(Press-News.org) Real estate is precious. Some creatures defend territories extending over several kilometres, but when Jayne Yack (Carleton University, Canada) encountered miniature newborn warty birch caterpillars (Falcaria bilineata) she wondered if she might have discovered one of the world’s smallest, and youngest, territorial critters. ‘We had noticed that tiny warty birch caterpillars produced vibrations’, says Yack, who first encountered the feisty little creatures in 2008. She also noticed that the tiny caterpillars – 1 to 2 mm long – reside in solitude on birch leaves, making her speculate whether they are warning off intruders with the vibrations they transmit through their leaves from their leaf tip residences. Yack and her colleagues report in Journal of Experimental Biology that the minute caterpillars are territorial, warning off intruders with vibrations produced by scraping their rear ends along the leaf, in addition to beating the leaf tip with their thorax, to defend the world’s smallest territory.
To find out more about the tiny caterpillars , Yack, Sarah Matheson, Leonardo Turchen and Emilie Mauduit (also from Carleton University) first needed to collect female two-lined hooktip moths (F. bilineata), ready to lay eggs on leaves and pieces of paper in the lab, in order to collect the caterpillar youngsters and transfer them to the centre of a single birch leaf as soon as they emerged from the eggs, to find out which region of the leaf they prefer to inhabit. A day later, almost 90% of the youngsters had wriggled to the tip of the leaf to set up home.
Having determined that the youngsters establish a territory, the team filmed the tiny caterpillars as they scouted their minute home range, rested and fed, rarely straying more than a few body lengths from the tip. And from time to time the youngsters beat the leaf with their head and thorax, producing a percussive tone, in addition to dragging oar-shaped hairs on their rear along the leaf, producing a buzzing scraping sound, while simultaneously striking the leaf with the head end of their bodies. ‘The sounds produced by these caterpillars are not audible humans, so we had to use specialized equipment to pick up the vibrations’, says Yack.
Once she was certain that the teeny creatures were territorial, Yack and her colleagues wondered how the youngsters would react when an intruder came calling. Placing an interloper near the centre of an occupied leaf, the team sat back and watched each encounter unfold. Sometimes the intruder turned tail and headed off in search of another leaf after approaching the resident, which had been frantically scraping at the leaf sending urgent warnings as the trespasser advanced. However, on other occasions the occupant secured themselves to the leaf with a silken thread before flinging themselves over the edge – after a protracted period of leaf scraping – as the threat approached, leaving themselves dangling safely beneath the leaf. Yet the caterpillars never came to physical blows, biting or thrashing each other. The outcome of each contest depended entirely on the warning vibrations transmitted through the leaf. Yack suspects that the youngsters might prefer this more diplomatic form of conflict resolution to ensure they both survive.
But why defend a leaf tip? Yack suggests that the tip may be more succulent than other parts of the leaf, offering the resident better nutrition, in addition to providing the occupant with a springboard for escape, if necessary. She also suggests that intruders are unable to approach residents ensconced at the tip from behind, limiting their opportunities for attack, and could even allow the tiny caterpillars to appear larger than they are as the leaf might amplify the resident’s warning signals. Whatever the reason, tiny newborn warty birch caterpillars could tip the scales as the tiniest kings in their leaf tip castles
*******************************
Press release distributed 1 April 2025
IF REPORTING THIS STORY, PLEASE MENTION JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY AS THE SOURCE AND, IF REPORTING ONLINE, PLEASE CARRY A LINK TO: https://journals.biologists.com/jeb/article-lookup/doi/10.1242/jeb.249796
REFERENCE: Matheson, S. M., Turchen, L. M., Mauduit, E. and Yack, J. E. (2025). Buzzing boundaries: tiny caterpillars vibrate to defend leaf tip territories. J. Exp. Biol. 228, jeb249796. doi:10.1242/jeb.249796
DOI: 10.1242/jeb.249796
Registered journalists can obtain a copy of the article under embargo from http://pr.biologists.com. Unregistered journalists can register at http://pr.biologists.com to access the embargoed content. The embargoed article can also be obtained from Kathryn Knight (kathryn.knight@biologists.com)
This press release gives access to authorised media who may wish to report on this story. Full attribution is required and if reporting online a link to https://journals.biologists.com/jeb is also required. The story posted here is COPYRIGHTED. Advance permission is required before any and every reproduction of each article in full from permissions@biologists.com.
END
Newborn warty birch caterpillars defend the world’s smallest territory
Warty Birch caterpillars are the tiniest kings in their leaf tip castles
2025-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exposure to air pollution in childhood is associated with reduced brain connectivity
2025-04-01
A new study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has found that children exposed to higher levels of air pollution in early and mid childhood have weaker connections between key brain regions. The findings, published in Environment International, highlight the potential impact of early exposure to air pollution on brain development.
The research showed reduced functional connectivity within and between certain cortical and subcortical brain networks. These networks are systems of interconnected brain structures that work together to perform different cognitive functions, such as thinking, perceiving and controlling ...
Researchers develop test using machine learning to help predict immunotherapy response in lymphoma patients
2025-04-01
LOS ANGELES — Researchers with City of Hope, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, with its National Medical Center in Los Angeles ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report, and MSK have created a tool that uses machine learning to assess a non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patient’s likely response to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy before starting the treatment, according to study results published today in Nature Medicine.
CAR T cell therapy ...
New UNSW research reveals dramatically higher loss of GDP under 4°C warming
2025-04-01
New projections by the UNSW Institute for Climate Risk & Response (ICRR) reveal a 4°C rise in global temperatures would cut world GDP by around 40% by 2100 – a stark increase from previous estimates of around 11%.
The recently-published analysis fixes an oversight in the current economic model underpinning global climate policy, toppling previous carbon benchmarks.
The results support limiting global warming to 1.7 °C, which is in line with significantly faster decarbonisation goals like the Paris Agreement, and far lower than the 2.7°C supported ...
Discovery of Quina technology challenges view of ancient human development in East Asia
2025-03-31
While the Middle Paleolithic period is viewed as a dynamic time in European and African history, it is commonly considered a static period in East Asia. New research from the University of Washington challenges that perception.
Researchers discovered a complete Quina technological system — a method for making a set of tools — in the Longtan site in southwest China, which has been dated to about 50,000 to 60,000 years ago. Quina technology was found in Europe decades ago but has never before been found in East Asia.
The team published its findings March ...
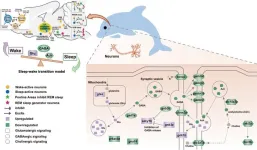
Whales and dolphins sleep by turning off one half of their brains at a time; scientists discover more about the genes and pathways that enable this phenomenon
2025-03-31
Whales and dolphins sleep by turning off one half of their brains at a time; scientists discover more about the genes and pathways that enable this phenomenon.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4c9g5gm
Article Title: Evolution of canonical circadian clock genes underlies unique sleep strategies of marine mammals for secondary aquatic adaptation
Author Countries: China
Funding: This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development (R&D) Program of China (grant no. 2022YFF1301600) to G.Y. & S.X., the Key Project ...
A new clue to how multicellular life may have evolved
2025-03-31
Life emerged on Earth some 3.8 billion years ago. The “primordial soup theory” proposes that chemicals floating in pools of water, in the presence of sunlight and electrical discharge, spontaneously formed organic molecules. These building blocks of life underwent chemical reactions, likely driven by RNA, eventually leading to the formation of single cells.
But what sparked single cells to assemble into more complex, multicellular life forms?
Nature Physics published a new insight about a possible driver of this key step in evolution — the fluid ...
ALL ALS consortium launches website to advance ALS research
2025-03-31
ALL ALS Consortium Launches Website to Advance ALS Research
The Access for All in ALS (ALL ALS) Consortium announced the launch of its official website, creating a central hub for information about its initiatives and clinical research studies. ALL-ALS.org is designed to inform and engage researchers, clinicians, and current and prospective study participants.
The ALL ALS Consortium formed in fall 2023 with funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The consortium consists of 35 clinical sites in the United States and Puerto Rico, led by researchers at Barrow Neurological Institute in Phoenix, Arizona and Massachusetts ...
Many TB cases may have gone undetected in prisons in Europe and the Americas during COVID-19
2025-03-31
EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:30 P.M. EST on Monday, March 31, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Many TB Cases May Have Gone Undetected in Prisons in Europe and the Americas During COVID-19
A new study found that reported diagnoses for tuberculosis were consistently lower than expected throughout the pandemic, even though incarceration rates remained largely consistent and TB detection among the general population managed to reverse after an early-pandemic decline.
Incarcerated populations have a high risk of developing tuberculosis ...
Predicting older people’s frailty helps doctors intervene earlier
2025-03-31
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00.01 AM BST ON TUESDAY 1 APRIL
The new Electronic Frailty Index 2 (eFI2) is now available to 60% of England’s GPs thanks to research funded by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) and conducted by researchers at the University of Leeds and UCL
GP data on 36 health problems such as dementia, falls and fractures will help medical professionals to more accurately identify older people’s frailty and intervene earlier
Interventions may include a holistic assessment and treatment plan, falls prevention, targeted medicines review, and resistance exercise ...
New study validates lower limits of human heat tolerance
2025-03-31
A study from the University of Ottawa’s Human and Environmental Physiology Research Unit (HEPRU) has confirmed that the limits for human thermoregulation—our ability to maintain a stable body temperature in extreme heat—are lower than previously thought.
This research, led by Dr. Robert D. Meade, former Senior Postdoctoral Fellow and Dr. Glen Kenny, Director of HEPRU and professor of physiology at uOttawa's Faculty of Health Sciences, highlights the urgent need to address the impacts of climate change on human health.
The study found that many regions may soon experience heat and humidity levels that exceed the safe limits ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
[Press-News.org] Newborn warty birch caterpillars defend the world’s smallest territoryWarty Birch caterpillars are the tiniest kings in their leaf tip castles