(Press-News.org) Consumers often have a distorted view when they compare information that involves numbers, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"As a consumer, would your preference for a dishwasher depend on whether its warranty level is expressed in months rather than years?" write authors Mario Pandelaere (Ghent University, Belgium), Barbara Briers (Tilburg University, the Netherlands), and Christophe Lembregts (Ghent University, Belgium).
To most consumers, the answer is "yes." The difference between an 84-month and a 108-month warranty looks bigger than the difference between a seven-year and a nine-year warranty, despite the fact that both differences are exactly the same.
"Qualitative information can usually be specified in alternative units," the authors write. "In many cases, however, the specific unit in which information is described is arbitrary. For instance, product quality ratings may be expressed on a scale from 0 to 10 or on a scale from 0 to 100," the authors write. "People typically fail to realize that the unit of quantitative information is arbitrary. They just focus on the number of scale units used to express a certain difference."
As a result, higher numbers seem to represent bigger quantities. This "unit effect" is the reason why consumers perceive a bigger difference between ratings 90 and 95 out of 100 than they do between a 9 or 9.5 out of 10.
In an additional study, the authors found that the unit effect can be used to encourage healthy food choices. In one experiment, participants exiting the lab were offered the choice between a complimentary apple or a Twix® bar. The energy content of these two choices was either expressed in Kilojoules (247 for the apple versus 1029 for the Twix®) or Kilocalories (59 for the apple versus 246 for the Twix®). "Participants more often chose the apple when the energy content was expressed in Kilojoules than in Kilocalories as the former difference (782 Kilojoules) looks much bigger in the latter one (187 Kilocalories).
However, the authors found that the effect was not replicated when people pay close attention to specific attribute information or when people are reminded of the arbitrary nature of the unit in which information is expressed.
###
Mario Pandelaere, Barbara Briers, and Christophe Lembregts. "How to Make a 29% Increase Look Bigger: The Unit Effect in Option Comparisons." Journal of Consumer Research: August 2011 (published online February 1, 2011). More information: http://ejcr.org.
Pay attention! Many consumers believe 36 months is longer than 3 years
2011-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Consumer beware: Rejecting an option may make you more likely to choose it later
2011-02-15
People make purchasing decisions by choosing between alternatives or by rejecting certain options. But a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research finds that focusing on ruling out an option can lead consumers to reverse their preferences.
"Consider the decision to purchase an iPhone or a Blackberry," write authors Juliano Laran (University of Miami) and Keith Wilcox (Babson College). "If a consumer prefers a business phone, a choice task would lead her to purchase a Blackberry. In this research we demonstrate that rejecting alternatives makes consumers more likely ...
Few women seek help for sexual issues after cancer treatment, but many want it
2011-02-15
Many women who survive breast and gynecologic cancers want medical help for their sexual issues, but most do not get it. A survey of hundreds of cancer survivors, published online in the journal Cancer, confirms that more than forty percent want medical attention for their sexual health needs.
"Some women have the courage to raise sexual concerns with their doctor, although repeated studies show they prefer the doctor to initiate the discussion," said Stacy Tessler Lindau, MD, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Chicago Medical Center ...
World phosphorous use crosses critical threshold
2011-02-15
MADISON — Recalculating the global use of phosphorous, a fertilizer linchpin of modern agriculture, a team of researchers warns that the world's stocks may soon be in short supply and that overuse in the industrialized world has become a leading cause of the pollution of lakes, rivers and streams.
Writing in the Feb. 14 edition of the journal Environmental Research Letters, Stephen Carpenter of the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Elena Bennett of McGill University report that the human use of phosphorous, primarily in the industrialized world, is causing the widespread ...
George Clooney or Saddam Hussein? Why do consumers pay for celebrity possessions?
2011-02-15
A new study in the Journal of Consumer Research sheds some light into why someone would pay $48,875 for a tape measure that had belonged to Jackie Kennedy or $3,300 for Bernie Madoff's footstool.
"Why do people pay money for celebrity possessions?" write authors George E. Newman (Yale University), Gil Diesendruck (Bar-Ilan University), and Paul Bloom (Yale University). "Celebrity items often have little functional value. And because the objects themselves tend to be relatively common artifacts (clothing, furniture, etc.) they are often physically indistinguishable from ...
How do consumers react when friends provide poor service in a business arrangement?
2011-02-15
When your friend is a service provider, things can get complicated. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, a problem can lead to feelings of betrayal or empathy, depending on the circumstances.
"Imagine that you are planning to celebrate your birthday at your favorite restaurant. You ask the owner to hold a sea-view table for you and he indicates that he will try to do so. When you arrive at the restaurant, however, he tells you that all of the sea-view tables have been taken. What would your reaction be?" write authors Lisa C. Wan (Lingnan University), ...
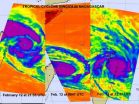
NASA satellites see Cyclone Bingiza move across northern Madagascar
2011-02-15
Tropical Cyclone Bingiza has made landfall in northeastern Madagascar, and NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites captured visible infrared satellite data of the storm's progression over the weekend, revealing the power behind the storm.
The movement and landfall of Tropical Cyclone Bingiza was captured over the weekend of Feb. 12-13 in a series of infrared satellite imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. Aqua and Terra provided companion visible images to the infrared images of Bingiza's track across northern ...
Heart patients should be referred to Cardiac Rehabilitation before leaving hospital
2011-02-15
Healthcare practitioners can increase the number of patients with heart disease referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program by 40 per cent, helping them to reduce their risk of dying and improve their quality of life, say researchers at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre.
Previous studies, including one by Taylor in 2004, indicate that participating in cardiac rehab after a cardiac illness, such as a heart attack, can reduce the risk of death by approximately 25 per cent, a reduction similar to that of other standard therapies such as cholesterol-lowering medications (statins) ...
Earliest humans not so different from us, research suggests
2011-02-15
That human evolution follows a progressive trajectory is one of the most deeply-entrenched assumptions about our species. This assumption is often expressed in popular media by showing cavemen speaking in grunts and monosyllables (the GEICO Cavemen being a notable exception). But is this assumption correct? Were the earliest humans significantly different from us?
In a paper published in the latest issue of Current Anthropology, archaeologist John Shea (Stony Brook University) shows they were not.
The problem, Shea argues, is that archaeologists have been focusing ...
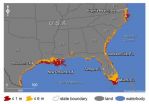
Rising seas will affect major US coastal cities by 2100
2011-02-15
Rising sea levels could threaten an average of 9 percent of the land within 180 U.S. coastal cities by 2100, according to new research led by University of Arizona scientists.
The Gulf and southern Atlantic coasts will be particularly hard hit. Miami, New Orleans, Tampa, Fla., and Virginia Beach, Va. could lose more than 10 percent of their land area by 2100.
The research is the first analysis of vulnerability to sea-level rise that includes every U.S. coastal city in the lower 48 with a population of 50,000 or more.
The latest scientific projections indicate that ...
Monitoring killer mice from space
2011-02-15
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 15, 2011 – The risk of deadly hantavirus outbreaks in people can be predicted months ahead of time by using satellite images to monitor surges in vegetation that boost mouse populations, a University of Utah study says. The method also might forecast outbreaks of other rodent-borne illnesses worldwide.
"It's a way to remotely track a disease without having to go out and trap animals all the time," says Denise Dearing, professor of biology at the University of Utah and co-author of the study published online Wednesday, Feb. 16, in the journal Global ...