Nature’s viny vampire: Discovering what drives parasitic Cuscuta campestris
Suppression of the CcMCA1 gene has potential in halting invasive plant species
2025-03-27
(Press-News.org)
The parasitic vine Cuscuta campestris grows by latching onto the stems and leaves of plants and inserting organs called haustorium into the host plant tissues to draw nutrients. The haustorium is formed when ion channels in the cell membrane are stimulated during coiling and induce a reaction within the cell.
Further, Cuscuta campestris has many types of ion channels, but which ones were linked to the development of haustorium were previously unknown.
“For the first time, the genes involved in sensing mechanical stimuli that lead to the climbing of vines, such as morning glories and bindweed, have been discovered,” declared Osaka Metropolitan University Professor Koh Aoki of the Graduate School of Agriculture.
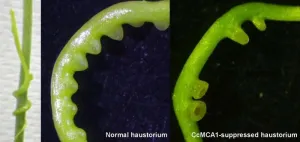
Professor Aoki led an OMU team in discovering that when the expression of the gene Cuscuta campestris MID1-COMPLEMENTING ACTIVITY1 (CcMCA1) was suppressed, the number of haustorium per centimeter decreased.
“We want to continue to identify other ion channel genes involved in this process and aim to explain the various mechanisms of plant senses on the microscopic level,” Professor Aoki added. “Furthermore, we hope this will lead to the development of measures to control plants that cause harm economically to crops.”
The findings were published in Plant and Cell Physiology.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-27
A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Institute of Science Tokyo has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality).
Like our left and right hands, many molecules exist in two mirror-image forms. Yet life on Earth has a striking preference: ...
2025-03-27
People living with Long Covid often feel dismissed, disbelieved and unsupported by their healthcare providers, according to a new study from the University of Surrey.
The study, which was published in the Journal of Health Psychology, looked at how patients with Long Covid experience their illness. The study found that many patients feel they have to prove their illness is physical to be taken seriously and, as a result, often reject psychological support, fearing it implies their symptoms are "all in the mind".
Professor ...
2025-03-27
Wearable mobile health technology could help people with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) to stick to exercise regimes that help them to keep the condition under control, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied the behaviour of recently-diagnosed T2D patients in Canada and the UK as they followed a home-based physical activity programme – some of whom wore a smartwatch paired with a health app on their smartphone.
They discovered that MOTIVATE-T2D participants were more likely to start and maintain purposeful exercise at if they had the support of wearable technology- the study successfully recruited 125 participants with an 82% ...
2025-03-27
An extinct lineage of parasitic wasps dating from the mid-Cretaceous period and preserved in amber may have used their Venus flytrap-like abdomen to capture and immobilise their prey. Research, published in BMC Biology, finds that the specimens of Sirenobethylus charybdis — named for the sea monster in Greek mythology which swallowed and disgorged water three times a day — date from almost 99 million years ago and may represent a new family of insects.
The morphology of S. charybdis indicates the wasps were ...
2025-03-27
A new species of fossil from 444 million years ago that has perfectly preserved insides has been affectionately named ‘Sue’ after its discoverer’s mum.
The result of 25 years of work by a University of Leicester palaeontologist and published in the journal Palaeontology, the study details a new species of multisegmented fossil and is now officially named as Keurbos susanae.
Lead author Professor Sarah Gabbott from the School of Geography, Geology and the Environment said: “‘Sue’ is an inside-out, legless, headless wonder. Remarkably her insides are a mineralised ...
2025-03-27
New modelling analysis suggests that proposed funding cuts by major donor countries to foreign aid could undo decades of progress made to end HIV/AIDS as a public health threat and new infections and deaths could surge back to levels not seen since the early 2000s.
The study estimates there could be between 4.4 million to 10.8 million additional new HIV infections by 2030 in low-and-middle income countries (LMICs) and between 770,000 to 2.9 million HIV-related deaths in children and adults by 2030.
The greatest impact from potential funding ...
2025-03-26
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows an association between the amount of sodium consumed in the diet and the risk of both general and abdominal obesity. The study is by Annika Santalahti, Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland, and colleagues.
General obesity is a person’s obesity status as measured by their body mass index (BMI), with WHO international guidelines stating a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more means a person is living with obesity. Abdominal obesity is where fat accumulates around the abdomen and internal organs there, leading ...
2025-03-26
San Diego—March 26, 2025– In a manuscript published today in the American Journal of Psychiatry titled Psychiatric Genetics in Clinical Practice: Essential Knowledge for Mental Health Professionals, authors provide updated guidelines on what mental health professionals should know about the latest advances in genetics and how genetics can inform clinical psychiatric practice.
Key findings highlight the importance of understanding the genetic architecture of psychiatric disorders, the potential applications of genetic information in risk assessment, diagnosis, treatment selection, and patient education, ...
2025-03-26
At hypersonic speeds, complexities occur when the gases interact with the surface of the vehicle such as boundary layers and shock waves. Researchers in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in The Grainger College of Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign were able to observe new disturbances in simulations conducted for the first time in 3D.
Fully 3D simulations require a great deal of processing power, making the work expensive to compute. Two things made it possible for Deborah Levin and her Ph.D. student Irmak Taylan Karpuzcu to conduct the research: Time on Frontera, the National Science Foundation-funded leadership-class computer system at the Texas ...
2025-03-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4:00 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 26, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS — People living in more disadvantaged neighborhoods may be more likely to develop dementia than people living in neighborhoods with fewer disadvantages, according to a study published on March 26, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that neighborhood factors cause dementia; it only shows an association.
Neighborhood status was determined by factors such as income, employment, education and disability.
“Our findings show that the community in which you live influences your risk of developing dementia,” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nature’s viny vampire: Discovering what drives parasitic Cuscuta campestris
Suppression of the CcMCA1 gene has potential in halting invasive plant species