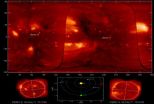
(Press-News.org) Beginning on February 6, 2011, the two STEREO spacecraft are 180 degrees apart providing Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) scientists with a 360-degree view of the Sun. NASA's STEREO (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory) spacecraft were launched on October 25, 2006, and have been gathering spectacular images of solar activity, especially solar storms, since the mission began.
A key component of the STEREO mission is NRL's Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI), a suite of five scientific telescopes that observe the solar corona and inner heliosphere from the surface of the Sun to the orbit of Earth. These unique observations are made in "stereo" by the two nearly identical solar-powered STEREO observatories with one observatory ahead of Earth in its orbit and the other trailing behind. The two observatories trace the flow of energy and matter from the Sun to Earth. The instruments aboard STEREO reveal the three-dimensional structure of coronal mass ejections, the powerful eruptions of plasma and magnetic energy from the Sun's outer atmosphere, or corona.
SECCHI Project Scientist and NRL researcher, Dr. Angelos Vourlidas, explains the significance of this opportunity for the 360-degree view of the Sun, "for the first time, we can take snapshots of the entire atmosphere of a star. To put it in perspective, before STEREO we were like a person trying to get the pulse of a city by watching through a half-open window – not an easy task. Now, STEREO has thrown wide open the window and we can watch the Sun and its activity in its full three-dimensional glory." Each STEREO telescope sees half the Sun at a time. By combining the two views, NRL researchers can map of the entire solar atmosphere continuously.
Before the three-dimensional view was available, researchers had to wait until an active region rotated across the visible-from-Earth disk in order to study the properties. The problem of having to wait for the proper views to appear is that the corona is highly variable, filled with regions that come and go in a matter of days and explosions that can alter the corona landscape in a matter of hours.
With this capability of a three-dimensional view of the Sun, Vourlidas sees the potential for advances in the field of heliophysics. "We can solve the puzzles behind the evolution and structure of the solar atmosphere, including its violent eruptions, because we will be able to observe every feature and source of activity at the same time all over the Sun and follow their connections that can extend to large distances around the Sun," he explains. This opportunity for the STEREO spacecraft to view the Sun in three-dimension will be available for the next eight years.
STEREO is the third mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes Program. STEREO is sponsored by NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Goddard Science and Exploration Directorate manages the mission, instruments, and science center. The Johns Hopkins University applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Md., designed and built the spacecraft and is operating them for NASA during the mission.
INFORMATION:
NRL researchers view the sun in 3-D
2011-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists develop method to identify fleetingly ordered protein structures
2011-02-09
LA JOLLA, CA – February 8, 2011 - A team of scientists from The Scripps Research Institute and the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) have developed a novel technique to observe previously unknown details of how folded structures are formed from an intrinsically disordered protein. The insights could help scientists to better understand the mechanism of plaque formation in neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases.
The results of the study, which has broad implications for the field, were recently published in an advanced, online ...
New techniques for stapling peptides could spur development of drugs for cancer
2011-02-09
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Researchers at the University at Buffalo have devised two new ways of "stapling" peptide helices to prevent these medically important molecules from losing their shape and degrading in the presence of enzymes.
The discovery could help speed the development of peptide-based drugs against diseases including cancer. UB scientists say the methods they pioneered are simpler than existing techniques, one of which employs an expensive ruthenium catalyst to connect chemical side chains that protrude from the main body of helical peptides.
"There's a lot of potential ...
Gene protects lung from damage due to pneumonia, sepsis, trauma, transplants
2011-02-09
Lung injury is a common cause of death among patients with pneumonia, sepsis or trauma and in those who have had lung transplants. The damage often occurs suddenly and can cause life-threatening breathing problems and rapid lung failure.
There are no effective treatments. Patients usually are put on ventilators to give their lungs a chance to heal, but there is little else doctors can do but wait and hope for the best.
Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have identified a gene that limits damage to the lung during acute ...
Electronic cigarettes hold promise as aid to quitting
2011-02-09
A study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researchers reports that electronic cigarettes are a promising tool to help smokers quit, producing six-month abstinence rates nearly double those for traditional nicotine replacement products.
In a study published online ahead of print in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, researchers found that 31 percent of respondents reported having quit smoking six months after first purchasing an electronic cigarette, a battery-powered device providing tobacco-less doses of nicotine in a vaporized solution. ...
Not just for raincoats
2011-02-09
Researchers from Northwestern University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have studied individual water droplets and discovered a miniature version of the "water hammer," an effect that produces the familiar radiator pipe clanging in older buildings.
In piping systems, the water hammer occurs when fluid is forced to stop abruptly, causing huge pressure spikes that can rupture pipe walls. Now, for the first time, the researchers have observed this force on the scale of microns: such pressure spikes can move through a water droplet, causing it to be impaled ...
Growing population of adult survivors of congenital heart disease requires specialized care
2011-02-09
Philadelphia, PA, February 8, 2011 – For the one in 200 adults in Western societies born with congenital heart disease, adult survivors face a lifelong process of medical interactions. Treatments received during neonatal, childhood, and adolescent years affect future adult events. In the January/February issue of Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases ten articles explore our current understanding of adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) in survivors.
This issue of Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases is dedicated to exploring the path to and current understanding of lifelong ...
Medication education key to successful adherence in patients with diabetes
2011-02-09
Researchers at the Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of California, San Diego say that medication education is a key factor in helping patients with diabetes better stick to their drug treatments plans. The study, currently on line in the February issue of the journal Annals of Pharmacotherapy, points to the need for pharmacists and other health care providers to assess reasons why some patients don't adhere to their medication plans, and to provide counseling opportunities to help them.
"Counseling can be more effective if pharmacists ...
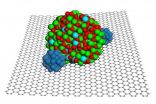
A paperweight for platinum
2011-02-09
RICHLAND, Wash. -- A new combination of nanoparticles and graphene results in a more durable catalytic material for fuel cells, according to work published today online at the Journal of the American Chemical Society. The catalytic material is not only hardier but more chemically active as well. The researchers are confident the results will help improve fuel cell design.
"Fuel cells are an important area of energy technology, but cost and durability are big challenges," said chemist Jun Liu. "The unique structure of this material provides much needed stability, good ...
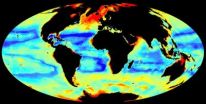
Understanding patterns of seafloor biomass
2011-02-09
Analysis of a comprehensive database has revealed strong links between biological productivity in the surface oceans and patterns of biomass and abundance at the seafloor, helping to explain large regional differences. The research was conducted by an international, multi-institutional research team including scientists from the National Oceanography Centre (NOC), and incorporated data from the Census of Marine Life (CoML).
The vast majority of the biological production in the world's oceans occurs within sunlit surface waters – the so-called photic zone. Through the ...
Cross-border conservation vital to protect birds in a climate-change world
2011-02-09
Countries need to increase co-operation over conservation to protect birds and other wildlife in an era of climate change, according to a new continental-scale study.
Experts have established a new conservation index to help policy-makers to deal with the effects of climate change on birds in Africa, and it could assist governments across the world to protect wildlife areas and help species as climate change forces them to move to new areas.
It is the first categorisation of protected areas to show how conservationists might deal with climate change and the shuffling ...