(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of children ages 9 to 10, moderately preterm birth was associated with long-term cognitive problems independent of socioeconomic status, genetics, and other risk factors. These findings underscore the need for continued follow-up of all preterm children, with particular focus on those born before 34 weeks’ gestational age, because they may face greater developmental challenges over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Samson Nivins, PhD, email samson.nivins@ki.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.4580)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.4580?guestAccessKey=c0957767-f5eb-4d6d-88a4-15c747418b57&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=041425
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Gestational age and cognitive development in childhood
JAMA Network Open
2025-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals how inherited genes help shape the course of cancer
2025-04-14
New York, NY [April 14, 2025]—A new multicenter study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in collaboration with the National Cancer Institute-funded Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC) and colleagues around the world, has discovered that the genes we are born with—known as germline genetic variants—play a powerful, underappreciated role in how cancer develops and behaves.
Published in the April 14 online issue of Cell [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.03.026], the study is the first to detail how millions of inherited genetic differences influence the activity of thousands of proteins within tumors. Drawing on data ...
UC Berkeley analysis finds steep increase of self-harm among California girls, multiracial youth
2025-04-14
The number of California teens who have been treated for self-harm has ballooned in recent years, with an especially concerning increase among multiracial girls, according to new research from the University of California, Berkeley, published today (Monday, April 14) in JAMA Pediatrics.
Using data from California emergency departments and inpatient care facilities from 2005 to 2021 — 231,232 reports in total — researchers examined both how the rate of annual nonfatal self-harm incidents has changed, as well as rate differences based on age, sex, and race and ethnicity.
The study ...
Study sheds light on how inherited cancer mutations drive tumor growth
2025-04-14
Most cancer genome studies have focused on mutations in the tumor itself and how such gene variants allow a tumor to grow unchecked. A new study, led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, takes a deep dive into inherited cancer mutations measured in a healthy blood sample and reports how those mutations might take a toll on the body’s cells starting at birth, perhaps predisposing a person to develop cancers at various stages of life.
The authors analyzed the inherited genomes of more than 1,000 cancer patients and determined how inherited mutations — ...
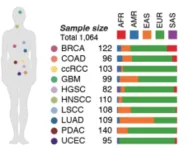
Popular CT scans could account for 5% of all cancer cases a year
2025-04-14
Popular CT Scans Could Account for 5% of All Cancer Cases A Year
Radiation from imaging could lead to lung, breast and other future cancers, with 10-fold increased risk for babies
CT scans may account for 5% of all cancers annually, according to a new study out of UC San Francisco that cautions against overusing and overdosing CTs.
The danger is greatest for infants, followed by children and adolescents. But adults also are at risk, since they are the most likely to get scans.
Nearly 103,000 cancers are predicted to result from the 93 million CTs that were ...
Deep-sea mining risks leads study to urge shift to circular solutions
2025-04-14
Deep-sea mining (DSM) not only poses significant environmental, social, and economic risks that may have far-reaching implications for coastal communities and Small Island Developing States (SIDS), it is also likely to negatively affect the business community, including insurers and investors, says a new study by researchers from the University of British Columbia and the Dona Bertarelli Philanthropy.
DSM operations are expected to increase the negative impact on environmental indicators by up to 13 per cent, a change categorized as having “great” significance, relative to the “without” DSM scenario, ...
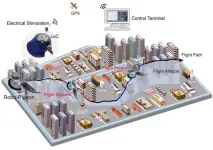
Dynamically controlled flight altitudes in robo-pigeons via locus coeruleus neurostimulation
2025-04-14
Background
Robo-pigeon / Cyborg pigeon is a new type of hybrid intelligent robotic system developed by combining micro-implantable brain-computer interface (BCI) and micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) technologies. By integrating the perception, motion and autonomous intelligence of real pigeons with the high precision, repeatability and controllability of MEMS, a flexible and efficient "biological flight platform" is formed, which has a broad application prospect in key fields such as disaster rescue, national defense security and environmental monitoring.
However, ...
Using AI to monitor inaccessible locations of nuclear energy systems
2025-04-14
Whether it’s for your vehicle or your home, from small-scale uses to the largest, the debate over the most efficient and cost-effective fuels continues. Currently, there’s no shortage of options either.
Nuclear power provides an alternative to more conventional energy options but requires rigorous systems monitoring and safety procedures. Machine learning could make keeping a close eye on key elements of nuclear systems easier and response time to issues faster.
Syed Bahauddin Alam, an assistant professor ...
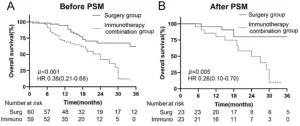
Outcomes for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with pulmonary metastasis: Surgical vs. immunotherapy
2025-04-14
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with over 70% of patients diagnosed at an advanced stage due to the absence of symptoms. A key characteristic of advanced HCC is extrahepatic metastasis, particularly pulmonary metastasis, which is associated with a poor prognosis.
Although multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors have limited efficacy when used alone in advanced HCC, their combination can enhance outcomes for patients with pulmonary metastases. Meanwhile, pulmonary metastasectomy ...
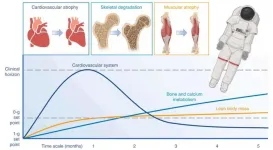
How flexible wearables protect astronauts' health in space
2025-04-14
A review published recently in Wearable Electronics examines the current applications and persistent challenges of flexible wearable technologies in aerospace medicine. As human space exploration progresses toward extended-duration missions, the imperative for real-time monitoring of astronauts' physiological and psychological well-being has become increasingly critical. The unique space environment characterized by microgravity conditions, cumulative radiation exposure, and extreme thermal fluctuations presents multifaceted health risks to crew members.
Flexible wearable systems, equipped ...
Pregnancy complications contribute to cardiovascular risk for overweight women, study finds
2025-04-14
Complications during pregnancy (or adverse pregnancy outcomes), like gestational diabetes and newly developed high blood pressure, act as nature’s stress test and may uncover an individual’s risk for heart disease later in life, according to new research published in the JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The study also highlights how weight management before pregnancy may not only improve maternal health but also reduce future cardiovascular disease risk.
The observational study, which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Gestational age and cognitive development in childhoodJAMA Network Open