(Press-News.org)
Steroid hormone levels in healthy adults are influenced by oral contraceptives and smoking, as well as other lifestyle choices and factors such as biological sex and age, according to new research that has just been published in leading international journal Science Advances.
The objective of the research was to expand knowledge and understanding of steroid hormone levels, including corticoids and sex hormones, in healthy women and men over a broad age range. This is the first study to analyse such a large number of hormones in nearly 1,000 healthy people, filling a major gap in the knowledge of molecules that are important for our day-to-day well-being.
The work was conducted by members of the Milieu Interieur consortium and led by Dr Darragh Duffy (Institut Pasteur) and Dr Molly Ingersoll (Institut Pasteur and Institut Cochin (Inserm U1016, CNRS, Université Paris Cité). Dr Jamie Sugrue, a Trinity College Dublin graduate, now a Marie Curie-funded postdoctoral researcher at the Institut Pasteur, is the co-first author. Dr Sugrue also worked with Trinity’s Professor Cliona O’Farrelly to secure a Research Ireland Ulysses grant, which kickstarted the ongoing collaboration between Trinity researchers and the Pasteur and Milieu Interieur consortium teams.
The team involved in this current study found that hormone levels vary according to an individual’s age and sex, but that they are also associated with many other factors, such as genetics and common behaviours.
Notably, many steroid hormone levels, beyond sex hormones, are influenced by oral contraceptive use in women, while in men, smoking was associated with altered levels of nearly every steroid hormone measured.
Additionally, measurement of hormones in the same donors 10 years after the original visit showed that decreases in specific androgens were associated with diverse diseases in aging men, implying that these hormones – which are associated with physical characteristics, and supporting strong bones and red blood cell production – play a role in disease development.
This finding – among others – gives the team numerous avenues to pursue in future research.
Dr Sugrue said: “Even in healthy people, immune responses can vary dramatically. As a first step towards understanding how hormones impact immunity, we worked to understand how hormones themselves vary among people. Our study provides a significant resource for the research community, and generates many new hypotheses for further research. Our next steps will focus on understanding how variation in hormone levels contribute to differences in the immune response between people.”
“My current project is specifically focused on variation in antiviral immune responses in healthy people, and in many ways is a continuation of work that I started during my PhD with Prof. Cliona O'Farrelly at Trinity, where we worked on how antiviral immune system variation can confer resistance to hepatitis C virus infection. By incorporating the hormone measures into my current analysis I hope to uncover exciting new insights.”
Cliona O’Farrelly, Professor of Comparative Immunology in Trinity’s School of Biochemistry and Immunology, added: “If the COVID pandemic taught us anything it was how different all our immune systems are, and being part of the Milieu Interieur collaboration is giving us Trinity researchers a wonderful opportunity to study the molecular and genetic mechanisms responsible for these differences at scale.”
Co-first author, Dr Léa G Deltourbe, Institut Pasteur & Institut Cochin, added: “This study brings much needed data to a subject that is receiving a lot of interest in the mainstream news and on social media platforms, providing a strong basis for investigating the role of steroid hormones in health and disease, including the impact of endocrine disruptors, the link between stress and cortisol, and the role of sex hormones on our well-being.”
As one example, understanding the potential effects of the contraceptive pill on physical and mental health should lead to a better quality of life for women choosing to use this form of medication.
The exciting results in this paper were first presented to an international audience at the Sex Differences in Immune Health conference recently hosted by Trinity College Dublin.
END
TUCSON, Ariz., March 27, 2025 – Researchers from Critical Path Institute’s® (C-Path) Predictive Safety Testing Consortium have proposed glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) as a more liver-specific biomarker for detecting liver injury, supporting clearer decision-making. Currently, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase (ALT and AST) are considered the “gold standard” biomarkers in clinical practice and drug development. However, these biomarkers are not specific to the liver and can reflect changes in other tissues, which may lead to unclear diagnoses, particularly in individuals with muscle conditions ...
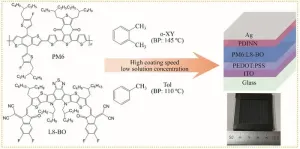
In a recent advancement, researchers have developed a high-speed doctor-blading technique that enhances the efficiency of organic solar cells (OSCs) while using eco-friendly, non-halogenated solvents. This innovative method not only addresses the environmental and scalability challenges of traditional solvents, such as chloroform, but also achieves impressive power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of 18.20% and 17.36% with green solvents like o-xylene and toluene, respectively. With a module efficiency of 16.07%, this breakthrough sets the stage for more sustainable, ...
TUCSON, Ariz., March 26, 2025 – Critical Path Institute® (C-Path)Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Consortium and Electronic Clinical Outcome Assessment (eCOA) Consortium are pleased to announce the successful conclusion of the eCOA: Getting Better Together Initiative. This initiative, driven by a shared commitment to advancing patient-focused drug development, has culminated in meaningful, lasting changes that will benefit all stakeholders across the eCOA ecosystem.
Beginning in 2019, this C-Path-led collaborative, pre-competitive initiative brought ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
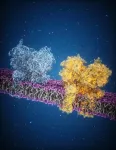
In an effort to understand how brain cells exchange chemical messages, scientists say they have successfully used a highly specialized microscope to capture more precise details of how one of the most common signaling molecules, glutamate, opens a channel and allows a flood of charged particles to enter. The finding, which resulted from a study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers, could advance the development of new drugs that block or open such signaling channels to treat conditions as varied as epilepsy and some intellectual disorders.
A report on the experiments, funded by the National ...
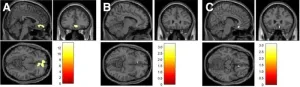
Reston, VA (March 16, 2025)—For the first time, scientists have confirmed a neurobiochemical link between dopamine and cognitive flexibility, according to new research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. PET imaging shows that the brain increases dopamine production when completing cognitively demanding tasks, and that the more dopamine released, the more efficiently the tasks are completed. Armed with this information, physicians may soon be able to develop more precise treatment strategies for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Cognitive flexibility is the ability to adapt one’s thinking and behavior appropriately to ...
Most humans have long-lived infections in various tissues—including in the nervous system—that typically do not result in disease. The microbes associated with these infections enter a latent stage during which they quietly hide in cells, playing the long game to evade capture and ensure their own survival. But a lack of natural models to study these quiescent stages has led to gaps in scientists’ understanding of how latency contributes to pathogen persistence and whether these stages can be targeted by the immune system.
Now, a team led by University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine researchers ...
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) invites you to a congressional briefing:
Title: The Impact of Obesity and Opportunity for CMS to Address
When: Tuesday, April 1, from 12 to 1 p.m. ET
Where: Virtual
Click to RSVP
GSA is a professional membership organization committed to promoting the best available interdisciplinary aging research to advance innovations in practice and policy. This is especially key to managing the chronic condition of obesity in health care.
Older people with obesity and overweight require access to proven treatment options and care to improve overall health and reduce other related health care costs. ...
Appalachia is globally recognized as a key supplier of non-timber forest products (NTFPs) with growing demand for its resources. Nearly half of the woodland medicinal species in the global nutraceutical market come from the region, contributing to a multibillion-dollar industry.
Species such as ginseng, slippery elm, and black cohosh are prominent understory sources of medicinal material. Appalachian edible products are also gaining popularity beyond the region. Ramps, a wild Appalachian plant, can sell for more than $20 per pound in places such as New York City.
Spanning 205,000 square miles, Appalachia is home to over ...
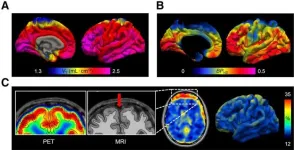
Reston, VA (March 28, 2025)—A novel PET imaging approach can effectively quantify a key enzyme associated with brain inflammation, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The first-in-human study, which imaged the COX-2 enzyme, offers a never-before-seen view of inflammation in the brain, opening the door for COX-2 PET imaging to be used in clinical and research settings for various brain disorders.
COX-2 is an enzyme in the brain that can be markedly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers say that the density of COX-2 in the brain may be a biomarker and effect of inflammation, ...
Music is central to human emotion and culture. Does our ability to enjoy music have a biological basis? A genetic twin study, published in Nature Communications, shows that music enjoyment is partly heritable. An international team led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, uncovered genetic factors that influence the degree of music enjoyment, which were partly distinct from genes influencing general enjoyment of rewarding experiences or musical ability.
Music plays an important role in human emotion, social bonding, and cultural expression. As Darwin already noted, music "must ...