(Press-News.org) In this week's PLoS Medicine, Ian Sinha and colleagues from the Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, UK, make recommendations for the development of core outcome sets for clinical trials, based upon a review of the literature. They advise that when using the Delphi process to develop core outcome sets for clinical trials, patients and clinicians should be involved, researchers and facilitators should avoid imposing their views on participants, and the attrition of participants must be minimized.
INFORMATION:
Funding: IPS was funded by the NIHR Medicines for Children Research Network Clinical Trials Unit and Co-ordinating Centre. The Medicines for Children Research Network is part of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), and is funded by the Department of Health. IPS was funded by Department of Health grant RNC/013/011. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: RLS is a member of the PLoS Board of Directors.
Citation: Sinha IP, Smyth RL, Williamson PR (2011) Using the Delphi Technique to Determine Which Outcomes to Measure in Clinical Trials: Recommendations for the Future Based on a Systematic Review of Existing Studies. PLoS Med 8(1): e1000393. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000393
IN YOUR COVERAGE PLEASE USE THIS URL TO PROVIDE ACCESS TO THE FREELY AVAILABLE PAPER: http://www.plosmedicine.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pmed.1000393
PRESS-ONLY PREVIEW OF THE ARTICLE: To obtain a preview PDF of this study please email press@plos.org
CONTACT:
Ian P. Sinha
Institute of Child Health
University of Liverpool
Alder Road
Liverpool, Merseyside L12 2AP
United Kingdom
(0044)1512284811
iansinha@liv.ac.uk
Developing core outcome sets for clinical trials needs patient input
2011-01-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Emergency care for childbirth complications -- out of reach for rural women in Zambia?
2011-01-26
Most women in rural Zambia deliver their babies at home without skilled care because of the long distances involved in reaching emergency obstetric care, so it is crucial to address the geographic and quality barriers to health care use. These are the key findings from a study by Sabine Gabrysch from Ruprecht-Karls-Universität, Heidelberg, Germany and colleagues at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine published in this week's PLoS Medicine.
In sub-Saharan Africa, a woman's lifetime risk of dying during or following pregnancy is as high as 1 in 31 (compared ...
Pay-for-performance does not improve patient health
2011-01-26
BOSTON, Mass. (Jan. 26, 2011)—As news outlets throughout Europe and the U.S. report on the plummeting health of Western adults and children, there is no shortage of culprits. One villain often bandied about is the "fee for service" system of incentives for physicians. Clearly, if doctors are financially rewarded for simply performing more procedures, costs will soar at the expense of patient health.
Enter Pay-for-Performance, an emerging movement in which physicians are rewarded not for what they do, but for quality of care and patient outcomes. Under such a system, ...
Workplace noise-related hearing loss affects sleep quality -- Ben Gurion U. researchers
2011-01-26
BEER-SHEVA, ISRAEL, January 25, 2011 – Sustained exposure to loud workplace noise may affect quality of sleep in workers with occupational-related hearing loss, according to a new study by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers.
Published in the journal Sleep, the study compared the sleep quality of individuals at the same workplace, some with workplace noise-related hearing loss and some without.
Workers with hearing loss had a higher average age and longer duration of exposure than those without hearing impairments. Also, 51 percent of those with hearing ...
RAND study: No direct military benefit from use of alternative fuels by armed forces
2011-01-26
If the U.S. military increases its use of alternative fuels, there will be no direct benefit to the nation's armed forces, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Any benefits from investment in alternative fuels by the U.S. Department of Defense will accrue to the nation as a whole rather than to mission-specific needs of the military, researchers found. The study is based on an examination of alternative jet and naval fuels that can be produced from coal or various renewable resources, including seed oils, waste oils and algae.
In response to a congressional ...
Rogue storm system caused Pakistan floods that left millions homeless
2011-01-26
Last summer's disastrous Pakistan floods that killed more than 2,000 people and left more than 20 million injured or homeless were caused by a rogue weather system that wandered hundreds of miles farther west than is normal for such systems, new research shows.
Storm systems that bring widespread, long-lasting rain over eastern India and Bangladesh form over the Bay of Bengal, at the east edge of India, said Robert Houze, a University of Washington atmospheric sciences professor. But Pakistan, on the Arabian Sea west of India, is substantially more arid and its storms ...
Operation makes dementia patients faster and smarter
2011-01-26
Researchers from the University of Gothenburg and Sahlgrenska University Hospital are the first in the world to show that an operation can help patients with dementia caused by white matter changes and hydrocephalus.
Presented in the American Journal of Neurosurgery, the results are based on the world's first study to demonstrate the effects of a shunt operation using a placebo control. 14 patients were followed for an average of three and a half years after the operation, with half being given a non-functioning shunt – in other words a sham operation – and the other ...
No leftovers for T. rex
2011-01-26
T.rex hunted like a lion, rather than regularly scavenging like a hyena, reveals new research published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The findings end a long-running debate about the hunting behaviour of this awesome predator.
Scientists from the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) used an ecological model based on predator relationships in the Serengeti to determine whether scavenging would have been an effective feeding strategy for T.rex.
Previous attempts to answer the question about T.rex's hunting behaviour have focused on its morphology. ...
Researchers register new species using DNA-based description
2011-01-26
The previously unknown species of ribbon worm discovered in Kosterhavet National Park in 2007 has now been scientifically named using a new method. Pseudomicrura afzelii, a form of nemertean or ribbon worm, has been described and registered by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, using DNA technology.
"We've shown that it's possible to move away from the traditional, highly labour-intensive way of describing a new species. Developments in molecular biology have made it possible to determine the genetic code for selected parts of DNA both quickly and cheaply." ...
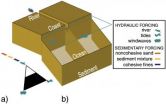
A clearer picture of how rivers and deltas develop
2011-01-26
By adding information about the subsoil to an existing sedimentation and erosion model, researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft, The Netherlands) have obtained a clearer picture of how rivers and deltas develop over time. A better understanding of the interaction between the subsoil and flow processes in a river-delta system can play a key role in civil engineering (delta management), but also in geology (especially in the work of reservoir geologists). Nathanaël Geleynse et al. recently published in the journals Geophysical Research Letters and Earth and ...
Insects that deter predators produce fewer offspring
2011-01-26
Scientists studied the defences used by caterpillars that transform into large white butterflies, called Pieris brassicae. The insects regurgitate semi-digested cabbage leaves to make them smell and taste unpleasant to predators. The team found, however, that frequent use of this defence reduces the caterpillars' growth rate and the number of eggs they produce. It remains unclear why their defences affect them in this way, but the loss of nutrition from frequent regurgitation is thought to play a part.
Caterpillars are a target of pest control, as they destroy food ...