(Press-News.org) The study, published in the journal Addiction and funded by Cancer Research UK, looked at survey data on vaping habits in England, Wales and Scotland before and after the UK Government announced plans to restrict vaping, including by banning disposable vapes, in January 2024.
The team found that the proportion of people vaping increased by nearly a quarter each year from January 2022 to January 2024, but stayed constant between January 2024 and January this year, including for young people.
After January 2024, they also found a substantial decline in the proportion of vapers mainly using disposable e-cigarettes. Among 16- to 24-year-olds, the proportion mainly using disposables almost halved, from 63% to 35%.
Lead author Dr Sarah Jackson (UCL Institute of Epidemiology & Health Care) said: “Action is likely still required to reduce high vaping rates, but now that the situation has stabilised policymakers may be reassured that it would be sensible to avoid stricter policy options currently under review. Some of the options being considered may be more likely to have the unintended consequence of deterring smokers from using vapes to quit smoking.
“Our results also suggest that the Government’s ban on disposables, coming into force in June, may have limited impact on vaping rates in general, given that vapers are already moving away from disposable vapes. It seems likely that people using these products will move to re-usable versions rather than stop vaping completely.
“The study highlights the value of up-to-date information about vaping and smoking trends, which allow policies to be based on the best possible evidence.
“The research cannot tell us why vaping rates have levelled off, but we have in the past seen changes in smoking habits before a policy change, with people adapting their behaviour in anticipation of a new policy.”
The UK Government announced plans to ban disposable vapes in January 2024. This ban will come into force on 1 June this year. The Tobacco and Vapes Bill, currently working its way through Parliament, includes powers to potentially restrict the packaging, marketing and flavours of vapes.
Senior author Professor Jamie Brown (UCL Institute of Epidemiology & Health Care) said: “While it is understandable that policymakers want to take action to reduce vaping among children and never smokers, smoking remains the number one public health priority. These findings should reassure policymakers that they can prioritise measures, such as restrictions on marketing, packaging and display, which are least likely to undermine how helpful vapes are for people trying to quit smoking. It is important that these measures are introduced alongside other messaging and policies that continue to encourage and support smokers to quit smoking, such as mass media campaigns and the swap to stop scheme.”
For the study, researchers used data from the Smoking Toolkit Study, an ongoing survey that interviews a different representative sample of adults in England, Wales and Scotland each month. They looked at data collected between January 2022 and January 2025 from 88,611 people (16 and over).
They found that, between January 2022 and January 2024, the prevalence of vaping among those 16 and over increased from 8.9% to 13.5%. For those aged 16 to 24, prevalence increased from 17% to 26.5%.
In January 2024, nearly half (43.6%) of all vapers aged 16 and over mainly used disposables. This fell to less than a third (29.4%) a year later. The fall was steeper among 16- to 24-year-olds.
In study limitations, the researchers noted that the survey only asked vapers what device they mainly used, meaning that the proportion of vapers using disposables in some form would likely be higher. They also said it was possible people under-reported their use of disposable vapes following the Government’s announcement.
END
Rapid rise in vaping in Britain has stalled
2025-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Young minds, big ideas: Florida’s first Invention Convention ignites innovation at USF
2025-04-15
TAMPA, Fla. (April 15, 2025) – The University of South Florida recently hosted the inaugural Invention Convention Florida at the University of South Florida, an event noted for showcasing the creativity and problem-solving of the next generation of changemakers. Moere than 150 K–12 student inventors from across the state visited USF’s Tampa campus on April 12 to present original solutions to real-world challenges ranging environmental issues to everyday inconveniences.
Invention Convention Florida, ...
New study reveals how to make prescribed forest fires burn safer and cleaner
2025-04-15
Prescribed burns literally fight fire with more fire. Often referred to as a “beneficial fire,” they target areas at risk for wildfires and burn away material that could otherwise fuel a future blaze.
However, all fires, whether accidental or planned, produce smoke that can cause health and respiratory issues, especially in nearby communities. Burning fires release harmful chemicals, like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), that are carcinogenic – PAHs can cause cancer, lung damage, and lead to weakened immunity in those who inhale smoke.
Recently, in a study published in Atmospheric ...
Inactive components in agricultural runoff may be hidden contributors to drinking water hazards
2025-04-15
Inactive ingredients in agricultural, pharmaceutical and other common products have typically been excluded from consideration as potential contaminants in drinking water. However, while these chemicals are inert in certain products, they still can pose hazards when combined with other materials during the drinking water treatment process.
A new study from researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis reveals how large this impact might be. Jean Brownell, a graduate student working with Kimberly Parker, associate professor of energy, environmental & chemical engineering, ...
Colombia’s peatlands could be a crucial tool to fight climate change. But first we have to find them
2025-04-15
UC Santa Cruz Assistant Professor of Environmental Studies Scott Winton has been wading through thick, smelly muck in the tropics for almost a decade. He wouldn’t have it any other way. As a wetland ecologist and biogeochemist, he’s been hard at work investigating an important and mysterious topic: peatlands.
Peatlands are a special type of wetland with enormous potential to either help or hurt global efforts to address climate change. If we want peatlands on our side, we’ll have to protect them. But that’s difficult to do, since we still don’t ...
Researchers refine a hybrid music therapy intervention for patients with cardiac and pulmonary conditions
2025-04-15
CLEVELAND – A new study from University Hospitals Connor Whole Health found that it was feasible to conduct a hybrid music therapy intervention for patients with heart failure and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Participants reported positive effects on their mental health, and the pilot uncovered solutions to improve future research with this population. The findings from this study were recently published in BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.
Patients with chronic illnesses such as heart failure and COPD face significant challenges due ...
Research Spotlight: Combining dexmedetomidine with spinal anesthesia prolongs pain relief and decreases shivering during surgery
2025-04-15
Heitor Medeiros, MD, and A. Sassan Sabouri, MD, of the Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, are the lead and corresponding authors, respectively, of a paper published in the British Journal of Anaesthesia (BJA).
How would you summarize your study?
Spinal anesthesia is widely used to numb patients during surgery, but its effects sometimes wear off too soon. Many anesthetists have experimented with adding extra drugs to extend pain relief. Dexmedetomidine demonstrated results in multiple randomized clinical trials suggesting it could prolong numbness ...
Pennington Biomedical’s 2025 Bray Obesity Symposium to offer on-demand continuing education for physicians
2025-04-15
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
April 15, 2025
BATON ROUGE – The 2025 Bray Obesity Symposium welcomes all health physicians and researchers interested in the latest in metabolic health to register for the on-demand online offerings. The online-only content is available to access upon registration, and the symposium has been designated by the American Board of Obesity Medicine, or ABOM, as a Group One Primary Medicine Continuing Medical Education partner.
The symposium is an intensive Board Review Course in preparation for the ABOM’s certification exam, including materials ...
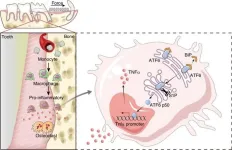
Unlocking faster orthodontic treatments: the role of atf6 in bone remodeling
2025-04-15
Orthodontic treatments often take years, but a breakthrough discovery could drastically shorten this period. Researchers have uncovered that ATF6, a protein activated in macrophages during corticotomy, accelerates tooth movement by promoting inflammation and boosting the production of TNFα, a key factor in bone remodeling. This finding paves the way for faster, more efficient orthodontic procedures, minimizing both treatment time and patient discomfort. The study highlights the potential for non-invasive therapies that could reshape the future of orthodontic care.
Corticotomy, a surgical procedure aimed at accelerating tooth movement, ...
SwRI-led Lucy mission survey of main belt asteroid Donaldjohanson imminent
2025-04-15
SAN ANTONIO — April 15, 2025 —The Southwest Research Institute-led Lucy mission is preparing to survey the next target in its epic 4-billion-mile, 12-year, 11-asteroid tour. On April 20, 2025, NASA’s Lucy spacecraft will fly past the three-mile-wide main belt asteroid (52246) Donaldjohanson as a test run to the main event: visiting the never-before-explored Trojan asteroids in the Jupiter system.
For billions of years, these mysterious space rocks have been gravitationally trapped in two swarms leading and trailing Jupiter in orbit around the Sun, holding clues to the formation of our solar system. NASA’s Lucy spacecraft will be the ...
New bat cell lines and reagents help to study bat antiviral immune responses against hantaviruses and coronaviruses
2025-04-15
New bat cell lines and reagents help to study bat antiviral immune responses against hantaviruses and coronaviruses
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: https://plos.io/3E5BYAJ
Article title: Expanding the bat toolbox: Carollia perspicillata bat cell lines and reagents enable the characterization of viral susceptibility and innate immune responses
Author countries: Canada, United States
Funding: see manuscript END ...