(Press-News.org) Healthcare practitioners can increase the number of patients with heart disease referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program by 40 per cent, helping them to reduce their risk of dying and improve their quality of life, say researchers at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre.
Previous studies, including one by Taylor in 2004, indicate that participating in cardiac rehab after a cardiac illness, such as a heart attack, can reduce the risk of death by approximately 25 per cent, a reduction similar to that of other standard therapies such as cholesterol-lowering medications (statins) and aspirin. In spite of this evidence, only 20 to 30 per cent of patients are referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program after hospital discharge, a phenomenon observed in many countries.
Researchers at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre explored multiple strategies to increase referrals to cardiac rehabilitation programs at 11 hospitals across Ontario, including using a discharge checklist for doctors and allied health professionals, electronic referral in medical records and talking with patients at the bedside.
According to the study, "Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation Referral Strategies on Utilization Rates," published in the February 14 edition of the Journal Archives of Internal Medicine, a combined approach – a checklist or electronic referral and talking with patients – can increase referrals by 45 per cent. By targeting both healthcare providers and patients, over 70 per cent of eligible patients enroll in cardiac rehab.
"Every patient discharged from the hospital with a heart condition should be referred to a cardiac rehab program," says Dr. Sherry Grace, principal investigator and Director of Research for the Cardiovascular Rehabilitation and Prevention Program at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, University Health Network.
"Cardiac rehab is a key component of the continuum of cardiac care. We shouldn't just discharge patients from the hospital without ensuring there is a link to these proven rehab services to support patients in their recovery," says Dr. Grace, who is also an associate professor in the School of Kinesiology & Health Science at York University.
Cardiac rehabilitation offers a comprehensive approach to health by combining medical treatments and lifestyle modification. Patients are able to benefit from a variety of services, including: education sessions, nutritional assessment with a dietician, risk factor treatment (hypertension, cholesterol and smoking cessation) by physicians and nurse practitioners, medication review with a pharmacist, targeted exercise prescription by an exercise physiologist, nurse or kinesiologist and supervised exercise.
Joe Walters, a 55 year old supervisor, lost 30 pounds through the Centre's Cardiac Rehabilitation Program at Toronto Western Hospital (TWH) after having being diagnosed with an irregular heart beat in August 2009.
"The cardiac rehab program was truly motivational. It opened my eyes to the number of people who have heart problems like me, and it was refreshing to know it came with a built-in support network," says Joe who notes work-related stress contributed to his weight gain and heart trouble. "I highly recommend a cardiac rehab program for anyone with a heart condition."
Joe graduated from the program in April 2010, but continues to attend classes to keep the weight off.
Dr. Caroline Chessex, Clinical Director of the Cardiovascular Rehabilitation and Prevention Program at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, is part of a multidisciplinary team who treats patients like Joe by developing a personalized exercise program tailored to each patient's cardiac risk profile.
"Our goal is to develop strategies for patients to reduce or eliminate their risk of coronary artery disease, prevent or minimize hospitalization, decrease mortality and improve quality of life," says Dr. Chessex, noting that patients can prolong their life and reduce their risk of having a second heart attack, or needing a second heart surgery.
Beyond the physical and psychological benefits, cardiac rehabilitation saves money. Cardiac bypass surgery, the most common type of open-heart surgery, costs approximately $23,000 for each patient, but rehabilitation costs $1,000-1,500 per patient.
"The return on investment is obvious. Focusing on expensive cardiac interventions and then discharging patients without a systematic approach for support just doesn't make sense," says Dr. Grace. "Cardiac rehab is the right step towards prevention and it saves money."
###
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and Heart and Stroke Foundation funded this study.
Peter Munk Cardiac Centre
The Peter Munk Cardiac Centre is the premier cardiac centre in Canada. Since it opened in 1997, the Centre has saved and improved the lives of cardiac patients from around the world. Each year, approximately 17,000 patients receive the innovative and compassionate care from the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre multidisciplinary heart team. In addition, the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre trains more cardiologists and cardiovascular surgeons than any hospital in Canada. The Centre is based at Toronto General Hospital – a member of University Health Network, which also includes Toronto Western Hospital and Princess Margaret Hospital. All three are research hospitals affiliated with the University of Toronto.
York University
York University is a leading interdisciplinary research and teaching university in Canada. York offers a modern, academic experience at the undergraduate and graduate level in Toronto, Canada's most international city. The third largest university in the country, York is host to a dynamic academic community of 50,000 students and 7,000 faculty and staff, as well as 200,000 alumni worldwide. York's 10 Faculties and 28 research centres conduct ambitious, groundbreaking research that is interdisciplinary, cutting across traditional academic boundaries. This distinctive and collaborative approach is preparing students for the future and bringing fresh insights and solutions to real-world challenges. York University is an autonomous, not-for-profit corporation.
Heart patients should be referred to Cardiac Rehabilitation before leaving hospital
2011-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Earliest humans not so different from us, research suggests
2011-02-15
That human evolution follows a progressive trajectory is one of the most deeply-entrenched assumptions about our species. This assumption is often expressed in popular media by showing cavemen speaking in grunts and monosyllables (the GEICO Cavemen being a notable exception). But is this assumption correct? Were the earliest humans significantly different from us?
In a paper published in the latest issue of Current Anthropology, archaeologist John Shea (Stony Brook University) shows they were not.
The problem, Shea argues, is that archaeologists have been focusing ...
Rising seas will affect major US coastal cities by 2100
2011-02-15
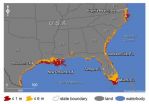
Rising sea levels could threaten an average of 9 percent of the land within 180 U.S. coastal cities by 2100, according to new research led by University of Arizona scientists.
The Gulf and southern Atlantic coasts will be particularly hard hit. Miami, New Orleans, Tampa, Fla., and Virginia Beach, Va. could lose more than 10 percent of their land area by 2100.
The research is the first analysis of vulnerability to sea-level rise that includes every U.S. coastal city in the lower 48 with a population of 50,000 or more.
The latest scientific projections indicate that ...
Monitoring killer mice from space
2011-02-15
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 15, 2011 – The risk of deadly hantavirus outbreaks in people can be predicted months ahead of time by using satellite images to monitor surges in vegetation that boost mouse populations, a University of Utah study says. The method also might forecast outbreaks of other rodent-borne illnesses worldwide.
"It's a way to remotely track a disease without having to go out and trap animals all the time," says Denise Dearing, professor of biology at the University of Utah and co-author of the study published online Wednesday, Feb. 16, in the journal Global ...
Breast cancer screening with MRI benefits women with radiation therapy history
2011-02-15
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Breast cancer screening with MRI can detect invasive cancers missed on mammography in women who've undergone chest irradiation for other diseases, according to a new study published online and in the April print edition of Radiology.
Women who receive radiation therapy as children and young adults for diseases like Hodgkin's lymphoma face a significantly greater risk of breast cancer later in life. The incidence of breast cancer increases approximately eight years after chest irradiation, and 13 percent to 20 percent of women treated with moderate- to ...
Updated heart disease prevention guidelines for women focus more on 'real-world' recommendations
2011-02-15
Practical medical advice that works in the "real world" may more effectively prevent cardiovascular disease in women than recommendations based only on findings in clinical research settings, according to the 2011 update to the American Heart Association's cardiovascular disease prevention guidelines for women.
First published in 1999, the guidelines until now have been primarily based on findings observed in clinical research. That alone often doesn't consider the personal and socioeconomic factors that can keep women from following medical advice and treatment.
"These ...
New study finds no cognitive impairment among ecstasy users
2011-02-15
The drug known as ecstasy has been used by 12 million people in the United States alone and millions more worldwide. Past research has suggested that ecstasy users perform worse than nonusers on some tests of mental ability.
But there are concerns that the methods used to conduct that research were flawed, and the experiments overstated the cognitive differences between ecstasy users and nonusers.
In response to those concerns, a team of researchers has conducted one of the largest studies ever undertaken to re-examine the cognitive effects of ecstasy, funded by a ...
Poor sleep quality is associated with greater disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients
2011-02-15
DARIEN, Ill. – A study in the Feb. 15 issue of the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that poor sleep quality correlated with higher levels of depressive symptoms, greater pain severity, increased fatigue, and greater functional disability in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). The study suggests that addressing sleep problems via pharmacological or behavioral interventions may have a critical impact on the health and lives of patients with RA.
The study represents a cross-sectional examination of the relationship between sleep quality and functional disability ...
Teamwork ability for kids: Non-competitive Children's Birthday Games
2011-02-15
Why Choose Non-Competitive Games? - Many adults find it difficult not to be a bad loser, and it is even more difficult for children who have yet to learn how to lose. However, the art of losing should not be taught on birthdays, as these should be very special celebrations with lots of happiness, fun and a merry atmosphere.
In traditional competitive games such as sack racing or egg and spoon races, children are pitted against each other to create winners and losers. Non-competitive games on the other hand avoid competition and instead often require teamwork. They produce ...
Swissotel Odessa, Ukraine: The First Five-Star Hotel Of The International Hotel Chain On The Black Sea
2011-02-15
Swissôtel Hotels & Resorts is about to add another Eastern European deluxe hotel to its portfolio: Swissôtel Odessa, expected to open in spring 2013. Swissôtel Hotels & Resorts signed yesterday a management contract in Odessa with the Ukrainian investors, Interpoint Development.
Swissôtel Odessa will include 333 modern and contemporary rooms, varying from the classic category "Swiss Advantage" to Presidential Suites. Furthermore the hotel will provide a lobby lounge-bar with a library, two restaurants and a brasserie with an extensive terrace overlooking the Black Sea, ...
888poker and Canadian Poker Tour announce Super Caribbean Cruise Qualifiers
2011-02-15
888poker is proud to announce it is offering its players packages to join the Canadian Poker Tour's Super Cruise in the Caribbean from 3-10 April 2011.
This ideal 7-day cruise vacation leaves from the coast of Florida and offers breathtaking scenery, sandy beaches and a No-Limit Texas Hold'em tournament onboard the Royal Caribbean's Freedom of the Seas.
The $5,000 package includes:
• Airfare ($1,000)
• Luxury Cabin accommodation ($2,300)
• Event Buy-in ($1,200)
• Spending money ($500)
So how can you get there? 888poker players from Canada can qualify via ...