(Press-News.org) CHAMPAIGN, lll. — A review of more than 160 studies of human and animal subjects has found "clear and compelling evidence" that – all else being equal – happy people tend to live longer and experience better health than their unhappy peers.
The study, in the journal Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being, is the most comprehensive review so far of the evidence linking happiness to health outcomes. Its lead author, University of Illinois professor emeritus of psychology Ed Diener, who also is a senior scientist for the Gallup Organization, of Princeton, N.J., analyzed long-term studies of human subjects, experimental human and animal trials, and studies that evaluate the health status of people stressed by natural events.
"We reviewed eight different types of studies," Diener said. "And the general conclusion from each type of study is that your subjective well-being – that is, feeling positive about your life, not stressed out, not depressed – contributes to both longevity and better health among healthy populations."
A study that followed nearly 5,000 university students for more than 40 years, for example, found that those who were most pessimistic as students tended to die younger than their peers. An even longer-term study that followed 180 Catholic nuns from early adulthood to old age found that those who wrote positive autobiographies in their early 20s tended to outlive those who wrote more negative accounts of their young lives.
There were a few exceptions, but most of the long-term studies the researchers reviewed found that anxiety, depression, a lack of enjoyment of daily activities and pessimism all are associated with higher rates of disease and a shorter lifespan.
Animal studies also demonstrate a strong link between stress and poor health. Experiments in which animals receive the same care but differ in their stress levels (as a result of an abundance of nest mates in their cages, for example) have found that stressed animals are more susceptible to heart disease, have weaker immune systems and tend to die younger than those living in less crowded conditions.
Laboratory experiments on humans have found that positive moods reduce stress-related hormones, increase immune function and promote the speedy recovery of the heart after exertion. In other studies, marital conflicts and high hostility in married couples were associated with slow wound healing and a poorer immune response.
"I was almost shocked and certainly surprised to see the consistency of the data," Diener said. "All of these different kinds of studies point to the same conclusion: that health and then longevity in turn are influenced by our mood states."
While happiness might not by itself prevent or cure disease, the evidence that positive emotions and enjoyment of life contribute to better health and a longer lifespan is stronger than the data linking obesity to reduced longevity, Diener said.
"Happiness is no magic bullet," he said. "But the evidence is clear and compelling that it changes your odds of getting disease or dying young."
"Although there are a handful of studies that find opposite effects," Diener said, "the overwhelming majority of studies support the conclusion that happiness is associated with health and longevity. Current health recommendations focus on four things: avoid obesity, eat right, don't smoke, and exercise. It may be time to add 'be happy and avoid chronic anger and depression' to the list."
INFORMATION:
Editor's note: To contact To contact Ed Diener, e-mail: ediener@cyrus.psych.uiuc.edu. The paper, "Happy People Live Longer: Subjective Well-Being Contributes to Health and Longevity," is available online or from the News Bureau.
Study: Happiness improves health and lengthens life
2011-03-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For alcoholics, new help in abstaining -- without thinking about it
2011-03-02
Alcoholism is a tough addiction to kick. Eventually, most people return to drinking. But some Dutch and German psychological scientists have tested a short-term regime that promises to help alcoholics stay sober. Their study is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association of Psychological Science.
Heavy drinkers tend to behave impulsively in response to temptation. Meanwhile, their "reflective," or controlled, responses—the thoughts that would help them resist drinking—are often weak. Most therapies, including Cognitive Behavior Therapy, primarily ...
Researchers pinpoint patients who receive greatest benefit from heart failure treatment
2011-03-02
Mild heart failure patients with a particular condition that results in disorganized electrical activity throughout the heart benefit substantially from cardiac resynchronization therapy with defibrillator (CRT–D), according to a study published in the American Heart Association journal Circulation.
In patients with the condition, known as left bundle branch block or LBBB, CRT-D therapy reduced heart failure progression and the risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias, fast and potentially life-threatening heart rhythms. Heart failure patients without LBBB did not receive ...
Scientists discover genetic switch that increases muscle blood supply
2011-03-02
Many people suffer from a devastating condition known as critical limb ischemia (CLI) that can lead to muscle wasting and even amputation. The disease is linked to the blockage of blood flow to the skeletal muscle and current treatment options include rehabilitative exercise and surgical bypass of blood vessels. New preclinical research suggests there may be a way to restore blood supply in skeletal muscle without traditional intervention.
Scientists at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) and the Salk Institute for Biological Studies ...
OFC/NFOEC 2011: Advances in wireless, data centers, cloud computing, network capacity
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 1—The world's largest international conference on
optical communications will take place March 6-10 at the Los Angeles Convention Center. The Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC) is the premier telecom meeting where experts from industry and academia share their results, experiences, and insights on the future of electronic and wireless communication and optical technologies. More than 10,000 attendees and an exhibit with 500 companies are expected.
CONFERENCE HIGHLIGHTS
Plenary ...
For first time, scientists show an HIV vaccine impacts the genetic makeup of the virus
2011-03-02
An AIDS vaccine tested in people, but found to be ineffective, influenced the genetic makeup of the virus that slipped past. The findings suggest new ideas for developing HIV vaccines.
The results were published Feb. 27 in Nature Medicine.
This is the first evidence that vaccine-induced cellular immune responses against HIV-1 infection exert selective pressure on the virus. "Selective pressure" refers to environmental demands that favor certain genetic traits over others.
The senior author of the multi-institutional study is Dr. James I. Mullins, University of Washington ...
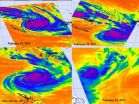
NASA tracks the brief life of Tropical Cyclone Atu in the southern Pacific
2011-03-02
Tropical Cyclone Atu had a brief but memorable life last week, and NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a day-by-day look at its growth and death.
AIRS provides infrared images of atmospheric phenomena, oceans and land areas around the world. Basically, infrared data takes the temperature of these things. When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Atu from February 21 through the 25 it saw thunderstorm cloud tops grow colder as the clouds grew higher and thunderstorms became more powerful. When ...
NASA's Glory Satellite scheduled for launch March 4
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Glory spacecraft is scheduled for launch on Friday, March 4. Technical issues with ground support equipment for the Taurus XL launch vehicle led to the scrub of the original Feb. 23 launch attempt. Those issues have been resolved.
The March 4 liftoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., is targeted for 5:09:43 a.m. EST, in the middle of a 48-second launch window. Spacecraft separation occurs 13 minutes after launch.
Data from the Glory mission will allow scientists to better understand how the sun and tiny atmospheric particles called aerosols ...
Tanning bed exposure can be deadly when complicated by medication reactions
2011-03-02
INDIANAPOLIS – Tanning bed exposure can produce more than some tanners may bargain for, especially when they self-diagnose and use the radiation to treat skin eruptions, according to research conducted by the Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Dermatology.
"There are many reasons to be cautious of tanning bed radiation but some people use tanning beds to 'self-treat' skin eruptions," said Jeffrey B. Travers, M.D., Ph.D., senior author of a study published online in the Archives of Dermatology. "If the skin eruption is eczema or even psoriasis, a tanning ...
Discovery of source of glycogen 'manufacturing' errors sheds light on fatal disease
2011-03-02
Indiana University scientists have solved a perplexing mystery regarding one of the body's main energy storage molecules, in the process shedding light on a possible route to treatment of a rare but deadly disease in teenagers.
The disease occurs when a genetic mutation causes excessive amounts of phosphate to build up in glycogen. Glycogen is a chain-like molecule the body uses to temporarily store glucose when it's not needed to provide energy for cellular activities. The excess phosphate causes unnatural glycogen structures to appear in the body, including the brain, ...
Emergency mental health lessons learned from Continental Flight 3407 disaster
2011-03-02
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- When a disaster's physical evidence is gone -- debris removed, shooter arrested, ashes cold -- the psychological effects of the disaster on emergency responders and civilians involved still may burn.
Emergency mental health, a field often overlooked in the chaos, is a vital component of any disaster response, but may not be well represented in emergency preparedness planning.
Trained mental health responders to the Continental Flight 3407 disaster outside Buffalo in 2009 share their lessons learned on mental health preparedness in an article that ...