Ohio State study reveals new insights into neurodegeneration using human ‘mini brains’
Research findings could lead to treatments for frontotemporal lobar degeneration and Alzheimer’s
2025-04-09
(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine have discovered a new way that neurons act in neurodegeneration by using human neural organoids – also known as “mini-brain” models – from patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD).
Understanding this new pathway could help researchers find better treatments for FTLD and Alzheimer’s, the two most common forms of dementia that lead to cognitive decline.
Researchers used advanced techniques to study neurons from patients and mice, including growing human neural organoids (“mini brains”) that can feature several cell-types found in the brain.
They found the protein GRAMD1B plays a significant role in how cholesterol and lipid stores are managed in neurons. When GRAMD1B levels are altered, it changes the balance of cholesterol, lipid stores and amount of modified tau in the cells, all of which are linked to brain diseases.
The study is published online in the journal Nature Communications.
“Scientists know that GRAMD1B plays a role in other parts of the body like the adrenal gland and intestine but until now the protein has never been studied in the brain. The findings are exciting because by targeting GRAMD1B, we can potentially develop new therapies to help people with FTLD and Alzheimer's,” said study corresponding author Hongjun “Harry” Fu, PhD, assistant professor of neuroscience at Ohio State.
About 50,000 to 60,000 Americans live with FTLD. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia. An estimated 6.9 million Americans who are age 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's dementia today, according to the Alzheimer’s Association’s 2024 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures report.
The work was supported by the BrightFocus Foundation’s Alzheimer's Disease Research, National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health, The Ohio State University Chronic Brain Injury Discovery Theme pilot grant, and The Ohio State University Neurological Research Institute seed grant.
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-09
A pivot from fossil fuels to clean energy technologies by 2060 would improve energy security and reduce trade risks for most nations, according to an April 9 study in Nature Climate Change.
Lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, and rare earth minerals are among the prized materials for countries and corporations racing to secure supplies for energy systems that do not add greenhouse gases to our atmosphere. Unlike fossil fuels, natural reserves of these materials are most concentrated in the Global South, shuffling the geopolitics of energy and global trade.
“Most people ...
2025-04-09
New research from the University of Sydney has revealed poor oral health is significantly associated with higher instances of migraines, abdominal and body pain in women.
Published in Frontiers in Pain Research, the world-first study identified specific oral microbes correlated with certain pain conditions, suggesting a potential relationship between the oral microbiome and the nervous system.
The findings highlight the importance of good oral health to potentially mitigate pain and improve overall wellbeing, prompting further exploration into the role of oral microbiota in chronic unexplained ...
2025-04-09
A review published in The Laryngoscope indicates that climate change’s effects on pollen seasons and concentrations are contributing to increasing rates of allergic rhinitis, or hay fever.
When investigators assessed research published between 2000 and 2023, they identified 30 studies that reported on the current epidemiological state of allergic rhinitis, described factors related to climate change, and observed how global warming is affecting pollen seasons and allergy symptoms.
Sixteen studies reported longer pollen seasons and/or higher pollen concentrations related to climate change. As an example, total pollen emissions in the U.S. are projected to increase by 16–40% ...
2025-04-09
Several states, including Georgia, offer state-funded pre-kindergarten programs to students regardless of their family’s income. New research in Economic Inquiry investigates whether such programs offer long-lasting academic benefits to all students.
Using enrollment lottery data from a large school district in metro Atlanta, investigators found that lottery-winning enrollees of school-based pre-kindergarten entered kindergarten more prepared in both math and reading than non-winning peers. Gains tended to fade by the end of kindergarten, however, and some negative achievement effects ...
2025-04-09
Hydrogels, which are soft materials formed by crosslinking polymers, could have a variety of medical applications. In research published in Advanced Science, investigators developed an injectable hydrogel containing components of fish swim bladders and used it to repair damaged heart tissue.
The fish swim bladder is an organ that aids fish in floating in water and is composed of collagen, glycosaminoglycans, and elastin, closely resembling parts of the human heart.
Experiments revealed that the researchers’ fish swim bladder–based hydrogel enhances cardiac cell adhesion and stretching while promoting new ...
2025-04-09
New research published in the Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging has uncovered changes in brain connectivity during chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
In the study of 55 patients with breast cancer and 38 controls without cancer, investigators conducted functional magnetic resonance imaging scans of participants’ brains over several months.
Scans from patients revealed changes in brain connectivity, particularly in the frontal-limbic system (involved in executive functions) and the cerebellar cortex (linked to memory) throughout the course of treatment. These changes got worse and spread more as chemotherapy continued.
“The ...
2025-04-09
Risky driving by parents and other motorists who do the school run is putting children in danger, according to a study published in the peer-reviewed journal Traffic Injury Prevention.
Double parking, not obeying traffic controls and other unsafe behavior occurs at the majority (98%) of elementary schools during morning drop-off times.
The authors analyzed data from more than 500 schools in Canada and say hazardous driving is an “urgent and serious” issue. The most observed misdemeanour was to drop a student ...
2025-04-09
According to a new RAND survey, over 80% of public school-based pre-kindergarten (pre-K) teachers use multiple curriculum materials. Some combine materials that focus on a particular domain – such as literacy or numeracy – while others use material that covers many domains at once, and some use both. More than two-thirds reported using materials that they created themselves, often in conjunction with commercial curricula.
Most public school-based pre-K educators surveyed believe their instructional materials are high quality, especially ...
2025-04-09
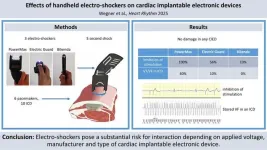
Philadelphia, April 9, 2025 – Research has found that handheld electro-shockers commonly used for self defense can potentially interact with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) such as pacemakers, putting individuals at risk. The study in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, the Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society, published by Elsevier, shows that the individual interactive risk is primarily based on the applied voltage, but also on the manufacturer and type of implanted CIED.
The use of TASER pistols by security forces has been controversial ...
2025-04-09
Doctor Elodie Bouzbib, from Public University of Navarra (UPNA), together with Iosune Sarasate, Unai Fernández, Manuel López-Amo, Iván Fernández, Iñigo Ezcurdia and Asier Marzo (the latter two, members of the Institute of Smart Cities) have succeeded, for the first time, in displaying three-dimensional graphics in mid-air that can be manipulated with the hands.
'What we see in films and call holograms are typically volumetric displays,' says Bouzbib, the first ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ohio State study reveals new insights into neurodegeneration using human ‘mini brains’
Research findings could lead to treatments for frontotemporal lobar degeneration and Alzheimer’s