Lie detection: Misconceptions, pitfalls and opportunities for improvement
2011-02-17
(Press-News.org) Unlike Pinocchio, liars do not usually give telltale signs that they are being dishonest. In lieu of a growing nose, is there a way to distinguish people who are telling the truth from those who aren't? A new report in Psychological Science in the Public Interest, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, discusses some of the common misconceptions about those proficient in the art of deception, reviews the shortcomings of commonly used lie-detection techniques, and presents new empirically supported methods for telling liars from truth-tellers with greater accuracy.
Trapping a liar is not always easy. Lies are often embedded in truths and behavioral differences between liars and truth-tellers are usually very small. In addition, some people are just very good at lying. Lie detectors routinely make the common mistakes of overemphasizing nonverbal cues, neglecting intrapersonal variations (i.e., how a person acts when they are telling the truth versus when they are lying), and being overly confident in their lie-detection skills.
In this report, Aldert Vrij of the University of Portsmouth, Anders Granhag of the University of Gothenburg, and Stephen Porter of the University of British Columbia review research suggesting that verbal methods of deception detection are more useful than nonverbal methods commonly believed to be effective, and that there are psychological differences between liars and truth-tellers that can be exploited in the search for the truth.
In an information-gathering interview suspects are asked to give detailed statements about their activities through open questions—for example, "What did you do yesterday between 3 p.m. and 4 p.m.?" This interview style encourages suspects to talk and allows for opportunities to identify inconsistencies between the answer and available evidence. Asking very specific questions that a suspect is unlikely to anticipate may also help in lie detection.
Lying can be more cognitively demanding than truth-telling—it requires more brain power to come up with a lie and keep track of it (e.g., who was told what) than it does to tell the truth. Imposing cognitive load on interviewees by asking them to recall the events in reverse order may also be useful in weeding out liars from those telling the truth.
This research has important implications in a variety of settings, including the courtroom, police interviews, and screening individuals with criminal intent, for instance, identifying potential terrorists.
###
For more on this topic, please read the full report here: http://www.psychologicalscience.org/journals/pspi/pspi_10_6.pdf
Psychological Science in the Public Interest is a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. It publishes an eclectic mix of thought-provoking articles on the latest important advances in psychology. For a copy of the article "Pitfalls and Opportunities in Nonverbal and
Verbal Lie Detection" and access to other Psychological Science in the Public Interest research findings, please contact Keri Chiodo at 202-293-9300 or kchiodo@psychologicalscience.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-02-17
Northwestern University scientists have discovered a new mechanism in the core gears of the circadian clock. They found the loss of a certain gene, dubbed "twenty-four," messes up the rhythm of the common fruit fly's sleep-wake cycle, making it harder for the flies to awaken.
The circadian clock drives, among other things, when an organism wakes up and when it sleeps. While the Northwestern study was done using the fly Drosophila melanogaster, the findings have implications for humans.
The research will be published Feb. 17 in the journal Nature.
"The function of ...
2011-02-17
Up to two-thirds of Earth's permafrost likely will disappear by 2200 as a result of warming temperatures, unleashing vast quantities of carbon into the atmosphere, says a new study by the University of Colorado Boulder's Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences.
The carbon resides in permanently frozen ground that is beginning to thaw in high latitudes from warming temperatures, which will impact not only the climate but also international strategies to reduce fossil fuel emissions, said CU-Boulder's Kevin Schaefer, lead study author. "If we want ...
2011-02-17
VIDEO:
Nobody enjoys colonoscopies, including mice. University of Missouri researchers are excited about the potential of using genetic biomarkers to predict colon cancer caused by inflammation. A new method developed at...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Nobody enjoys colonoscopies, including mice. University of Missouri researchers are excited about the potential of using genetic biomarkers to predict colon cancer caused by inflammation. A new method developed ...
2011-02-17
WASHINGTON—February 16, 2011—Despite the unpredictable economy, nearly three-quarters (73%) of New Jersey residents think spending money on research to improve health globally is important to jobs and incomes in the state, according to a new statewide poll commissioned by Research!America. The poll data will be released today at a meeting in Washington, DC, of prominent global health research and development (R&D) experts and New Jersey business, academia and nonprofit leaders. This is part of a six-state effort by Research!America.
According to the poll, most of the ...
2011-02-17
The California Health Interview Survey (CHIS), the nation's largest state health survey and a primary source of information on California's diverse population, released its latest data today on more than 100 topics affecting the health and well-being of the state's residents.
The random–digit-dial telephone survey, conducted every two years by the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research, gathers essential information from tens of thousands of California households on a wide variety of topics, from health insurance and public program participation to diabetes, obesity ...
2011-02-17
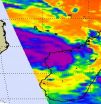
Infrared satellite data from NASA is showing some strong thunderstorms over west-central Madagascar today as Tropical Storm Bingiza continues to hug the western coast of the island nation.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Bingiza today, Feb. 16 at 10:17 UTC (5:17 a.m. EST). The image revealed some strong convection over the west-central coast where thunderstorm cloudtops were high and dropping moderate to heavy rainfall. Infrared data can provide temperature information ...
2011-02-17
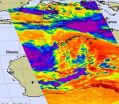
NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image today of tropical cyclones affecting Australia in the western and northern areas of the country. Newly formed Tropical Storm Carlos is bringing heavy rains and gusty winds to Darwin and the Northern Territory, while Tropical Storm Dianne is bringing rains and winds to Western Australia.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Australia today, Feb. 16 at 05:17 UTC (12:17 a.m. EST/ 2:47 p.m. Australia/Darwin local time. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of both tropical storms and found ...
2011-02-17
ESA's Herschel space observatory has discovered a population of dust-enshrouded galaxies that do not need as much dark matter as previously thought to collect gas and burst into star formation.
The galaxies are far away and each boasts some 300 billion times the mass of the Sun. The size challenges current theory that predicts a galaxy has to be more than ten times larger, 5000 billion solar masses, to be able form large numbers of stars.
The new result is published today in a paper by Alexandre Amblard, University of California, Irvine, and colleagues.
Most of the ...
2011-02-17
A recent multicenter clinical trial of atorvastatin, a type of cholesterol-lowering drug, found that although the drug did not inhibit plasma HIV RNA levels, it did inhibit expression of cellular markers of immune activation and inflammation in patients with HIV infection. Since immune activation and inflammation are associated with progression of HIV infection, the implication is that the statin may inhibit disease progression and help in the infection's management. The findings are in a study, available online, published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases.
The investigators, ...
2011-02-17
As a child grows, a short stature is not usually cause for concern, but it is often the only sign of a condition called Turner syndrome. Prevalent in girls, Turner syndrome is a genetic defect that short-circuits normal growth and leads to cardiac and renal problems. It is not commonly detected until age 10 or older when a youngster's unusually short height raises suspicions.
This lag before diagnosis of the condition can delay the start of growth hormone therapy, which can help in achieving normal or near-normal adult stature. Yale School of Medicine researchers are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Lie detection: Misconceptions, pitfalls and opportunities for improvement