(Press-News.org) DALLAS – Feb. 8, 2011 – The popular drug dutasteride may not be a cost-effective way to prevent prostate cancer in men who are at elevated risk of developing the disease, according to findings by a UT Southwestern Medical Center researcher.
In a study available in the January issue of Cancer Prevention Research, investigators found that the medication, at an annual cost of $1,400, is impractical when compared to the marginal impact on survival and quality of life in at-risk groups. The drug is indicated for the treatment of enlarged prostates but also is widely prescribed for chemoprevention.
"Because prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, the implications of this data are significant since there could be millions of men who would be eligible for anti-cancer drugs," said Dr. Yair Lotan, associate professor of urology at UT Southwestern. "Prior to instituting a chemoprevention strategy to a large population, the utility and cost need to be well understood. Whether a medication improves survival, how it affects quality of life, and what its financial implications will be are all critical issues. Because dutasteride typically is prescribed for the lifetime of the patient, and therefore taken daily for decades, the cost issue is particularly relevant."
Prior research has shown that dutasteride reduced the relative risk of prostate cancer over a four-year period by 22.8 percent, but questions have remained about its cost-effectiveness. The current study analyzed the lifetime health-related costs of the drug in patients at greater risk of developing prostate cancer and compared them to other factors, such as quality and length of life.
Dr. Lotan and his colleague, Dr. Robert Svatek of UT Health Science Center at San Antonio, used a Markov probability model to compare the lifetime cost of taking dutasteride with no therapy. They used data from a previous trial and studies that evaluated outcomes of patients with prostate cancer, including treatment-related complications to create the model. The primary outcome was measured in quality-adjusted life years (QALY), which takes into account both quality and quantity of life.
"The study found that dutasteride was not cost-effective for chemoprevention unless and until a strategy is developed for targeting very high-risk patients and the cost of the drug decreases," said Dr. Lotan. "For the average man, the drug provides minimal survival benefits, and the reduction on treatment-related complications does not compensate for the high costs of every man taking the drug for many years."
###
Visit http://www.utsouthwestern.org/urology to learn more about clinical services in urology at UT Southwestern.
This news release is available on our World Wide Web home page at
http://www.utsouthwestern.edu/home/news/index.html
To automatically receive news releases from UT Southwestern via e-mail,
subscribe at www.utsouthwestern.edu/receivenews
Dutasteride not a cost-effective way to prevent prostate cancer in some men
2011-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MU researcher says the next large central US earthquake may not be in New Madrid
2011-02-09
COLUMBIA, Mo. – This December marks the bicentennial of the New Madrid earthquakes of 1811-12, which are the biggest earthquakes known to have occurred in the central U.S.
Now, based on the earthquake record in China, a University of Missouri researcher says that mid-continent earthquakes tend to move among fault systems, so the next big earthquake in the central U.S. may actually occur someplace else other than along the New Madrid faults.
Mian Liu, professor of geological sciences in the College of Arts and Science at MU, examined records from China, where earthquakes ...
The international digital divide
2011-02-09
The developed nations must invest in information and communications technologies (ICT) in the developing world not only the close the so-called digital divide but to encourage sustainable economic development and to create new markets for international commerce.
Many observers have suggested that the gap between those with access to ICT and those without it is growing. But, all world citizens should have the opportunity to benefit from open access to ICT. The benefits are obvious to those given access in terms of education and opportunity, but ICT availability in developing ...
Study: Consumers value safer food more than current analyses suggest
2011-02-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Government regulators could more realistically assess the value of improving food safety if they considered the fact that consumers typically want to avoid getting sick – even if it means they have to pay a little extra for safer food, researchers say.
In the world of food regulation, cost-benefit analyses are a primary tool for assessing the societal benefits of mandating more stringent – and more expensive – processing practices. In most cases, regulators determine a dollar value associated with pursuing new rules by estimating how many illnesses and ...
Thoughts of hopes, opportunities keep people from clinging to failing investments
2011-02-09
It's a common problem in the business world—throwing good money after bad. People cling to bad investments, hoping that more time, effort, and money will rescue their turkey of a project. A new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, finds that changing people's mindsets can make them more likely to abandon a failing investment.
"These situations happen all the time," says Assistant Professor Daniel C. Molden, of Northwestern University, who conducted the study with his graduate student Chin Ming Hui. "They happen ...
Study shows delayed-enhancement MRI may predict, prevent strokes
2011-02-09
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 8, 2011 – Researchers at the University of Utah's Comprehensive Arrhythmia and Research Management (CARMA) Center have found that delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging (DE-MRI) holds promise for predicting the risks of strokes, the third leading cause of death in the U.S. Their latest study on a novel application of this technology appears in the Feb. 15 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. (http://content.onlinejacc.org/cgi/content/abstract/57/7/831)
The study included 387 patients who were treated for atrial fibrillation ...
Brief diversions vastly improve focus, researchers find
2011-02-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study in the journal Cognition overturns a decades-old theory about the nature of attention and demonstrates that even brief diversions from a task can dramatically improve one's ability to focus on that task for prolonged periods.
The study zeroes in on a phenomenon known to anyone who's ever had trouble doing the same task for a long time: After a while, you begin to lose your focus and your performance on the task declines.
Some researchers believe that this "vigilance decrement," as they describe it, is the result of a drop in one's "attentional ...
JAMA features NJIT biomedical engineer helping stroke patients
2011-02-09
The Journal of the American Medical Society ("Medical News & Perspectives", Jan. 19, 2011) featured the research of NJIT Associate Professor Sergei Adamovich, a biomedical engineer. Adamovich and his research partners, physical therapists Alma Merians, PhD, PT, and Eugene Tunik, PhD, PT, at the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, have developed innovative robotic and virtual reality-based video game therapies to help stroke patients regain use of hands and arms.
JAMA reported that the efforts of this team are making headway. Twenty-four patients who ...
Why leatherback turtles linger in South Pacific Gyre, and why it matters
2011-02-09
VIDEO:
Tagging and tracking leatherback sea turtles has produced new insights into the turtles' behavior in a part of the South Pacific Ocean long considered an oceanic desert. The new data...
Click here for more information.
Leatherbacks. They are the Olympians of the turtle world – swimming farther, diving deeper and venturing into colder waters than any other marine turtle species. But for all their toughness, they have still suffered a 90 percent drop in their population ...
Tool makes search for Martian life easier
2011-02-09
RICHLAND, Wash. – Finding life on Mars could get easier with a creative adaption to a common analytical tool that can be installed directly on the robotic arm of a space rover.
In a recent paper published online in the journal Planetary and Space Science, a team of researchers propose adding a laser and an ion funnel to a widely used scientific instrument, the mass spectrometer, to analyze the surfaces of rocks and other samples directly on Mars' surface. The researchers demonstrated that the combined system could work on the spot, without the sample handling that mass ...
Hydrogels used to make precise new sensor
2011-02-09
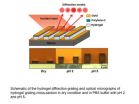
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are developing a new type of biological and chemical sensor that has few moving parts, is low-cost and yet highly sensitive, sturdy and long-lasting.
The "diffraction-based" sensors are made of thin stripes of a gelatinous material called a hydrogel, which expands and contracts depending on the acidity of its environment.
Recent research findings have demonstrated that the sensor can be used to precisely determine pH - a measure of how acidic or basic a liquid is - revealing information about substances in liquid environments, said ...