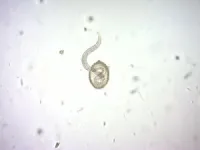
(Press-News.org) In an analysis of soil samples from twelve parks in Dublin, Ireland, park entrances were more heavily contaminated with infective roundworm eggs than any other tested park location. Jason Keegan of Trinity College in Dublin, Ireland, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Dogs and cats are often infected with parasitic roundworms in the Toxocara genus. Infected animals can release the roundworm eggs into the environment, and humans can become infected after accidental ingestion of the eggs. Many infected humans never experience symptoms, but some may experience mild or severe symptoms such as eye infection. Infection with Toxocara is one of the most widespread parasitic infections in the world.
While prior studies have shown that soils in public parks are commonly contaminated with Toxocara roundworm eggs, few have explored whether certain areas within parks are more contaminated than others. To address that question, Keegan and colleagues collected and analyzed soil samples from within 12 parks in Dublin, Ireland, focusing on park entrances, playgrounds, the sidelines of sports fields, and popular areas for sitting on grass.
The analysis showed that park entrances were more heavily contaminated with roundworm eggs than the other park locations. The second-most contaminated areas were playgrounds. Closer examination of the detected eggs found that most were potentially infective, and most were of the species Toxocara canis—the common dog roundworm.
On the basis of these findings, the researchers call for increased preventive efforts focused on encouraging dog owners to properly dispose of dog feces at park entrances and playgrounds. They note that the success of such efforts should be monitored with regular measurements of Toxocara eggs at these sites. They specifically designed the analytical method used for this study to be accessible and affordable, so it could serve as a standardized monitoring strategy, easing comparison between sites and over time.
The authors add: "Park entrances had the most Toxocara eggs, and most of these eggs likely came from dogs. By providing signage, bins and a means to clean up after your dog in these locations, we could reduce the level of contamination. That’s the next step in the research."
####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases: https://plos.io/3E7WEYK
Citation: Keegan JD, Airs PM, Brown C, Dingley AR, Courtney C, Morgan ER, et al. (2025) Park entrances, commonly contaminated with infective Toxocara canis eggs, present a risk of zoonotic infection and an opportunity for focused intervention. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 19(3): e0012917. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012917
Author Countries: Ireland, United Kingdom
Funding: This research was funded by The Irish Research Council's Postdoctoral Fellowship programme (GOIPD/2020/510 to JDK and CVH). https://research.ie/ The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Park entrances may be hotspots for infective dog roundworm eggs
New study could help inform efforts to reduce risk of spread among animals and to humans
2025-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Commercial fusion power plant closer to reality following research breakthrough
2025-03-27
Successfully harnessing the power of fusion energy could lead to cleaner and safer energy for all – and contribute substantially to combatting the climate crisis. Towards this goal, Type One Energy has published a comprehensive, self-consistent, and robust physics basis for a practical fusion pilot power plant.
This groundbreaking research is presented in a series of six peer-reviewed scientific papers in a special issue of the prestigious Journal of Plasma Physics (JPP), published by Cambridge University Press.
The articles serve as the foundation for the company’s first fusion power plant project, which Type One Energy is developing with the Tennessee ...
The Protein Society announces its 2024 Best Paper recipients
2025-03-27
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Contact:
John Kuriyan, Editor-in-Chief
Protein Science Journal
Raluca Cadar
The Protein Society
Phone: (844) 377-6834
E-mail: rcadar@proteinsociety.org
LOS ANGELES, CA – The Protein Society, the premier international society dedicated to supporting protein research, announces the winners of the 2024 Protein Science Best Paper Awards, published in its flagship journal, Protein Science. The recipients will be recognized and present their research at the 39th Annual Symposium of The Protein Society, June 26 – 29, 2025, in San Francisco, USA.
The ...
Bing Ren appointed Scientific Director and Chief Executive Officer of the New York Genome Center
2025-03-27
The New York Genome Center (NYGC) is pleased to announce the appointment of Bing Ren, PhD, as its new scientific director and chief executive officer. Dr. Ren will also join Columbia University as a professor in the Departments of Genetics and Development, Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, and Systems Biology and as the associate director of the Roy and Diana Vagelos Institute for Basic Biomedical Science within the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Dr. Ren is renowned for his pioneering research in genomics and epigenetics, with a focus on the regulatory processes that control gene expression. His work has advanced our understanding of how genetic ...
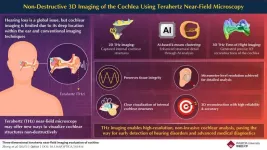
Terahertz imaging: a breakthrough in non-invasive cochlear visualization
2025-03-27
Advancements in healthcare and technology have significantly increased the average human lifespan. However, with longer life comes a higher prevalence of age-related disorders that affect overall well-being. One such condition is hearing loss in older adults, which can severely impact communication, social interactions, and daily functioning.
Hearing relies on the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound waves into neural signals. Any structural or functional impairment of the cochlea ...
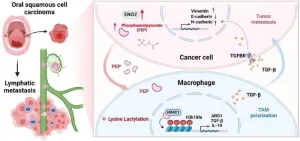
ENO2: a key player in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metastasis
2025-03-27
A recent study published in Engineering has shed new light on the mechanisms underlying the metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). The research identified enolase 2 (ENO2), a crucial glycolytic enzyme, as a significant factor associated with lymphatic metastasis in HNSCC.
HNSCC is an aggressive cancer with a relatively low 5-year overall survival rate. Cervical lymph node metastasis is a major cause of cancer-related death in HNSCC patients, and effective therapies for metastatic HNSCC are currently lacking. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanisms of HNSCC metastasis ...
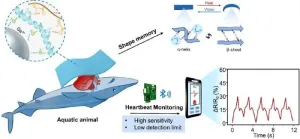
Biocompatible hydrogel enables wearable electronics for monitoring marine life health
2025-03-27
In a recent development published in Engineering, researchers have introduced a novel hybrid keratin (KE) hydrogel integrated with liquid metal (LM), offering new possibilities for monitoring the health of marine inhabitants. This innovation addresses the limitations of traditional wearable electronics in terms of biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and conductivity.
Monitoring the health and migration of marine organisms is crucial for maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems, advancing climate change studies, and safeguarding human health. However, developing sensors for marine organisms is challenging due to the complex ...
We must not ignore eugenics in our genetics curriculum, says professor
2025-03-27
To encourage scientists to speak up when people misuse science to serve political agendas, biology professor Mark Peifer of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill argues that eugenics should be included in college genetics curriculums. In an opinion paper publishing March 27 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Genetics, Peifer explains how he incorporated a discussion of eugenics into his molecular genetics course last year and why understanding the history of the field is critical for up-and-coming scientists.
“Eugenics is not dead but continues to influence science and policy today,” writes Peifer ...
Semaglutide and Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Risk Among Patients With Diabetes
2025-03-27
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that semaglutide use was associated with an increased risk of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in patients with diabetes. However, the study’s retrospective design presents limitations, as it can only infer associations rather than establish causality; further studies are needed.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Chun-Ju Lin, MD (doctoraga@gmail.com) and James Cheng-Chung ...
Electronic Screen Use and Sleep Duration and Timing in Adults
2025-03-27
About The Study: Daily screen use was associated with later bedtimes and approximately 50 minutes less sleep each week in this study. Associations were greater among those with evening chronotypes, who are at risk for poor sleep due to social jetlag (i.e., misalignment between circadian rhythms and social commitments). These findings confirm disruptions to sleep from electronic screens are not limited to children and adolescents. Further work is needed to understand the best mechanisms for intervention.
Corresponding Author: To ...
State Minimum Wage and Food Insecurity Among US Households With Children
2025-03-27
About The Study: In this pooled cross-sectional study, findings suggest that state legislatures that elected to increase their state minimum wage may have also improved state food security rates among households with children at risk for economic hardship. The findings provide policymakers with actionable evidence to consider in setting minimum wages that could reduce the burden of food insecurity among U.S. children and families.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Megan R. Winkler, PhD, RN, email megan.winkler@emory.edu.
To ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
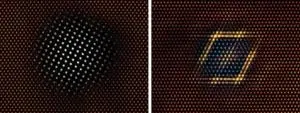
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Park entrances may be hotspots for infective dog roundworm eggsNew study could help inform efforts to reduce risk of spread among animals and to humans