(Press-News.org) We have developed an 'anytime' intelligence test, in other words a test that can be interrupted at any time, but that gives a more accurate idea of the intelligence of the test subject if there is a longer time available in which to carry it out", José Hernández-Orallo, a researcher at the Polytechnic University of Valencia (UPV), tells SINC.
This is just one of the many determining factors of the universal intelligence test. "The others are that it can be applied to any subject – whether biological or not – at any point in its development (child or adult, for example), for any system now or in the future, and with any level of intelligence or speed", points out Hernández-Orallo.
The researcher, along with his colleague David L. Dowe of the Monash University, Clayton (Australia), have suggested the use of mathematical and computational concepts in order to encompass all these conditions. The study has been published in the journal Artificial Intelligence and forms part of the "Anytime Universal Intelligence" project, in which other scientists from the UPV and the Complutense University of Madrid are taking part.
The authors have used interactive exercises in settings with a difficulty level estimated by calculating the so-called 'Kolmogorov complexity' (they measure the number of computational resources needed to describe an object or a piece of information). This makes them different from traditional psychometric tests and artificial intelligence tests (Turing test).
Use in artificial intelligence
The most direct application of this study is in the field of artificial intelligence. Until now there has not been any way of checking whether current systems are more intelligent than the ones in use 20 years ago, "but the existence of tests with these characteristics may make it possible to systematically evaluate the progress of this discipline", says Hernández-Orallo.
And what is even "more important" is that there were no theories or tools to evaluate and compare future intelligent systems that could demonstrate intelligence greater than human intelligence.
The implications of a universal intelligence test also impact on many other disciplines. This could have a significant impact on most cognitive sciences, since any discipline depends largely on the specific techniques and systems used in it and the mathematical basis that underpins it.
"The universal and unified evaluation of intelligence, be it human, non-human animal, artificial or extraterrestrial, has not been approached from a scientific viewpoint before, and this is a first step", the researcher concludes.
INFORMATION:
References:
José Hernández-Orallo y David L. Dowe. "Measuring Universal Intelligence: Towards an Anytime Intelligence Test". Artificial Intelligence 174(18): 1508�, diciembre de 2010. DOI: 10.1016/j.artint.2010.09.006.
On the hunt for universal intelligence
2011-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows smaller rows contribute to more soybean yields in colder climates
2011-01-28
Madison, WI January 27, 2011 – Soybean production has continued to increase in the Northeast United States with more and more first time growers planting the crop and many experienced growers planting alongside corn crops. To save on time and expenses, some farmers plant soybeans with a corn planter in 30-inch rows instead of 7.5-inch rows with the regularly used grain drill.
Dr. William Cox, a Cornell University scientist, investigated the response of two soybean varieties in row widths of 7.5, 15, and 30 inches at four seeding rates in a study funded by a USDA Hatch ...
First large-scale, physics-based space weather model transitions into operation
2011-01-28
The first large-scale, physics-based space weather prediction model is transitioning from research into operation.
Scientists affiliated with the National Science Foundation (NSF) Center for Integrated Space Weather Modeling (CISM) and the National Weather Service reported the news today at the annual American Meteorological Society (AMS) meeting in Seattle, Wash.
The model will provide forecasters with a one-to-four day advance warning of high speed streams of solar plasma and Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
These streams from the Sun may severely disrupt ...
Altered gene protects some African-Americans from coronary artery disease
2011-01-28
A team of scientists at Johns Hopkins and elsewhere has discovered that a single alteration in the genetic code of about a fourth of African-Americans helps protect them from coronary artery disease, the leading cause of death in Americans of all races.
Researchers found that a single DNA variation - having at least one so-called guanine nucleotide in a base pair instead of a combination without any guanine - on a gene already linked to higher risk of coronary disease in other races is linked in blacks to decreased risk. Specifically, the study showed that otherwise ...
Surgery for obstructive sleep apnea reduces daytime drowsiness
2011-01-28
DETROIT – Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who undergo surgery to improve their breathing get a better night's sleep and therefore are less drowsy during the day, according to a new study from Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit.
The study finds surgery greatly reduces daytime sleepiness – a common side effect from this disorder in which the upper airway is partially or completely blocked during sleep – when compared to other non-surgical treatments for obstructive sleep apnea.
"This study validates what patients have told us regarding their improved alertness after ...
A mix of tiny gold and viral particles -- and the DNA ties that bind them
2011-01-28
Scientists have created a diamond-like lattice composed of gold nanoparticles and viral particles, woven together and held in place by strands of DNA. The structure – a distinctive mix of hard, metallic nanoparticles and organic viral pieces known as capsids, linked by the very stuff of life, DNA – marks a remarkable step in scientists' ability to combine an assortment of materials to create infinitesimal devices.
The research, done by scientists at the University of Rochester Medical Center, Scripps Research Institute, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, was published ...
Team looks to the cow rumen for better biofuels enzymes
2011-01-28
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When it comes to breaking down plant matter and converting it to energy, the cow has it all figured out. Its digestive system allows it to eat more than 150 pounds of plant matter every day. Now researchers report that they have found dozens of previously unknown microbial enzymes in the bovine rumen – the cow's primary grass-digestion chamber – that contribute to the breakdown of switchgrass, a renewable biofuel energy source.
The study, in the journal Science, tackles a major barrier to the development of more affordable and environmentally sustainable ...
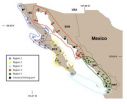
Study finds common ground for ecosystems and fishing in Northwest Mexico
2011-01-28
Researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego have completed a new study on the geography of commercial fisheries in Northwest Mexico and the results could have far-ranging implications for the sustainable future of marine wildlife in the area.
The scientists, led by Scripps postdoctoral researcher Brad Erisman, analyzed data from local fisheries offices around the region that includes Baja California as well as Gulf of California coasts from Sonora south to Nayarit. The region accounts for more than 60 percent of fishing production in Mexico.
The ...
Test shows dinosaurs survived mass extinction by 700,000 years
2011-01-28
University of Alberta researchers determined that a fossilized dinosaur bone found in New Mexico confounds the long established paradigm that the age of dinosaurs ended between 65.5 and 66 million years ago.
The U of A team, led by Larry Heaman from the Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, determined the femur bone of a hadrosaur as being only 64.8 million years old. That means this particular plant eater was alive about 700,000 years after the mass extinction event many paleontologists believe wiped all non-avian dinosaurs off the face of earth, forever.
Heaman ...
Researchers identify biomarkers of poor outcomes in preemies
2011-01-28
Researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have identified biomarkers of poor outcomes in preterm infants that may help identify new approaches to prevention.
Ardythe Morrow, PhD, a researcher at the Cincinnati Children's Perinatal Institute, has identified a polymorphism – a variant in a particular DNA sequence – in a gene important to the development of the immune system. She found that this polymorphism raises the risk of bad outcomes in preterm infants, including death; necrotizing enterocolitis, which is the death of intestinal tissue; and gram ...
Memory training explored as strategy for addiction treatment
2011-01-28
People with addictions to stimulants tend to choose instant gratification or a smaller but sooner reward over a future benefit, even if the future reward is greater. Reduced value of a future reward, called "delay discounting" by neuroscientists, is the major challenge for treatment of addiction. A new study in the February 2011 (Vol. 69, Issue 3) Biological Psychiatry appears to present a strategy for increasing the value of future rewards in the minds of addicts.
"The hope is for a new intervention to help addicts," said Warren K. Bickel, professor and director of ...