Therapy-related b-lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment for multiple myeloma with unusual surface light chain expression: a case report
2025-04-10
(Press-News.org) Background
Therapy-related B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) following treatment for multiple myeloma is a rare occurrence. Despite its rarity and the lack of recognition by the World Health Organization as a distinct disease entity, previous publications indicate its possible emergence following myeloma treatment.
Case presentation
The patient is a 65-year-old gentleman with a history of IgG kappa multiple myeloma, status post multiple lines of therapy. The patient presented with a fever, and a complete blood count showed cytopenia. Bone marrow morphologic evaluation revealed numerous blasts. Immunophenotypic analysis demonstrated that these blasts were B lymphoblasts, despite MYC and unusual surface kappa light chain expression. A diagnosis of B-ALL with surface kappa light chain expression post-myeloma treatment was made. Ancillary studies indicated that the B-ALL and the previous myeloma were clonally unrelated. Next-generation gene sequencing revealed pathogenic mutations in KDM6A and KRAS.
Conclusions
In summary, we present an interesting case of B-lymphoblastic leukemia with unusual surface light chain expression in a patient who has previously undergone myeloma treatment. This case represents therapy-related B-ALL. Although it has not been categorized as a WHO-recognized disease entity, our case provides additional evidence supporting that myeloma treatment, particularly lenalidomide therapy, is associated with secondary B-ALL. Furthermore, the ClonoSEQ test result in the current case indicates that therapy-related B-ALL is clonally unrelated to the preceding MM. The identification of new predominant clones in follow-up bone marrow samples of myeloma patients should alert clinicians to the possible emergence of a secondary B-cell neoplasm.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2771-165X/JCTP-2024-00046
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Pathology.
Journal of Clinical and Translational Pathology (JCTP) is the official scientific journal of the Chinese American Pathologists Association (CAPA). It publishes high quality peer-reviewed original research, reviews, perspectives, commentaries, and letters that are pertinent to clinical and translational pathology, including but not limited to anatomic pathology and clinical pathology. Basic scientific research on pathogenesis of diseases as well as application of pathology-related diagnostic techniques or methodologies also fit the scope of the JCTP.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-10
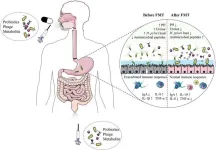
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a widespread bacterial infection associated with gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. While conventional antibiotic-based treatments have been the gold standard for eradication, their efficacy has been steadily declining due to the alarming rise in antibiotic resistance. This has spurred interest in alternative therapies, one of which is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT).
FMT is a novel therapeutic approach that involves transferring microbiota from a healthy donor to a patient’s ...
2025-04-10
Large granular lymphocytic leukemias (LGLLs) are a heterogeneous group of rare chronic lymphoproliferative disorders characterized by the clonal proliferation of cytotoxic lymphocytes. Among them, T-cell LGLL (T-LGLL) and NK-cell LGLL (NK-LGLL) are the most prominent. Due to overlapping morphological, clinical, and immunophenotypic characteristics, distinguishing these disorders from related entities such as T-prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL), adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL), Sézary syndrome (SS), and aggressive NK-cell leukemia (ANKL) presents a significant diagnostic challenge. This review integrates recent molecular insights and updates from the WHO 5th edition ...
2025-04-10
Chemicals used as food preservatives, flavoring agents, dyes, pesticides, cosmetics, cleaners, and other industrial materials are being increasingly recognized as a health hazard. Their rampant use has led to an increase in the prevalence of various chemical toxicity-induced diseases, including hormonal disruption, cancer, neurological disorders, skin conditions, and occupational poisoning. Numerous chemicals are known to trigger “carcinogenesis” or cancer development by exerting genotoxic effects (direct or indirect interference with DNA replication and damage repair processes ...
2025-04-10
Scientists writing a policy forum article in the CABI One Health journal say the “plant world” needs to come out and claim its place at the One Health table as part of a desire to break down barriers that currently limit true cross-domain integration.
The researchers say that while plant health is increasingly recognized as a vital part of One Health, it lacks recognition and – historically focussed on health service provision, zoonotic diseases and antimicrobial resistance – One Health overlooks plant health in strategic plans.
They add that cross-sectoral approaches, core to One Health, are already used ...
2025-04-10
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a serious issue affecting thousands of people in the U.S. every year. For military service members, the impact is even more profound. Since 2000, over 492,000 cases of TBI have been reported, making it one of the defining injuries of modern warfare, according to the U.S. Department of Defense. Many veterans have experienced multiple TBIs, raising concerns about long-term effects on brain health. Given the subjective and nonspecific nature of symptom presentation, treatment and prognosis can be difficult.
Researchers ...
2025-04-10
The first few days of a human embryo’s development, known as pre-implantation, are important. It’s when the first cells are formed, and these decide if the embryo can survive, how it will implant in the womb and how the tissues of the fetus will develop.
Today there are still logistical, ethical and legal limitations to using human embryos for research purposes, so scientists use alternative models including stem cell-based and animal models.
In a new study published in Nature Cell Biology, Sophie Petropoulos, a researcher ...
2025-04-10
Discussion of "alternative facts" has gained sad notoriety in US politics. Yet the question has been around much longer: How do people conduct political debates – is the focus more on facts or personal opinions? A team of international researchers led by the Cluster of Excellence "The Politics of Inequality" looked into the matter. The researchers examined political rhetoric in eight million speeches by members of the US Congress between 1879 and 2022 to see if the focus of their language was more on data and facts or personal convictions and subjective interpretations.
The team noticed a significant decline in the use of evidence-based political ...
2025-04-10
Nursing poses major metabolic demands on mothers, to which they respond by eating more and saving energy to sustain milk production. There are significant hormonal changes during lactation, but how they lead to metabolic adaptations in nursing mothers remained unclear. In this study, which appeared in Nature Metabolism, leading researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and Pennington Biomedical Research Center uncovered a mechanism that connects prolactin, estrogen, the brain and metabolic adaptations during lactation.
“We worked with animal models to investigate ...
2025-04-10
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL THURSDAY 10 APRIL, 10AM LONDON TIME, 5AM EASTERN TIME.
Urgent action is needed to protect endangered species, human health and industry from the impacts of the Caspian Sea shrinking, research led by the University of Leeds has found.
Water levels in the Caspian Sea – the world’s largest landlocked water body – are getting lower, as hotter temperatures cause more water to evaporate than is flowing in. Even if global warming is limited to below 2°C, ...
2025-04-10
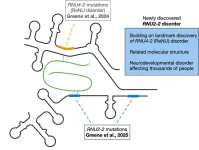
New York, NY [April 10, 2025]—A seminal study from researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and their collaborators in the United Kingdom, Belgium, Spain, the Netherlands, and Iceland has uncovered a new genetic cause of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs). The discovery offers both closure and hope to potentially thousands of families worldwide who have long been searching for answers.
The study, published in the April 10 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02159-5], reveals that mutations in a small, previously overlooked non-coding gene called RNU2-2 are responsible for relatively common NDD. Non-coding genes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Therapy-related b-lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment for multiple myeloma with unusual surface light chain expression: a case report