Van Andel Institute to recognize Dr. J. Timothy Greenamyre with 2025 Jay Van Andel Award for Outstanding Achievement in Parkinson’s Disease Research
2025-04-14
(Press-News.org) GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (April 14, 2025) — Van Andel Institute has named renowned physician-scientist J. Timothy Greenamyre, M.D., Ph.D., as recipient of its 2025 Jay Van Andel Award for Outstanding Achievement in Parkinson’s Disease Research.
The award will be presented during Grand Challenges in Parkinson’s Disease, VAI’s flagship annual Parkinson’s disease symposium, Sept. 9–10, 2025.
Greenamyre’s pioneering research into the interactions between genes and the environment has vastly improved our understanding of Parkinson’s development and progression. He has published more than 200 articles detailing new insights into the disease, including evidence linking exposure to certain pesticides to increased Parkinson’s risk. His work also has shed critical light onto the roles of mitochondria and the gene LRRK2 in the disease.
“Dr. Greenamyre is a trailblazer in Parkinson’s research. He embodies the very best of the scientific and clinical worlds,” said Darren Moore, Ph.D., chair of VAI’s Department of Neurodegenerative Science and co-chair of the 2025 symposium. “We look forward to recognizing and celebrating his exemplary achievements with the 2025 Jay Van Andel Award.”
Greenamyre joined the University of Pittsburgh in 2005 as the inaugural director of the Pittsburgh Institute of Neurodegenerative Diseases (PIND) and to establish the university’s Movement Disorders Division. Over the past two decades, Greenamyre has grown PIND and the division into powerhouses of collaborative, interdisciplinary research and innovation in neurodegenerative diseases. He also serves as the Love Family Professor of Neurology and director of the American Parkinson Disease Association Advanced Center for Parkinson’s Research at University of Pittsburgh.
Greenamyre has received numerous awards and accolades for his scholarship and contributions, including the 2007 Langston Award and the 2022 Robert A. Pritzker Award for Leadership in Parkinson’s Research from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. He was elected to the Association of American Physicians in 2015 and has been included on the “Best Doctors in America” list since the mid-1990s.
The Jay Van Andel Award for Outstanding Achievement in Parkinson’s Disease Research was established in 2012 in memory of VAI Founder Jay Van Andel, who battled Parkinson’s disease for a decade before his death in 2004. The annual award is given to scientists who have made exceptional contributions to Parkinson’s disease research and who have positively impacted human health.
As part of the award, Greenamyre will deliver the keynote lecture on the first day of Grand Challenges in Parkinson’s Disease.
The annual Grand Challenges in Parkinson’s Disease symposium and Rallying to the Challenge meeting, a parallel event for people with Parkinson’s hosted in partnership with Cure Parkinson’s, brings together scientists, medical professionals, and Parkinson’s advocates from across the globe to explore the latest breakthroughs in Parkinson’s research and treatment. The 2025 symposium will highlight the role of the endolysosomal pathway in the disease.
In addition to the Jay Van Andel Award lecture, the events will feature scientific talks by 20 speakers, a research poster session and advocacy discussions.
Registration for the 2025 Grand Challenges in Parkinson’s Disease symposium and Rallying to the Challenge meeting is open and may be completed at grandchallengesinpd.org.
###
ABOUT VAN ANDEL INSTITUTE
Van Andel Institute (VAI) is committed to improving the health and enhancing the lives of current and future generations through cutting-edge biomedical research and innovative educational offerings. Established in Grand Rapids, Michigan, in 1996 by the Van Andel family, VAI is now home to more than 500 scientists, educators and support staff, who work with a growing number of national and international collaborators to foster discovery. The Institute’s scientists study the origins of cancer, Parkinson’s and other diseases and translate their findings into breakthrough prevention and treatment strategies. Our educators develop inquiry-based approaches for K–12 education to help students and teachers prepare the next generation of problem-solvers, while our Graduate School offers a rigorous, research-intensive Ph.D. program in molecular and cellular biology. Learn more at vai.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-14
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 14 April 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, Threads, and LinkedIn
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
2025-04-14
Is sauerkraut more than just a tangy topping? A new University of California, Davis, study published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology suggests that the fermented cabbage could help protect your gut, which is an essential part of overall health, supporting digestion and protecting against illness.
Authors Maria Marco, professor with the Department of Food Science and Technology, and Lei Wei, a postdoctoral researcher in Marco’s lab, looked at what happens during fermentation — specifically, how the metabolites ...
2025-04-14
Philadelphia, April 14, 2024 – Researchers from the Epilepsy Neurogenetics Initiative (ENGIN) at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have completed a comprehensive natural history study of SCN8A-related disorders, which represent a spectrum of neurological symptoms. The study, using retrospective clinical information analyzed through novel data analysis methods, revealed a range of seizure types and neurodevelopmental features, and identifies potential targets for future clinical trials. The findings were published online on April 14, 2025, in Neurology®, the medical journal ...
2025-04-14
We’re living in a period where the gap between rich and poor is dramatic, and it’s continuing to widen. But inequality is nothing new. In a new study published in the journal PNAS, researchers compared house size distributions from more than 1,000 sites around the world, covering the last 10,000 years. They found that while inequality is widespread throughout human history, it’s not inevitable, nor is it expressed to the same degree at every place and time.
“This paper is part of ...
2025-04-14
LA JOLLA (April 18, 2025)—Industrial farming practices often deplete the soil of important nutrients and minerals, leaving farmers to rely on artificial fertilizers to support plant growth. In fact, fertilizer use has more than quadrupled since the 1960s, but this comes with serious consequences. Fertilizer production consumes massive amounts of energy, and its use pollutes the water, air, and land.
Plant biologists at the Salk Institute are proposing a new solution to help kick this unsustainable fertilizer habit.
In a new study, the researchers identified ...
2025-04-14
EMBARGOED UNTIL 15.00 US ET (20.00 BST) ON MONDAY 14 APRIL 2025
The study lead by Professor Dan Lawrence, of Durham University in the UK, found that across ten millennia, more unequal distributions of wealth correlated with longer-term human settlement.
However, the team are keen to stress that one factor is not causally dependent on the other, giving hope that humankind’s survival is not linked to ever increasing inequality.
The research is part of a Special Feature of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), entitled Global Dynamics of Wealth Inequality.
Sustainability is defined by the ...
2025-04-14
University of California, Davis researchers have developed a new, neuroplasticity-promoting drug closely related to LSD that harnesses the psychedelic’s therapeutic power with reduced hallucinogenic potential.
The research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, highlights the new drug’s potential as a treatment option for conditions like schizophrenia, where psychedelics are not prescribed for safety reasons. The compound also may be useful for treating other neuropsychiatric ...
2025-04-14
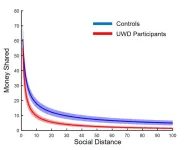
Are there areas of the brain, which regulate prosocial, altruistic behaviour? Together with colleagues from the universities in Lausanne, Utrecht and Cape Town, researchers from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) have studied a very special group of patients and established that the “basolateral amygdala” (part of the limbic system) plays an important role in this. In the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), they describe that this region calibrates social behaviour.
Prosocial ...
2025-04-14
PULLMAN, Wash. — Wealth inequality began shaping human societies more than 10,000 years ago, long before the rise of ancient empires or the invention of writing.
That’s according to a new study led by Washington State University archaeologist Tim Kohler that challenges traditional views that disparities in wealth emerged suddenly with large civilizations like Egypt or Mesopotamia. The research is part of a special issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, co-edited by Kohler and Amy Bogaard, an archaeologist at Oxford University in England.
Drawing on data from over 47,000 residential ...
2025-04-14
If the archaeological record has been correctly interpreted, stone alignments in Tanzania’s Olduvai Gorge are remnants of shelters built 1.7 million years ago by Homo habilis, an extinct species representing one of the earliest branches of humanity’s family tree.
Archaeological evidence that is unambiguously housing dates to more than 20,000 years ago—a time when large swaths of North America, Europe and Asia were covered in ice and humans had only recently begun living in settlements.
Between that time and the dawn of industrialization, the archaeological record is rich not only with evidence of settled life represented by housing, but also with evidence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Van Andel Institute to recognize Dr. J. Timothy Greenamyre with 2025 Jay Van Andel Award for Outstanding Achievement in Parkinson’s Disease Research