(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from Arizona State University, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL), Lehigh University and Louisiana State University has developed a groundbreaking high-temperature copper alloy with exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength.
The research team’s findings on the new copper alloy, published in prestigious journal Science, introduce a novel bulk Cu-3Ta-0.5Li nanocrystalline alloy that exhibits remarkable resistance to coarsening and creep deformation, even at temperatures near its melting point.
“Our alloy design approach mimics the strengthening mechanisms found in Ni-based superalloys,” said Kiran Solanki, a professor at the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering in the School for Engineering of Matter, Transport and Energy, and a co-author of the study.
Currently, nickel-based superalloys, known for their exceptional strength, corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, are the primary material used in applications where these properties are critical, such as aerospace components, gas turbine engines and chemical processing equipment.
New materials are especially needed throughout the aerospace and defense industries---think of the strength, durability and heat resistance needed for high-speed flight or deploy weaponry. This spurs the research community to continue to push the boundaries of high-impact technologies.
“We have to critically think about what we can do to solve engineering problem in a more outside the box way,” said Solanki. “At the end of the day, I'm more curious about what I don't know.”
Solanki's main research interests investigate the structure and property relationships of advanced materials across multiple length scales. His goal is to manufacture advanced, multifunctional materials for extreme applications including radiation, high rate, fatigue and prevent slow deformation under mechanical stresses, or creep.
“When we look inside our body, we try to look for fingerprints of cell mutation for cancer,” said Solanki. “Similarly, structural materials have a unique fingerprint when they are subjected to any event like radiation or heat. They will leave behind a fingerprint which causes them to fail or not to perform the way they should perform.”
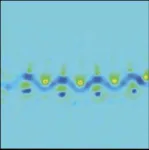
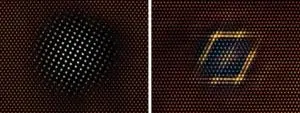
The newly engineered alloy owes its superior properties to a unique nanoscale structure featuring precisely ordered copper Lithium precipitates surrounded by a tantalum-rich atomic bilayer. The addition of precisely half a percent of lithium –no more, no less--to the previously immiscible Cu-Ta system alters the precipitate morphology. It changes the sphere-like precipitate in Cu-Ta system into forming a stable cuboidal structures that significantly enhance thermal and mechanical performance.
“And in this case, having a copper lithium precipitate with a stable bilayer of Ta is when we can alter high temperature fingerprint for failure,” said Solanki. “By manipulating fingerprints, we have developed a copper alloy that maintains its strength and structural integrity even after prolonged exposure to high temperatures.”
Key findings from the copper superalloy research include:
Enhanced Thermal Stability: The Cu-3Ta-0.5Li alloy remains stable at 800°C for over 10,000 hours, with minimal loss in yield strength.
High-Temperature Strength: The alloy outperforms existing commercial copper alloys, achieving a yield strength of 1120 MPa at room temperature.
Superior Creep Resistance: Cu-Ta-Li exhibits significantly lower creep deformation compared to conventional Cu-Ta alloys, making it ideal for high-stress, high-temperature environments.
The discovery opens new avenues for the development of next-generation copper alloys for applications in aerospace, energy and defense industries. Potential uses include heat exchangers, high-performance electrical components, weaponry and structural materials requiring durability in extreme conditions.
“This research not only advances our understanding of alloy design but also paves the way for materials that can withstand extreme environments,” said Kris Darling, another ARL co-author of the study. “The manipulation of fingerprints through nanostructuring in alloy could revolutionize the way we approach high-temperature material development.”
The study, titled A High-Temperature Nanostructured Cu-Ta-Li Alloy with Complexion-Stabilized Precipitates, is available in Science and was supported by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory, the National Science Foundation, and Lehigh University’s Nano-Human Interfaces Initiative.
END
Breakthrough copper alloy achieves unprecedented high-temperature performance
Strongest Cu-Ta-Li alloy to date demonstrates exceptional strength and stability for advanced engineering applications
2025-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Classroom talk plays a key part in the teaching of writing, study shows
2025-03-27
The way teachers manage classroom discussion with pupils plays a key role in the teaching of writing, a new study shows.
The research shows the importance of managing classroom discussion in a way that develops pupils’ understanding of the choices that writers make, and how those choices create particular effects for readers. This discussion helps pupils to think more about the choices that they make in their own writing.
The study reinforces the importance of dedicating time to discussion in secondary English lessons. It shows that time should be given to exploratory, speculative discussion that ...
Compelling data point to a single, unknown respiratory virus as cause of Kawasaki disease
2025-03-27
Research from Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago strongly suggests that Kawasaki disease is caused by a single respiratory virus that is yet to be identified. Findings contradict the theory that many different pathogens or toxins could cause this disease that can lead to serious cardiac complications in young children.
“The cause of Kawasaki disease has been a mystery for over 50 years,” said Anne Rowley, MD, pediatric infectious diseases expert and scientist at Manne Research Institute at Lurie Children’s, who is the lead author on the study published ...
Melting ice, more rain drive Southern Ocean cooling
2025-03-27
In brief
Surface waters in the Southern Ocean have been cooling in recent decades, counter to what climate models predict.
Scientists have quantified how much of the cooling observed since 1990 has been driven by an influx of freshwater that’s unaccounted for in state-of-the-art climate models.
The researchers discovered that freshwater inputs along the coast from melting ice sheets exert surprisingly strong influence on Southern Ocean surface temperatures and the broader climate system.
Global climate models predict that the ocean around Antarctica ...
Gasdermin D emerges as a potential therapeutic target for atrial fibrillation
2025-03-27
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common form of heart arrhythmia, a serious condition in which the heart beats so fast that its upper chambers, the atria, quiver. This irregular heartbeat can increase the risk of severe conditions, including heart failure, dementia and stroke.
“My lab has been studying the role of inflammation in the initiation and persistence of AF for many years. In this multidisciplinary study, we investigated the function of gasdermin D, a key participant in inflammatory pathways, in atrial heart cells and its potential contribution to AF,” said corresponding author Dr. Na Li, professor of medicine ...
Mapping the Earth’s crops
2025-03-27
As agricultural research continues to become more entwined with technology, smart farming – a phrase that encompasses research computing tools that help farmers to better address issues like crop disease, drought and sustainability – has quickly become a ubiquitous term in Ag labs across the country. The availability of NCSA resources like Delta for researchers, both nationally and on the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U. of I.) campus, has fostered a hotbed of cutting-edge research projects in the agricultural domain.
Yi-Chia Chang, a Ph.D. student at the ...
Rideshare data reveal discriminatory policing for speeding in Florida
2025-03-27
Using data on more than 220,000 individuals on the Lyft rideshare platform, researchers report that drivers of color are significantly more likely to receive speeding tickets than white drivers, and to face steeper fines, even when traveling at identical speeds. Racial profiling by law enforcement is a pressing social issue in the United States. Previous research analyzing police and judicial records suggests that racial and ethnic minorities face disproportionately higher rates of searches, fines, force, detentions, and incarceration compared to white civilians. However, research on racial bias in policing has long been hindered by data limitations ...
Unique genetic mutation underlies horses’ exceptional athleticism
2025-03-27
Researchers have revealed a secret behind horses' exceptional endurance – a mutation in the KEAP1 gene that boosts energy production while protecting against cellular oxidative stress. The findings – which shed light on a unique evolutionary adaptation that has shaped one of nature’s most powerful athletes – hold potential implications for human medicine. They also highlight how the recoding of a de novo stop codon – a strategy thought restricted to viruses – can facilitate adaptation in vertebrates. Long prized for their speed and endurance, horses possess remarkable physiological adaptations ...
Dopamine-producing brain circuit drives eating “for pleasure” in mice
2025-03-27
A previously overlooked dopamine-producing brain circuit drives hedonic eating, or eating for pleasure, according to a new study in mice. The findings offer insights into how GLP-1 agonist drugs like semaglutide affect appetite suppression and why pleasing and delicious foods can override these drugs’ effects. In a related Perspective, Dana Small argues that the findings indicate that the inter-individual differences in the adaptation of this circuit in response to GLP-1 drugs may account for differences in treatment efficacy in humans. “Future work that aims to minimize such adaptation could offer a promising avenue for the development of ...
Balancing national priorities and basic research in China
2025-03-27
As China rises as a global science power, its government has increased efforts to align basic research with national priorities, such as economic growth, environmental sustainability, and national security. In a Policy Forum, Andrew Kennedy discusses how this increasing emphasis on national priorities creates tension with basic research in China – a pattern that reflects broader global trends – and the potential risks of prioritizing near-term objectives over long-term scientific discovery. According to the author, neglecting curiosity-driven research while expanding support for near-term priorities is short-sighted. Without it, transformative innovations – from ...
Feeling the future: New wearable device mimics the complexity of human touch
2025-03-27
When it comes to haptic feedback, most technologies are limited to simple vibrations. But our skin is loaded with tiny sensors that detect pressure, vibration, stretching and more.
Now, Northwestern University engineers have unveiled a new technology that creates precise movements to mimic these complex sensations.
The study will be published on March 28 in the journal Science.
While sitting on the skin, the compact, lightweight, wireless device applies force in any direction to generate a variety of sensations, including ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough copper alloy achieves unprecedented high-temperature performanceStrongest Cu-Ta-Li alloy to date demonstrates exceptional strength and stability for advanced engineering applications