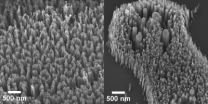
(Press-News.org) A new plant species is providing an insight into how evolution works and could help improve crop plants, scientists have revealed.
The new plant species, Tragopogon miscellus, appeared in the United States 80 years ago. It came about when two species in the daisy family, introduced from Europe, mated to produce a hybrid offspring.
The species had mated before in Europe, but the hybrids were never successful. However in America something new happened. The number of chromosomes in the hybrid spontaneously doubled, and at once it became larger than its parents and quickly spread.
Scientists studied the Tragopogon miscellus to understand how evolution works.
They found that the new plant species had relaxed control of gene expression in its earliest generations. But today, after 80 years of evolution, different patterns of gene expression are found in every plant.
"We caught evolution in the act," says Doug Soltis, co-leader of the research team. New and diverse patterns of gene expression may allow the new species to rapidly adapt in new environments.
Crossing different plant species to produce hybrids is a process used in farming to produce greater yields and stronger plants. Studying how this works in nature can give us new ideas to apply to agriculture.
The work was carried out at the University of Florida and Iowa State University and involved scientists from Queen Mary, University of London, Massey University in New Zealand, and Shanxi Normal University in China. It was published in the journal Current Biology.
Patterns of gene expression were examined in the new species, its parents, and newly made hybrids between the parents.
"What we found was a surprise," says Richard Buggs, lead author of the paper and Research Fellow at Queen Mary University of London. "It's as if hybridisation and chromosome doubling hit a re-set button on gene expression, turning them all on; this could allows subsequent generations to experiment by switching off different genes."
Pamela Soltis, distinguished curator at Florida Museum of Natural History said: "An amazing diversity of gene expression was found among individuals within populations of this young species, even though they originated just 40 generations ago from a single cross. This could be part of the secret of the species' success."
To retrace the evolution of the new species, the scientists re-made the species in the greenhouses at University of Florida, by crossing the two parent species: Tragopogon dubius and Tragopogon pratensis.
"The hardest part was getting the chromosome number to double," says Jennifer Tate from Massey University in New Zealand. "But the re-synthesised species looked exactly like the natural one."
Doug Soltis from the University of Florida said: "Hybridisation and chromosome doubling have played a major role in the evolution of flowering plants, and Tragopogon miscellus gives us an amazing window into this process."
Many crops species underwent hybridization and chromosome doubling during their domestication.
"Understanding the impacts this process has on genome structure may help understand how best to breed crops for high and stable yields," says Pat Schnable, Director of the Center for Plant Genomics at Iowa State University. "A recently arisen natural polyploid such as Tragopogon can give us unique insights into the early stages of this process."
INFORMATION:
For more information, or to arrange an interview with lead author Richard Buggs contact:
Bridget Dempsey
Communications Manager
Queen Mary, University of London
E: b.dempsey@qmul.ac.uk
T: 020 7882 7454
Notes:
The work was funded by the National Science Foundation.
doi:10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.016
END
eMaint Enterprises, headquartered in Marlton, New Jersey has provided maintenance management software solutions since 1986. Dedicated to successful CMMS implementation, eMaint is pleased to be a contributing sponsor of the CMMS-2011 Computerized Maintenance Management Summit, a learning and networking event designed for those seeking to implement a new CMMS/EAM or reimplement an existing CMMS/EAM for more effective maintenance management and decision support. The Summit will take place at the Reliability Performance Institute in Fort Myers, Florida on April 11 - 13, 2011.
eMaint's ...
A study by the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM), analysing the impact of the labour reforms introduced over the past 30 years and the living conditions of new generations, asserts that these reforms have been the origin and cause of the current development model based on the exploitation of young people.
"The study indicates that the Spanish economic development model over the past three decades – with high rates of economic growth and job creation – is based on the 'over-exploitation of the youngest generations of workers'", Pablo López Calle, author of the paper, ...
The tendency to perceive others as "us versus them" isn't exclusively human but appears to be shared by our primate cousins, a new study led by Yale researchers has found.
In a series of ingenious experiments, Yale researchers led by psychologist Laurie Santos showed that monkeys treat individuals from outside their groups with the same suspicion and dislike as their human cousins tend to treat outsiders, suggesting that the roots of human intergroup conflict may be evolutionarily quite ancient.
The findings are reported in the March issue of the Journal of Personality ...
Carbon nanofibers hold promise for technologies ranging from medical imaging devices to precise scientific measurement tools, but the time and expense associated with uniformly creating nanofibers of the correct size has been an obstacle – until now. A new study from North Carolina State University demonstrates an improved method for creating carbon nanofibers of specific sizes, as well as explaining the science behind the method.
"Carbon nanofibers have a host of potential applications, but their utility is affected by their diameter – and controlling the diameter of ...
Badbeat.com, the original and leading online poker staking business, will be donating 10% of ALL affiliate revenue generated by the Badbeat players on Friday 18th March to Comic Relief in support of Red Nose Day.
The Badbeat management has urged their players to help change lives both in the UK and across Africa, challenging them to raise as much money as possible playing poker day and night!
"Red Nose Day is a day like no other; when the whole country gets together to help change countless lives," said Badbeat Managing Director, John Conroy. "We're incredibly happy ...
MIAMI – March 17, 2010 -- University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science scientist Chris Langdon and colleagues developed a new tool to monitor coral reef vital signs. By accurately measuring their biological pulse, scientists can better assess how climate change and other ecological threats impact coral reef health worldwide.
During a March 2009 experiment at Cayo Enrique Reef in Puerto Rico, the team tested two new methods to monitor biological productivity. They compared a technique that measures changes in dissolved oxygen within ...
Using skin cells from adult siblings with schizophrenia and a genetic mutation linked to major mental illnesses, Johns Hopkins researchers have created induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) using a new and improved "clean" technique.
Reporting online February 22 in Molecular Psychiatry, the team confirms the establishment of two new lines of iPS cells with mutations in the gene named Disrupted In Schizophrenia 1, or DISC1. They made the cells using a nonviral "epiosomal vector" that jumpstarts the reprogramming machinery of cells without modifying their original ...
Researchers at the University of Granada have proved that neuropsychological rehabilitation helps in significantly reducing cognitive, emotional and behavioural after-effects in patients with acquired brain injury, generaly due to traumatic brain injury and ictus. These patients should not wait to be treated later by the social services, since early intervention (within six months after the traumatism) reduces further after-effects.
Despite the prevention campaigns launched for reducing traffic accidents and improving heart-friendly habits, traumatic brain injury and ...
A pilot study in healthy children and adolescents shows that it is feasible to screen for undiagnosed heart conditions that increase the risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). Adding a 10-minute electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) to a history and physical examination identified unsuspected cases of potentially serious heart conditions.
Although more research is needed, the preliminary results suggest that a relatively low-cost screening might help identify children who are at risk for sudden cardiac arrest, possibly preventing childhood death.
"In the United States, the ...
Halifax Savings research has shown that children in Wales have the highest ownership levels of games consoles and mobile phones across the nation and also spend the most amount of money on computer games and equipment.
They also do extremely well when it comes to owning an iPod or MP3 player and only fall down slightly on music downloads and mobile phone expenditure.
A full house for Welsh gamers
100% of the children surveyed in Wales owned a games console, well above the national average of 91%.
Children in Wales also spent the highest amount of money on computer ...