(Press-News.org) Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California at Berkeley have joined with researchers at Stanford University and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory to mount a three-pronged attack on one of the most obstinate puzzles in materials sciences: what is the pseudogap?
A collaboration organized by Zhi-Xun Shen, a member of the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Science (SIMES) at SLAC and a professor of physics at Stanford University, used three complementary experimental approaches to investigate a single material, the high-temperature superconductor Pb-Bi2201 (lead bismuth strontium lanthanum copper-oxide). Their results are the strongest evidence yet that the pseudogap phase, a mysterious electronic state peculiar to high-temperature superconductors, is not a gradual transition to superconductivity in these materials, as many have long believed. It is in fact a distinct phase of matter.
"This is a paradigm shift in the way we understand high-temperature superconductivity," says Ruihua He, lead author with Makoto Hashimoto of the paper in the March 25 issue of the journal Science that describes the team's findings. "The involvement of an additional phase, once fully understood, might open up new possibilities for achieving superconductivity at even higher temperatures in these materials." When the research was done Hashimoto and He were members of SIMES, of Stanford's Department of Applied Physics, and of Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source (ALS), where He is now a postdoctoral fellow.
The pseudogap mystery
Superconductivity is the total absence of resistance to the flow of electric current. Discovered in 1911, it was long thought to occur only in metals and only below a critical temperature (Tc) not far above absolute zero. "Ordinary" superconductivity commonly takes place at 30 kelvins (30 K) or less, equivalent to more than 400 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. Awkward as reaching such low temperatures may be, ordinary superconductivity is widely exploited in industry, health, and science.
High-Tc superconductors were discovered in 1986. "High" is a relative term; the highest-Tc superconductors function at temperatures five times higher than ordinary superconductors but still only about twice that of liquid nitrogen. Many high-Tc superconductors have been found, but the record holders for critical temperature remain the kind first discovered, the cuprates — brittle oxides whose structure includes layers of copper and oxygen atoms where current flows.
In all known superconductors electrons join in pairs (Cooper pairs) to move in correlated fashion through the material. It takes a certain amount of energy to break Cooper pairs apart; in ordinary superconductors, the absence of single-electron states below this energy constitutes a superconducting gap, which vanishes when the temperature rises above Tc. Once in the normal state the electrons revert to unpaired, uncorrelated behavior.
Not so for cuprate superconductors. A similar superconducting gap exists below Tc, but when superconductivity ceases at Tc the gap doesn't close. A "pseudogap" persists and doesn't go away until the material reaches a higher temperature, designated T* (T-star). The existence of a pseudogap in the normal state is itself anything but normal; its nature has been heatedly debated ever since it was identified in cuprates more than 15 years ago.
Attempts to explain what's going on in the pseudogap have coalesced around two main schools of thought. Traditional thinking holds that the pseudogap represents a foreshadowing of the superconducting phase. As the temperature is lowered, first reaching T*, a few electron pairs start to form, but they are sparse and lack the long-range coherence necessary for superconductivity — they can't "talk" to one another. As the temperature continues to fall, more such pairs are formed until, upon reaching Tc, virtually all conducting electrons are paired and act in correlation; they're all talking. In this scheme, there's only a single phase transition, which occurs at Tc.
Another school of thought argues that the appearance of the pseudogap at T* is also a true phase transition. The pseudogap does not represent a smooth shift to the superconducting state but is itself a state distinct from both superconductivity and normal "metallicity" (the usual state of delocalized, uncorrelated electrons). This new phase implies the existence of a "quantum critical point" — a point along a line at zero temperature where competing phases meet. In theory, with competing phases wildly fluctuating in the neighborhood of a quantum critical point, there may be entirely new routes to superconductivity.
"Promising as the 'quantum critical' paradigm is for explaining a wide range of exotic materials, high-Tc superconductivity in cuprates has stubbornly refused to fit the mold," says Joseph Orenstein of Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, a professor in physics at UC Berkeley, whose group conducted one of the research team's three experiments. "For 20 years, the cuprates managed to conceal any evidence of a phase-transition line where the quantum critical point is supposed to be found."
In recent years, however, hints have emerged. "New ultrasensitive probes have found fingerprints of phase transitions in high-Tc materials," Orenstein says, "although there's been no smoking gun. The burning question is whether we can discover the nature of the new phase or phases."
A multipronged attack on the pseudogap
In the Stanford-Berkeley study, three groups of researchers joined forces to probe the pseudogap phase on the same sample.
"Pb-Bi2201 was chosen because, first, it is structurally simple, and second, it has a relatively wide temperature range between Tc and T*," says Ruihua He. "This permits a clean separation of any remnant effect of superconductivity from genuine pseudogap physics."
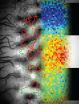
Groups led by Z.-X. Shen at beamline 5‑4 of the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) at SLAC and by Zahid Hussain, ALS Division Deputy for Scientific Support, at beamline 10.0.1 of Berkeley Lab's ALS, studied the sample with angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). In ARPES, a beam of x-rays directed at the sample surface excites the emission of valence electrons. By monitoring the kinetic energy and momentum of the emitted electrons over a wide temperature range the researchers map out the material's low-energy electronic band structure, which determines much of its electrical and magnetic properties.
At Stanford, researchers led by Aharon Kapitulnik of SIMES, a professor in applied physics at Stanford University, studied the same crystal of Pb-Bi2201 with the magneto-optical Kerr effect. In light reflected from the sample under a zero magnetic field, tiny rotations of the plane of polarization are measured as the temperature changes. The rotations are proportional to the net magnetization of the sample at different temperatures.
Finally, Orenstein's group at Berkeley applied time-resolved reflectivity to the sample. A pump pulse from a laser excites electrons many layers of atoms deep, temporarily affecting the sample's reflectivity. Probe pulses, timed to follow less than a trillionth of a second after the pump pulses, reveal changes in reflection at different temperatures.
All these experimental techniques had previously pointed to the possibility of a phase transition in the neighborhood of T* in different cuprate materials. But no single result was strong enough to stand alone.
ARPES experiments performed in 2010 by the same group of experimenters as in the present study revealed the abrupt opening of the pseudogap at T* in Pb-Bi2201. Variations in T* in different materials and even different samples, as well as in the surface conditions to which ARPES is sensitive, had left room for uncertainty, however.
In 2008, the Kerr effect was measured in another cuprate, also by the same group as in the present study, and showed a change in magnetization from zero to finite across T*. This was long-sought thermodynamic evidence for the existence of a phase transition at T*. But compared to the pronounced spectral change seen by ARPES, the extreme weakness of the Kerr-effect signal left doubt that the two results were connected.
Finally, since the late 1990s various experiments with time-resolved reflectivity in different cuprates have reported signals setting in near T* and increasing in strength as the temperature drops, until interrupted by the onset of a separate signal below Tc. The probe is complex and there was a lack of corroborating evidence for the same cuprates; the results did not receive wide attention.
Now the three experimental approaches have all been applied to the same material. All yielded consistent results and all point to the same conclusion: there is a phase transition at the pseudogap phase boundary – the three techniques put it precisely at T*. The electronic states dominating the pseudogap phase do not include Cooper pairs, but nevertheless intrude into the lower-lying superconducting phase and directly influence the motion of Cooper pairs in a way previously overlooked.
"Instead of pairing up, the electrons in the pseudogap phase organize themselves in some very different way," says He. "We currently don't know what exactly it is, and we don't know whether it helps superconductivity or hurts it. But we know the direction to take to move forward."
Says Orenstein, "Coming to grips with a new picture is a little like trying to steer the Titanic, but the fact that all three of these techniques point in the same direction adds to the mounting evidence for the phase change."
Hussain says the critical factor was bringing the Stanford and Berkeley scientists together. "We joined forces to tackle a more complex problem than any of us had tried on our own."
INFORMATION:
"From a single-band metal to a high-temperature superconductor via two thermal phase transitions," by Ruihua He, Makoto Hashimoto, Hovnatan Karapetyan, Jake Koralek, Jamie Hinton, Jean-Pierre Testaud, Vikram Nathan, Yoshiyuki Yoshida, Hong Yao, Kiyohisa Tanaka, Worawat Meevasana, Rob Moore, Donhui Lu, Sung-Kwan Mo, Motoyuki Ishikado, Hiroshi Eisaki, Zahid Hussain, Thomas Devereaux, Steven Kivelson, Joseph Orenstein, Aharon Kapitulnik, and Zhi-Xun Shen, appears in the March 25 issue of Science. This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory provides solutions to the world's most urgent scientific challenges including clean energy, climate change, human health, novel materials, and a better understanding of matter and force in the universe. It is a world leader in improving our lives and knowledge of the world around us through innovative science, advanced computing, and technology that makes a difference. Berkeley Lab is a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratory managed by the University of California for the DOE Office of Science. Visit our website at http://www.lbl.gov.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
Closing in on the pseudogap
Berkeley and Stanford researchers join forces to investigate a persistent puzzle of high-temperature superconductivity
2011-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
LateRooms.com - Perth Visitors to Enjoy Fremantle Street Arts Festival
2011-03-25
Performers from across the world will travel to Western Australia next month to take part in the annual Fremantle Street Arts Festival (FSAF).
Over the years, the event has grown to become the biggest of its kind in the country, attracting artists from as far afield as England, France, Japan and the US.
FSAF 2011 looks like it will be bigger and better than ever before, with the programme expanded to four days to coincide with the long Easter weekend (April 23rd to 26th).
Thousands of people are expected to pack the streets of Fremantle throughout the festival ...
NeuroImage: Multiplexing in the visual brain
2011-03-25
This press release is available in German.
"Neurons synchronize with different partners at different frequencies" says Dr. Dirk Jancke, Neuroscientist at the Ruhr-University in Bochum, Germany. A new imaging technique enabled to show that such functioning results in distinct activity patterns overlaid in primary visual cortex. These patterns individually signal motion direction, speed, and orientation of object contours within the same network at the same time. Together with colleagues at the University of Osnabrück, the Bochum scientists successfully visualized ...
Furniture, Electronics and Travel Savings with Latest DiscountVouchers.co.uk Weekly Deals
2011-03-25
New vouchers and deals introduced this week by popular voucher codes specialist DiscountVouchers.co.uk are able to save UK consumers money on leading brands right now. The latest weekly deals feature money off top name furniture plus also hotels, electrical and eating out to help consumers make the most of their budgets.
Available this week on the www.discountvouchers.co.uk website are deals which include -
- LoveFilm - EXCLUSIVE 30 Day Free Trial plus a GBP10 Amazon Voucher
- Movie buffs can enjoy this exclusive deal to save - DiscountVouchers.co.uk is home to ...
Sabrient Research Team Partners with Options Industry Veteran Stutland Volatility Group to Launch Stutland Volatility Funds
2011-03-25
Sabrient Systems and Stutland Volatility Group (SVG) announce the formation of Stutland Volatility Funds (SVF), an asset management firm offering a suite of long/short quant funds designed to deliver superior stock selection with enhanced risk management. SVF will benefit hedge funds, actively managed ETFs, mutual fund distributors and privately managed accounts for investors starting at $100,000.
"As U.S. markets approach 11 years of negative and near zero returns, simple buy-and-hold is no longer acceptable as a viable investment strategy," said SVG Managing Partner ...
Small code change, big effect
2011-03-25
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method which enables researchers to label any protein of their choice with any of a wide variety of previously available compounds, in living cells, by introducing a single reactive artificial amino acid. Published today in Angewandte Chemie, the new technique enables researchers to label even rare proteins very precisely for optical imaging and in the future likely also for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Carsten Schultz, Edward Lemke and colleagues tricked the ...
Case Western Reserve orthodontic researchers ask: Where's your retainer?
2011-03-25
Have you been wearing your retainer? It's a question countless parents ask of their children post-braces. Now Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine researchers are getting serious about the question.
"We found little written about the kinds of retainers prescribed and how compliant patients are in using them," said Case Western Reserve's Manish Valiathan, an assistant professor of orthodontics and a member of the American Board of Orthodontics. He notes that there is a dearth of information despite the devices being common in orthodontics practice.
Consequently ...
RakeTheRake's Poker World Exclusive - Victory for the Cereus Poker Network
2011-03-25
In a deal that is 99% complete and yet to be announced publicly, we can exclusively reveal that Victory Poker is due to leave the Cake Network to join The Cereus Poker Network imminently. Meanwhile Cake has news of its own: it is now owned by the PokerListings affiliate group.
Victory Poker, currently stable to pros such as Antonio Esfandiari, Lee Markholt, Paul Wasica and Andrew Robl to name but a few of the 20, only joined the Cake Network in the last quarter of 2010. But they are already on their way to greener pastures.
The Cereus network is currently only made ...
A diabetes drug, sitagliptin, also has a potential to prevent diabetes
2011-03-25
Diabetes type 2 is caused by insufficient levels of insulin to keep blood glucose under control. Excessive levels of another hormone, glucagon, can also contribute to diabetes type 2 by causing the liver to flood the body with stored glucose. Diabetes type 2 does not arise overnight, but slowly progresses for many years as a condition known as prediabetes. In prediabetes, blood sugar rises to excessive levels after a meal, but is normal or nearly normal after an overnight fast. Researchers are seeking ways to prevent prediabetes from progressing to diabetes. Besides diet ...
Johns Hopkins scientists link DNA 'end-caps' length to diabetes risk
2011-03-25
New evidence has emerged from studies in mice that short telomeres or "caps" at the ends of chromosomes may predispose people to age-related diabetes, according to Johns Hopkins scientists.
Telomeres are repetitive sequences of DNA that protect the ends of chromosomes, and they normally shorten with age, much like the caps that protect the end of shoelaces. As telomeres shorten, cells lose the ability to divide normally and eventually die. Telomere shortening has been linked to cancer, lung disease, and other age-related illnesses. Diabetes, also a disease of aging, ...
Drug-resistant pathogen found in large numbers in LA County
2011-03-25
Arlington, Va. (March 24, 2011) – Researchers with the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health have found high rates of the multi-drug resistant pathogen, carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) among the patient population in long-term acute care hospitals compared to general acute care hospitals across the county. These findings are particularly important because CRKP was thought to be contained to East Coast facilities and communities. These findings will be presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
[Press-News.org] Closing in on the pseudogapBerkeley and Stanford researchers join forces to investigate a persistent puzzle of high-temperature superconductivity