(Press-News.org) New bat cell lines and reagents help to study bat antiviral immune responses against hantaviruses and coronaviruses
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: https://plos.io/3E5BYAJ
Article title: Expanding the bat toolbox: Carollia perspicillata bat cell lines and reagents enable the characterization of viral susceptibility and innate immune responses
Author countries: Canada, United States
Funding: see manuscript
END
New bat cell lines and reagents help to study bat antiviral immune responses against hantaviruses and coronaviruses
2025-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Preterm birth might be predicted with high accuracy with new cheap, non-invasive test, based on cell-free DNA collected in standard early pregnancy testing
2025-04-15
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: https://plos.io/3RuCJ9v
Article title: Genome-wide nucleosome footprints of plasma cfDNA predict preterm birth: A case-control study
Author countries: China, United Kingdom
Funding: This work was supported by project grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81600404 to JT, 82270600 to JT, 81871177 to FY, 82271711 to XY, 82173001 to ZG]; Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation [2022A1515220204 to JT; 2024A1515012792 to ZG]; Guangzhou Key Laboratory ...
CVD researcher/clinician named editor-in-chief of Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine.
2025-04-15
DALLAS, April 15, 2025 — Ferhaan Ahmad, M.D., Ph.D., FAHA, is the new editor-in-chief of Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Heart Association, effective with the journal’s April issue, published today. Ahmad is the founding director of the Cardiovascular Genomics Program and associate professor of internal medicine-cardiovascular medicine at the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine in Iowa City, Iowa. He takes the helm leading Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine from Kiran Musunuru, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H, FAHA, who served as interim editor-in-chief ...
Holy shift: More Americans finding faith outside church
2025-04-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – A "remarkable" transformation is underway in American religious life, new Cornell-led research finds: Large numbers are leaving organized religion – not in favor of secular rationality, but to pursue spirituality in ways that better align with their individual values.
This reimagining of religion outside traditional institutions fits within broader social changes that have prioritized individual fulfilment and “finding” oneself, including shifting views about gender and sexuality and the rise of the internet. Spanning political views, it also reflects a revolt against ...
New analysis underscores health risks of e-cigarettes
2025-04-15
A Johns Hopkins Medicine-led analysis of medical information gathered on a diverse group of almost 250,000 people over four years has significantly clarified the link between the “exclusive” use of e-cigarettes and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as well as high blood pressure in a sub-group of adults 30 to 70 years of age.
The findings, supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health and published in the March. 15 edition of Nicotine & Tobacco Research, underscore the potential risks of e-cigarette ...
USTC develops high-performance biomimetic proton gating system
2025-04-15
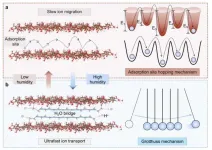
On January 17, 2025, Professor ZHANG Zhen’s team at the Suzhou Institute for Advanced Research, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), reported a solid-state proton gating membrane with an ultrahigh gating ratio of 5,740, surpassing existing technologies. The study was published in Nature Communications.
Biological ion channels exhibit strong gating effects due to their zero-current closed state. However, artificial nanochannels often demonstrate weaker gating capabilities because larger nanopores cannot fully block ion transport when in a closed ...
Uncovering the molecular drivers of liver cancer
2025-04-15
Liver cancer can arise spontaneously from healthy liver tissue. Recently, however, researchers have discovered an increasing correlation between some liver cancers and non-viral chronic liver disease (CLD).
One liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is associated with CLD in about 15–25% of cases. While increasing awareness and screening of cancers has improved the ability to detect liver cancer at earlier stages when it is more effectively treated, cancer prevention is always a primary goal of both healthcare providers and biomedical researchers.
The increasing prevalence of ...
A bowling revolution: Modeling the perfect conditions for a strike
2025-04-15
WASHINGTON, April 15, 2025 – With millions of dollars at stake across tournaments and more than 45 million regular annual participants, bowling continues to reign as a top sport in the U.S. A unified model that predicts how a bowling ball behaves down the lane, however, remains elusive.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Princeton, MIT, the University of New Mexico, Loughborough University, and Swarthmore College share a model that identifies the optimal location for bowling ball placement. Employing a system of ...
Simulate sound in 3D at a finer scale than humans can perceive
2025-04-15
WASHINGTON, April 15, 2025 – Surround-sound speakers can immerse you in a multimedia experience, but what if there was a speaker that could completely re-create a three-dimensional soundscape?
The AudioDome is more than just a loudspeaker arrangement — it’s a dome of speakers that can create an immersive sound experience that reproduces sound sources at any location when the listener is placed in the middle.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers ...
Screening history, stage at diagnosis, and mortality in screen-detected breast cancer
2025-04-15
About The Study: In this cohort study of older women with screen-detected estrogen receptor–positive or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative breast cancer, prior screening mammography was associated with earlier stage at breast cancer diagnosis and lower breast cancer mortality. These findings support the potential for routine screening to improve breast cancer outcomes. As with all observational studies, this study is limited by the potential effects of other differences between the screening and nonscreening groups.
Corresponding Author: To contact the ...
Pitt researchers release Phage images with unprecedented detail
2025-04-15
Researchers at Pitt have produced the most detailed image to date of a bacteriophage–phage for short–that has allowed them to see for the first time the structural makeup of the part of the phage that directly attaches to its target Mycobacterium cell.
“Now you've got like a spec sheet for going in and designing phages so that they’ll bind to different kinds of cells,” said Graham Hatfull, the Eberly Family Professor of Biotechnology in the Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences.
That’s important because of what a phage, which is a kind of virus, does after it binds to a bacterial cell: it pierces a hole in the cell membrane and injects ...