SOCIETY FOR ACADEMIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE
SAEM is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization dedicated to the improvement of care of the acutely ill and injured patient by leading the advancement of academic emergency medicine through education and research, advocacy, and professional development. To learn more, visit saem.org.
END
A new study in the peer-reviewed journal Stem Cells and Development describes the development of a co-culture system of neural organoids generated from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) fused with fetal leptomeninges from mice with fluorescently labeled meninges, called leptomeningeal neural organoid (LMNO) fusions. Click here to read the article now.
Vivian Gama, PhD, from Vanderbilt University, Julie Siegenthaler, PhD, from University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, and coauthors, present a proof-of-concept study that tests the stability of the different cell types in the leptomeninges (fibroblasts and macrophages) and the fused neural organoid ...
Interferometers, devices that can modulate aspects of light, play the important role of modulating and switching light signals in fiber-optic communications networks and are frequently used for gas sensing and optical computing.
Now, applied physicists at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have invented a new type of interferometer that allows precise control of light’s frequency, intensity and mode in one compact package.
Called a cascaded-mode interferometer, it is a single waveguide on a silicon-on-insulator ...
OKLAHOMA CITY – According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1 in 7 adults in the United States will experience a substance use disorder during their lifetime. University of Oklahoma College of Medicine faculty member Brandi Fink, Ph.D., is working with primary care clinics and health care systems to identify people with an alcohol use disorder and intervene early before the problem worsens.
Fink, an associate professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, created an assessment for patients to fill out on an iPad while waiting for an appointment ...
Businesses invest billions in marketing automation, and many assume that Automated Lead Nurturing (ALN) is a proven driver of sales. However, a new Journal of Marketing study reveals that ALN is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The research finds that while ALN improves engagement and enhances salesperson–lead interactions, its impact on sales conversions varies significantly across industries and customer segments.
Authored by Johannes Habel (University of Houston), Nathaniel Hartmann (University of South Florida), Phillip Wiseman (Texas Tech University), Michael Ahearne (University of ...
Until the 1990s, Venezuela was home to one of the most established democracies in Latin America. Today, however, it stands as one of the region’s most firmly entrenched authoritarian regimes.
How did this shift occur, and what can other countries learn from Venezuela’s transformation?
A new paper from political scientist Laura Gamboa at the University of Notre Dame chronicles the country’s 25-year evolution, during which Hugo Chávez and his successor, Nicolás Maduro, destroyed ...
TOOELE, UTAH, USA -- Wildlife conservation is critical to sustaining the planet’s biodiversity and health. But putting together a conservation plan is a tall order. First of all, you need to determine what species you’re conserving, along with their numbers, habitat needs, threats and how they fit into a complex ecosystem.
As pollinators for native plants and food crops, bees play a pivotal role in our ecosystem, according to Utah State University ecologist Joseph Wilson. He and undergraduate researcher Anthony Hunsaker took on the herculean task of documenting Utah’s bee species using online occurrence records from the Symbiota Collection of Arthropods ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- In his home office in Durham, Duke neuroscientist Richard Mooney shows a series of images of a bird’s brain on song.
In one, what looks like a pointillist painting illustrates a young zebra finch’s myriad attempts to sound more like an adult, capable of wooing a mate. In another, squiggly lines trace the ebb and flow of chemical signals in the reward circuit of the bird’s brain.
“Their songs don’t sound like much at first,” said Mooney, who has studied birdsong for four decades.
That’s because some things take considerable practice to master. Nobody walks onto a tennis court for the first time and plays ...
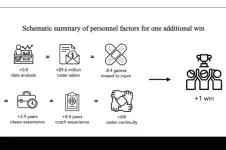
If you filled out a March Madness bracket this month, you probably faced the same question with each college match-up: What gives one team an edge over another? Is it a team’s record through the regular season? Or the chemistry among its players? Maybe it’s the experience of its coaching staff or the buzz around a top scorer.
All of these factors play some role in a team’s chance to advance. But according to a new study by MIT researchers, there’s one member who consistently ...
Relations between Europe and South America – and especially with Brazil - are at a favorable moment, due to factors such as the free trade agreement between Mercosur and the European Union, signed in December 2024 and currently being approved. However, in order to take advantage of this window of opportunity and be competitive, Brazil must continue to expand scientific and technological cooperation with European partners.
This assessment was made by the Brazilian Ambassador to Germany, Roberto Jaguaribe, ...
The Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 100 monoclonal antibodies to treat a range of diseases. Other antibodies are used by physicians to diagnose conditions or by scientists to advance research projects.
Even with significant expansion in the global market for antibodies used in clinical care and research, scientists recognize that there is still untapped potential for finding new antibodies. Many proteins group together in what are called protein complexes to carry out biological functions. The traditional method of generating antibodies by immunizing animals struggles to make antibodies related to these protein complexes.
The conventional ...