(Press-News.org) A newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration.
Despite the critical importance of accurately measuring pain in newborns, the review found that none of the available scales are backed by the high-quality evidence and methodological safeguards required to confirm their validity and reliability in clinical practice.
Neonatal pain assessment and management presents a challenge for clinical staff worldwide. Over 40 rating scales have been developed and adapted worldwide assessing different parameters and various types of pain.
Six to nine percent of all newborns require admission to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) due to either illness of prematurity. These infants endure multiple painful procedures daily, which can lead to long-term negative effects. Due to this, valid tools to support the assessment of pain are of great importance.
Infant pain scales lack robust evidence
The Cochrane review analysed 79 studies involving over 7,000 infants across 26 countries, evaluating 27 different clinical rating scales. All rating scales were found to be supported by very low-quality evidence, indicating major limitations in their effectiveness and clinical applicability.
“Over 70% of rating scales in this review did not assess content and structural validity, and both these factors are essential when selecting a measurement instrument,” says Kenneth Färnqvist, physiotherapist and PhD candidate at the Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden. “Without a strong foundation in these areas, other necessary measures, such as reliability, cannot be accurately evaluated. Future studies must prioritise rigorous validation to improve neonatal pain assessment.”
Measuring pain in newborns is particularly complex compared to adults. Such limitations may lead to an over- or under-estimation of pain, resulting in unnecessary sedation or inadequately treated pain, potentially jeopardising infant safety through treatment side-effects, including withdrawal symptoms or prolonged discomfort. Premature infants further complicate matters, as they often have a reduced ability to display robust pain behaviour due to their immaturity. The same is also true for ill or sedated infants.
“It is important to remember that clinical rating scales are only surrogates for pain measurement,” says Roger F. Soll, Professor of Neonatology at the University of Vermont. “Given the uncertainty highlighted in this review, clinical staff should avoid relying too heavily on the rating scales currently in practice and instead strive to decrease painful procedures as much as possible in this vulnerable population.”
Global collaboration needed to improve infant pain assessment
Despite the disappointing results, this review presents an opportunity for progress in neonatal pain assessment, particularly through global collaboration and innovation.
Emma Persad, doctor and PhD candidate at the Department of Women’s and Children’s Health at the Karolinska Institute, sees this as an opportunity for global collaboration and a call to action.
“This is our chance to unite clinicians and methodologists in developing a rigorously validated scale from scratch, one that meets all necessary checks before implementation in research and practice,” Emma says. “We look forward to beginning this impactful work and the implications it will have on assessing and managing neonatal pain worldwide.”
END
Weak evidence behind how we measure pain in babies
A newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration
2025-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel breath test shows promise for diagnosing and monitoring bacterial infections
2025-04-13
This release has been removed upon request of the submitting institution. Please contact Luke Paskins, luke.paskins@beyondpr.com for more information. END ...
AI-guided lung ultrasound marks a major breakthrough in tuberculosis diagnosis
2025-04-13
(Monday, 14 April 2025, Vienna, Austria) A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has demonstrated that an AI-powered lung ultrasound outperforms human experts by 9% in diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis (TB).1
The ULTR-AI suite analyses images from portable, smartphone-connected ultrasound devices, offering a sputum-free, rapid, and scalable alternative for TB detection. The results exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) benchmarks for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis, marking a major opportunity for accessible and efficient TB triage.
Despite previous global declines, TB rates rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023.2 Early ...
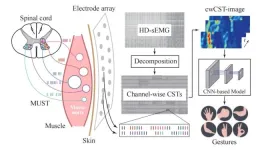
Towards hand gesture recognition using a channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model
2025-04-13
A research paper by scientists at Shanghai Jiao Tong University presented a novel channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model (cwCST-CNN) for hand gesture recognition.
The research paper, published on Mar. 21, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, leverage a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract both local and global features for classifying hand gestures, by decomposing high-density surface EMG (HD-sEMG) signals into channel-wise cumulative spike trains (cw-CSTs) ...
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
2025-04-12
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
New research has revealed that Schistosoma haematobium (S. haematobium), a parasitic infection affecting millions globally, can trigger cancer-related gene activity in the cervical lining, with changes becoming even more pronounced after treatment.1 Presented today at ESCMID Global 2025, this pivotal study sheds new light on how this often-overlooked parasitic disease may contribute to cervical cancer risk at the molecular level.
Schistosomiasis is a widespread parasitic disease, particularly prevalent in regions with poor access to clean water and sanitation.2 ...
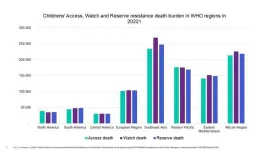
Over 3 million children died from AMR-related infections in 2022, major study shows
2025-04-12
A landmark study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that over 3 million children worldwide lost their lives in 2022 due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR)-related infections.1
The study underscores the urgent need for both regional and global strategies to control paediatric AMR, particularly in high-burden areas such as South-East Asia and Africa. AMR poses a critical threat to children, who are highly vulnerable to infections.2 Access to new antibiotic formulations is often much more limited for children because of product development delays.
The study data found ...
Study estimates proportion of adolescents living with overweight and obesity in England has increased by 50% between 2008 and 2023
2025-04-12
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that the proportion of adolescents living with overweight or obesity in England has increased by 50% from 2008-2010 (22%) to 2021-2023 (33%). The research, presented in two studies, is by Dr Dinesh Giri, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Bristol Royal Hospital for Children and Honorary Senior Lecturer, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, and Dr Senthil Senniappan, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Alder Hey Children’s Hospital, Liverpool, UK, and colleagues.
Previous ...
Welcome to the First International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems
2025-04-12
The First International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems (ICCBS 2025) will be held in Singapore, Republic of Singapore, from July 24 to July 26, 2025. This conference aims at providing a free, open, and diverse platform for experts, scholars, students and industry professionals from the fields of robotics, biomedical engineering, neural engineering, and related domains. The sponsor of the conference is Beijing Institute of Technology, and the organizer of the conference is the Journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems.
We look forward to welcoming experts, scholars and industry leaders from around ...
Breakthrough study identifies promising biomarker for early sepsis detection in neonates, children, and pregnant women
2025-04-11
Breakthrough study identifies promising biomarker for early sepsis detection in neonates, children, and pregnant women
A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has uncovered the potential of interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a powerful diagnostic biomarker for the early detection of sepsis in high-risk patient groups, including neonates, children and pregnant women. This study is the first to evaluate IL-6’s diagnostic performance in a real-world cohort across all three populations.1
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition resulting from the immune system’s overreaction to infection, remains a leading global cause of mortality, accounting ...
3-year study of tirzepatide shows that most patients only gain 5% or less from their lowest or ‘nadir’ weight
2025-04-11
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that around two thirds of participants of the SURMOUNT-1 trial had only regained 5% or less of their so-called nadir (or lowest weight) three years after beginning treatment with tirzepatide. The study is by Professor Louis Aronne, Comprehensive Weight Control Center, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA, and co-authors from Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN, USA, which funded the study.
Obesity management is a long-term journey during which fluctuations ...
Tirzepatide can produce clinically meaningful weight loss for at least 3 years in adults with overweight or obesity who don’t have diabetes
2025-04-11
Once-weekly treatment with tirzepatide can produce clinically meaningful and sustained weight loss for at least 3 years in adults with overweight or obesity who do not have diabetes, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Malaga, Spain (11-14 May). The findings also indicate that females and those without obesity-related complications may be more responsive to tirzepatide treatment.
The study, led by Dr Luca Busetto from the University of Padova in Italy and colleagues from Eli Lilly and Company that manufacture tirzepatide, is a continuation of the SURMOUNT-1 phase 3 trial of tirzepatide, a medication approved in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Weak evidence behind how we measure pain in babiesA newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration