(Press-News.org) New Curtin University research into the overlooked environmental impact of pet dogs has found far-reaching negative effects on wildlife, ecosystems and climate.
While ecological damage caused by cats has been extensively studied, the new research found dogs, as the world’s most common large carnivores, present a significant and multifaceted environmental threat.
Lead researcher Associate Professor Bill Bateman, from Curtin’s School of Molecular and Life Sciences, said the research found that human-owned, pet dogs disturb and directly harm wildlife, particularly shorebirds, even when leashed.
“As well as predatory behaviour like chasing wildlife, dogs leave scents, urine and faeces, which can disrupt animal behaviour long after the dogs have left,” Associate Professor Bateman said.
“Studies have found that animals like deer, foxes and bobcats in the US are less active or completely avoid areas where dogs are regularly walked, even in the absence of the dogs.
“Dog waste also contributes to pollution in waterways and inhibits plant growth, while wash-off from chemical treatments used to clean and guard dogs from parasites can add toxic compounds to aquatic environments.
“In addition, the pet food industry, driven by a vast global dog population, has a substantial carbon, land and water footprint.”
Associate Professor Bateman said addressing these challenges required a careful balance between reducing environmental harm and maintaining the positive role of dogs as companions and working animals.
“Dogs are incredibly important to people’s lives and their roles range from providing companionship to contributing to conservation efforts as detection dogs,” Associate Professor Bateman said.
“However, the sheer number of pet dogs globally, combined with uninformed or lax behaviours by some owners, is driving environmental issues that we can no longer ignore.”
The study also sheds light on barriers to sustainable pet ownership, finding that while the dog food industry is a key factor in national sustainability action plans, only 12 to 16 per cent of dog owners are willing to pay more for eco-friendly pet food, largely due to rising costs. Additionally, a lack of awareness among owners about the impact of dogs on the environment compounds the issue.
“Many owners simply don’t realise the environmental damage dogs can cause, from disturbing wildlife to polluting ecosystems,” Associate Professor Bateman said.
“Others may feel their individual actions won’t make a difference, leading to a ‘tragedy of the commons’ where shared spaces like beaches and woodlands suffer cumulative degradation.
“Restrictive measures such as banning dogs from sensitive areas are necessary for protecting vulnerable species but they are not a complete solution. We are calling for a collaborative effort between dog owners, conservation groups and policymakers to develop strategies that balance pet ownership with environmental care.”
The paper, ‘Bad Dog? The environmental effects of owned dogs,’ has been published in Pacific Conservation Biology and can be found online here: https://doi.org/10.1071/PC24071
END
Man’s best friend may be nature’s worst enemy, study on pet dogs finds
2025-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research in JNCCN finds stark disparities in treatment and survival time for people with pancreatic cancer
2025-04-09
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 9, 2025] — New research in the April 2025 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network found significant disparities based on race, socioeconomic status, and other factors when it came to quality of care and outcomes for people with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma (mPDAC)—which is associated with very high cancer mortality. The researchers used the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database to study 14,147 patients who were diagnosed ...
With new database researchers may be able to predict rare milky seas bioluminescent, glowing event
2025-04-09
For generations, sailors around the globe have reported a mysterious phenomenon: Vast areas of the ocean glow steadily at night, sometimes for months on end. The light is bright enough to read by and is oddly similar to the green and white aura cast by glow-in-the dark stars that have decorated children’s rooms. Stretching over ocean space as broad as 100,000 square kilometers, the light can, at times, even be seen from space.
This rare bioluminescent display was coined by sailors as “milky seas.” Despite being encountered for centuries, scientists still know very little about what causes this glowing effect because ...
Enhancing power distribution systems with renewable energy: a new configuration approach
2025-04-09
A groundbreaking study presents a comprehensive approach to restructuring medium-level voltage (MLV) distribution systems that enhances reliability while reducing both energy losses and carbon emissions.
The study introduces an innovative "N+1 bus configuration" for radial distribution systems (RDS) - a simple yet powerful modification to conventional power networks that adds just one additional tie line to existing systems. This seemingly minor change delivers remarkable improvements in system performance when combined with distributed renewable energy resources (DER).
The research team conducted extensive testing on both real-time radial ...
Engineers bring sign language to ‘life’ using AI to translate in real-time
2025-04-09
For millions of deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals around the world, communication barriers can make everyday interactions challenging. Traditional solutions, like sign language interpreters, are often scarce, expensive and dependent on human availability. In an increasingly digital world, the demand for smart, assistive technologies that offer real-time, accurate and accessible communication solutions is growing, aiming to bridge this critical gap.
American Sign Language (ASL) is one of the most widely used sign languages, consisting of distinct hand gestures that represent letters, ...
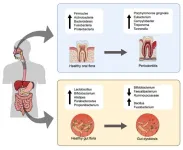
Bad breath, bad news: how gum disease could worsen liver conditions
2025-04-09
There is growing recognition in medicine that what happens in one part of the body can ripple through others. That idea is now being explored in a surprising place: the mouth. A new review by an international group of researchers has examined the mounting evidence linking periodontal disease—commonly known as gum disease—to chronic liver conditions, including cirrhosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), and alcohol-related liver disease. Though the mouth and liver are separated ...
Lighter and more flexible solar cells achieve world’s highest efficiency
2025-04-09
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (President Yi Chang-keun, hereinafter referred to as “KIER”) has successfully developed ultra-lightweight flexible perovskite/CIGS tandem solar cells and achieved a power conversion efficiency of 23.64%, which is the world’s highest efficiency of the flexible perovskite/CIGS tandem solar cells reported to date. The solar cells developed by the research team are extremely lightweight and can be attached to curved surfaces, making it a promising candidate for future applications in buildings, vehicles, aircraft, and more.
Crystalline silicon-based single-junction solar cells ...
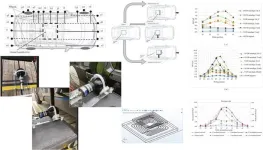
Vehicle-mounted wireless power transfer: ensuring safety through magnetic field management
2025-04-09
A comprehensive study has examined the magnetic field emissions (MFE) from vehicle-mounted wireless power transfer (WPT) systems, providing critical insights for ensuring user safety during electric vehicle charging. As wireless charging technology gains popularity for fleet vehicles and accessibility applications, understanding and controlling electromagnetic field exposure becomes increasingly important.
Researchers conducted extensive physical measurements around a vehicle equipped with an in-house designed WPT system, examining how various factors affect magnetic field emissions where users might be positioned during charging operations. The study specifically investigated:
- ...
Finding cancer’s ‘fingerprints’
2025-04-09
Cancer diagnoses traditionally require invasive or labor-intensive procedures such as tissue biopsies. Now, research published in ACS Central Science reveals a method that uses pulsed infrared light to identify molecular profiles in blood plasma that could indicate the presence of certain common cancers. In this proof-of-concept study, blood plasma from more than 2,000 people was analyzed to link molecular patterns to lung cancer, extrapolating a potential “cancer fingerprint.”
Plasma is the liquid portion of blood, depleted of any ...
Starch-based microplastics could cause health risks in mice, study finds
2025-04-09
Wear and tear on plastic products releases small to nearly invisible plastic particles, which could impact people’s health when consumed or inhaled. To make these particles biodegradable, researchers created plastics from plant starch instead of petroleum. An initial study published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows how animals consuming particles from this alternative material developed health problems such as liver damage and gut microbiome imbalances.
“Biodegradable starch-based plastics may not be as safe and health-promoting as originally assumed,” ...
A step toward cleaner iron extraction using electricity
2025-04-09
Iron and its alloys, such as steel and cast iron, dominate the modern world, and there’s growing demand for iron-derived products. Traditionally, blast furnaces transform iron ore into purified elemental metal, but the process requires a lot of energy and emits air pollution. Now, researchers in ACS Energy Letters report that they’ve developed a cleaner method to extract iron from a synthetic iron ore using electrochemistry, which they say could become cost-competitive with blast furnaces.
"Identifying oxides which can be converted to iron metal at low temperatures is an important ...