(Press-News.org) BEER-SHEVA, ISRAEL, January 25, 2011 – Sustained exposure to loud workplace noise may affect quality of sleep in workers with occupational-related hearing loss, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers.
Published in the journal Sleep, the study compared the sleep quality of individuals at the same workplace, some with workplace noise-related hearing loss and some without.
Workers with hearing loss had a higher average age and longer duration of exposure than those without hearing impairments. Also, 51 percent of those with hearing loss reported tinnitus (continual ringing in the ears) as opposed to 14 percent of those without hearing impairments.
Although tinnitus was reported as the main sleep disrupting factor, hearing impairment among workers exposed to harmful noise contributed to sleep impairment, especially to insomnia, regardless of age and years of exposure.
"The homogeneous study population exposed to identical harmful noise at the same workplace allowed us to compare sleep quality between similar groups differing only by hearing status," explains Tsafnat Test, a medical student who carried out this study as her B.Sc. thesis in the BGU Faculty of Health Sciences, supervised by Dr. Sheiner, Dr. Eyal, Dr. Canfi and Prof. Shoham-Vardi.
Two hundred and ninety eight male volunteers with occupational exposure to harmful noise were given a hearing test prior to the start of study. Ninety-nine of the participants were judged to have a hearing impairment and 199 had normal hearing.
The researchers explored various elements of sleep including difficulty falling asleep; waking too early or during the night; excessive daytime sleepiness or falling asleep during daytime; snoring; and excessive sleep movement.
INFORMATION:
The Influence of Hearing Impairment on Sleep Quality among Workers Exposed to Harmful Noise
Test Tsafnat1, Ayala Canfi, Ph.D.2; Arnona Eyal, M.D.3; Ilana Shoam-Vardi, Ph.D.4; Einat K. Sheiner, M.D.5
1Health Science Department, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel;
2Nuclear Research Center, Negev, Dimona, Israel, Department of Epidemiology and Health Systems Evaluation, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel;
3Occupational Medicine Clinic, Clalit Health Services, Beer-Sheva, Israel;
4Department of Epidemiology and Health Systems Evaluation, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel;
5Nuclear Research Center, Negev, Dimona, Israel
About American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (AABGU) plays a vital role in sustaining David Ben-Gurion's vision, creating a world-class institution of education and research in the Israeli desert, nurturing the Negev community and sharing the University's expertise locally and around the globe. With some 20,000 students on campuses in Beer-Sheva, Sede Boqer and Eilat in Israel's southern desert, BGU is a university with a conscience, where the highest academic standards are integrated with community involvement, committed to sustainable development of the Negev. AABGU is headquartered in Manhattan and has nine regional offices throughout the U.S. For more information, visit www.aabgu.org.
If the U.S. military increases its use of alternative fuels, there will be no direct benefit to the nation's armed forces, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Any benefits from investment in alternative fuels by the U.S. Department of Defense will accrue to the nation as a whole rather than to mission-specific needs of the military, researchers found. The study is based on an examination of alternative jet and naval fuels that can be produced from coal or various renewable resources, including seed oils, waste oils and algae.
In response to a congressional ...
Last summer's disastrous Pakistan floods that killed more than 2,000 people and left more than 20 million injured or homeless were caused by a rogue weather system that wandered hundreds of miles farther west than is normal for such systems, new research shows.
Storm systems that bring widespread, long-lasting rain over eastern India and Bangladesh form over the Bay of Bengal, at the east edge of India, said Robert Houze, a University of Washington atmospheric sciences professor. But Pakistan, on the Arabian Sea west of India, is substantially more arid and its storms ...
Researchers from the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital are the first in the world to show that an operation can help patients with dementia caused by white matter changes and hydrocephalus.
Presented in the American Journal of Neurosurgery, the results are based on the world's first study to demonstrate the effects of a shunt operation using a placebo control. 14 patients were followed for an average of three and a half years after the operation, with half being given a non-functioning shunt – in other words a sham operation – and the other ...
T.rex hunted like a lion, rather than regularly scavenging like a hyena, reveals new research published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The findings end a long-running debate about the hunting behaviour of this awesome predator.
Scientists from the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) used an ecological model based on predator relationships in the Serengeti to determine whether scavenging would have been an effective feeding strategy for T.rex.
Previous attempts to answer the question about T.rex's hunting behaviour have focused on its morphology. ...
The previously unknown species of ribbon worm discovered in Kosterhavet National Park in 2007 has now been scientifically named using a new method. Pseudomicrura afzelii, a form of nemertean or ribbon worm, has been described and registered by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, using DNA technology.
"We've shown that it's possible to move away from the traditional, highly labour-intensive way of describing a new species. Developments in molecular biology have made it possible to determine the genetic code for selected parts of DNA both quickly and cheaply." ...
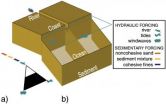
By adding information about the subsoil to an existing sedimentation and erosion model, researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft, The Netherlands) have obtained a clearer picture of how rivers and deltas develop over time. A better understanding of the interaction between the subsoil and flow processes in a river-delta system can play a key role in civil engineering (delta management), but also in geology (especially in the work of reservoir geologists). Nathanaël Geleynse et al. recently published in the journals Geophysical Research Letters and Earth and ...
Scientists studied the defences used by caterpillars that transform into large white butterflies, called Pieris brassicae. The insects regurgitate semi-digested cabbage leaves to make them smell and taste unpleasant to predators. The team found, however, that frequent use of this defence reduces the caterpillars' growth rate and the number of eggs they produce. It remains unclear why their defences affect them in this way, but the loss of nutrition from frequent regurgitation is thought to play a part.
Caterpillars are a target of pest control, as they destroy food ...
The successful Swedish model of reducing the impact of students' different social, cultural and economic backgrounds on academic outcome is severely threatened after 20 years of educational reforms. This is the main point made by Docent (Reader) Girma Berhanu from the University of Gothenburg in International Journal of Special Education.
Some of the previously very positive trends in the Swedish school system seem to have been put in reverse over the past 20 years, and students with special needs, immigrant students and socially disadvantaged students are getting the ...
"Seeing as psychopathic behavior is similar to that of a person with brain damage, it could be that it could benefit from similar forms of treatment," said Dr. Simone Shamay-Tsoory, who conducted the study.
People diagnosed as psychopathic have difficulty showing empathy, just like patients who have suffered frontal head injury. This has been shown in a new study from the University of Haifa. "Our findings show that people who have psychopathic symptoms behave as though they are suffering frontal brain damage," said Dr. Simone Shamay-Tsoory, who conducted the study.
Psychopathy ...
A new TV series featuring dinosaur detectives from The University of Manchester looking at how dinosaurs once lived, looked and functioned begins in the UK this week.
Presented by University of Manchester palaeontologist Dr Phil Manning, the series will be aired on the National Geographic Channel, starting in the UK on Thursday February 3rd, before being transmitted to many countries around the world.
It is the first ever series on dinosaurs commissioned by National Geographic, as previously documentaries have only aired as one or two-hour specials.
Jurassic CSI ...