Rise and shine: Natural light lessens morning fatigue
Light conditions in the morning before waking up affect restfulness
2025-04-14
(Press-News.org)
Sleep is a necessary part of people’s daily routine, but modern lifestyles and technology have ushered in an era of decreased rest time and subsequent fatigue. Further, the bedroom environment, such as light, sound, and temperature, is important for a good night's sleep, though this is often neglected in residential architecture.
In search of a conclusive remedy, common sleep studies use artificial light that is easy to control. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers, however, believe natural light could be more effective for re-creating actual living environments.
To test this, Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology student Xiaorui Wang and Professor Daisuke Matsushita led a team in examining whether introducing moderate light into the bedroom just before waking would improve morning wakefulness. Using light-shielding curtains and motorized closing devices, a comparative experiment was conducted on 19 participants under three conditions: natural light for 20 minutes before waking up (IA), natural light from dawn until waking up (IB), and no natural light before waking up (CC). After each session, participants’ sleepiness, alertness, and fatigue were measured with an electrocardiogram, electroencephalogram, and a survey.
Results revealed that participants were less sleepy in IA and IB conditions than in CC. In addition, IA was found to be one of the most effective methods for improving wakefulness, as too much light in IB caused adverse effects.
“In the future, we hope to control natural light in the sleep environment as it changes with the seasons and time of day, and to clarify how to introduce natural light that is suitable for a more comfortable awakening,” stated Professor Matsushita.
The findings were published in Building and Environment.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-14
Farmers in dozens of countries have embraced crops genetically engineered to produce proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) bacteria that kill some key pests yet are safe for people and wildlife. Although this biotech approach reduces reliance on insecticide sprays thereby providing economic and environmental benefits, resistance to Bt crops has evolved in at least 11 species of pests. Thus, effective ways to combat such pest resistance are urgently needed.
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a natural strategy for thwarting pest resistance to Bt proteins. The researchers at the University of Arizona and ...
2025-04-14
A new guideline to help health care providers manage obesity in children and adolescents takes a patient-centred approach, emphasizing behavioural and psychological supports that focus on outcomes valued by patients and their families.
The guidelinehttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241456, based on the latest evidence, is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
It was developed by Obesity Canada through an extensive, 4-year-long collaboration involving adolescents and caregivers with lived obesity experience, methodologists, health care providers, and more than 50 multidisciplinary ...
2025-04-14
New research from the University of Waterloo suggests increasing the ratio of dietary potassium to sodium intake may be more effective for lowering blood pressure than simply reducing sodium intake.
High blood pressure affects over 30 per cent of adults globally. It's the leading cause of coronary heart disease and stroke and may also lead to other afflictions like chronic kidney disease, heart failure, irregular heartbeats, and dementia.
"Usually, when we have high blood pressure, we are advised to eat less salt," said Anita Layton, professor of Applied Mathematics, ...
2025-04-14
A newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration.
Despite the critical importance of accurately measuring pain in newborns, the review found that none of the available scales are backed by the high-quality evidence and methodological safeguards required to confirm their validity and reliability in clinical practice.
Neonatal pain assessment and management presents a challenge for clinical staff worldwide. Over 40 rating scales have been developed and adapted worldwide assessing ...
2025-04-13
This release has been removed upon request of the submitting institution. Please contact Luke Paskins, luke.paskins@beyondpr.com for more information. END ...
2025-04-13
(Monday, 14 April 2025, Vienna, Austria) A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has demonstrated that an AI-powered lung ultrasound outperforms human experts by 9% in diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis (TB).1
The ULTR-AI suite analyses images from portable, smartphone-connected ultrasound devices, offering a sputum-free, rapid, and scalable alternative for TB detection. The results exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) benchmarks for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis, marking a major opportunity for accessible and efficient TB triage.
Despite previous global declines, TB rates rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023.2 Early ...
2025-04-13
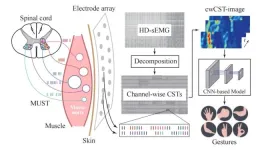
A research paper by scientists at Shanghai Jiao Tong University presented a novel channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model (cwCST-CNN) for hand gesture recognition.
The research paper, published on Mar. 21, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, leverage a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract both local and global features for classifying hand gestures, by decomposing high-density surface EMG (HD-sEMG) signals into channel-wise cumulative spike trains (cw-CSTs) ...
2025-04-12
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
New research has revealed that Schistosoma haematobium (S. haematobium), a parasitic infection affecting millions globally, can trigger cancer-related gene activity in the cervical lining, with changes becoming even more pronounced after treatment.1 Presented today at ESCMID Global 2025, this pivotal study sheds new light on how this often-overlooked parasitic disease may contribute to cervical cancer risk at the molecular level.
Schistosomiasis is a widespread parasitic disease, particularly prevalent in regions with poor access to clean water and sanitation.2 ...
2025-04-12
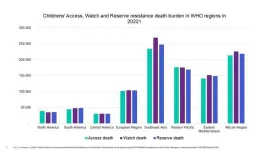
A landmark study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that over 3 million children worldwide lost their lives in 2022 due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR)-related infections.1
The study underscores the urgent need for both regional and global strategies to control paediatric AMR, particularly in high-burden areas such as South-East Asia and Africa. AMR poses a critical threat to children, who are highly vulnerable to infections.2 Access to new antibiotic formulations is often much more limited for children because of product development delays.
The study data found ...
2025-04-12
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that the proportion of adolescents living with overweight or obesity in England has increased by 50% from 2008-2010 (22%) to 2021-2023 (33%). The research, presented in two studies, is by Dr Dinesh Giri, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Bristol Royal Hospital for Children and Honorary Senior Lecturer, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, and Dr Senthil Senniappan, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Alder Hey Children’s Hospital, Liverpool, UK, and colleagues.
Previous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Rise and shine: Natural light lessens morning fatigue
Light conditions in the morning before waking up affect restfulness