(Press-News.org) Pacific Northwest farmers could someday be filling up their machinery's tanks with fuels produced from their own fields, according to ongoing research by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists.
Since 2003, Agricultural Research Service (ARS) microbiologist Hal Collins and agronomist Rick Boydston have been studying safflower, camelina, soybeans, mustard, canola, wheat, corn and switchgrass to assess their potential for bioenergy production. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency, and this research supports the USDA priority of developing new sources of bioenergy.
Collins and Boydston both work at the ARS Vegetable and Forage Crops Research Laboratory in Prosser, Wash., where they've found that the oilseed crops in their studies could someday help supply Washington State with renewable fuels. For instance, they've found that canola, which is already established as a summer crop in the Pacific Northwest, can also be grown in the winter both as a cover crop and potentially as a biofeedstock crop, because its seeds are around 40 percent oil.
Their results also suggest that it could take anywhere from 50 to 70 acres for a farmer with 1,000 acres and an onsite crusher and biodiesel facility to grow enough canola to produce the fuel needed to run on-farm operations.
The team also found that in field trials, camelina plants produced an average of 2,000 pounds of seeds per acre in 80 days, which translates into 700 pounds of oil—and eventually 93 gallons of oil—per acre. Safflower plants, meanwhile, produced around 3,000 to 3,500 pounds of seeds per acre, and white mustard seed meal could also be used as an organic fertilizer after the seeds were crushed to extract the oil for fuel.
Collins and Boydston also evaluated eleven switchgrass cultivars in their studies and found "Kanlow" to be the most promising cultivar for maximum production under sustainable irrigation strategies in the Pacific Northwest's Columbia Basin. Four years after the team planted the first crop, they measured yields of 14 dry tons per acre, which could translate into around 1,000 gallons of cellulosic ethanol per acre.
INFORMATION:
Read more about this research in the February 2011 issue of Agricultural Research magazine.
USDA is an equal opportunity provider, employer and lender. To file a complaint of discrimination, write: USDA, Director, Office of Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Ave., S.W., Washington, D.C. 20250-9410 or call (800) 795-3272 (voice), or (202) 720-6382 (TDD).
END
Moving to a new country is difficult—learning the cultural rules and meanings of your new home is especially challenging. A new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, finds that this process is easier for children, but quickly becomes more difficult after about the age of 15.
Psychological scientists have found that many aspects of learning and development have a critical window—if a developmental event doesn't happen by a particular age, it never will. For example, learning perfect pitch or learning to see with ...
Camden, N.J., February 3, 2011– Studies show drinking V8® 100% vegetable juice may be a simple way for people to increase their vegetable intake and may help them manage their weight – two areas of concern outlined in the newly released 2010 U.S. Dietary Guidelines for Americans.1
A study conducted by researchers at the University of California-Davis found that adults who drank one, 8-ounce glass of vegetable juice each day, as part of a calorie-appropriate Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, got nearly twice as many vegetable servings a day than those ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers have discovered the 100 million-year-old ancestor of a group of large, carnivorous, cricket-like insects that still live today in southern Asia, northern Indochina and Africa. The new find, in a limestone fossil bed in northeastern Brazil, corrects the mistaken classification of another fossil of this type and reveals that the genus has undergone very little evolutionary change since the Early Cretaceous Period, a time of dinosaurs just before the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana.
The findings are described in a paper in the open access ...
MBL, WOODS HOLE, MA—The ubiquitous freshwater "water flea," Daphnia pulex, may be too small to see, but it has amply proven its value as an "sentinel species" for the presence of toxins and pollutants in the environment.
Daphnia's response to exposure to toxic metals and other chemical pollutants is well studied, and this information is routinely used by groups such as the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to define regulatory limits, and to monitor industrial and municipal discharges.
This week, Daphnia pulex is receiving an enormous pat on the back from the ...
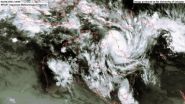
Earth observation scientists at the University of Leicester have recorded stunning images of tropical cyclone Yasi by orbiting satellites.
Japanese Meteorological Agency and European Space Agency satellite instruments have been observing the intense storm over Australia from their vantage points in space.
University of Leicester scientists have used two instruments, MTSAT-2 and MERIS, which have enabled the scientists to follow the progress of the storm as it headed towards and then struck the Australian coast. They have provided unique views from space of a storm ...
Cancer researchers have discovered that a type of regulatory RNA may be effective in fighting ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer isn't typically discovered until it's in the advanced stages, where it is already spreading to other organs and is very difficult to fight with chemotherapy. This new discovery may allow physicians to turn back the clock of the tumor's life cycle to a phase where traditional chemotherapy can better do its job.
Scientists at the Ovarian Cancer Institute Laboratory at the Georgia Institute of Technology have found in initial tests that a regulatory ...
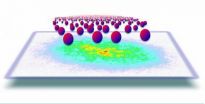
New experiments show that common scientific rules can apply to significantly different phenomena operating on vastly different scales.
The results raise the possibility of making discoveries pertaining to phenomena that would be too large or impractical to recreate in the laboratory, said Cheng Chin, associate professor in physics and the James Franck Institute at the University of Chicago. Chin and associates Chen-Lung Hung, Xibo Zhang and Nathan Gemelke published their results in the Jan. 26 Advance Online Publication (Feb. 10 print edition) of the journal Nature.
Chin ...
ATLANTA – The American College of Rheumatology today announced the release of two new provisional definitions of rheumatoid arthritis remission, which are to be applied to future RA clinical trials.
According to research presented in the March issue of Arthritis & Rheumatism, a person with RA who is enrolled in a clinical trial would need to meet one of the following definitions to be considered in remission:
1. Tender joint count, swollen joint count (on 28 joint counts), C-reactive protein (in mg/dl), and patient global assessment scores (on a scale of zero to 10) ...
Food versus fuel -- this rivalry is gaining significance against a backdrop of increasingly scarce farmland and a concurrent trend towards the use of bio-fuels. Researchers at the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) are helping to resolve this rivalry: They are working to effectively utilize residual field crop material – which has been difficult to use thus far – for the industrial production of bio-ethanol. They took a closer look at bacteria that transform cellulose into sugar, thereby increasing the energy yield from plants utilized. If this approach works, both ...
Mountain biking, also known as off-road biking, is a great way to stay physically active while enjoying nature and exploring the outdoors. The good news is that mountain biking-related injuries have decreased. A new study conducted by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital found the number of mountain bike-related injuries decreased 56 percent over the 14-year study period (1994 to 2007) – going from a high of more than 23,000 injuries in 1995 to just over 10,000 injuries in 2007.
"The large ...