(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
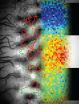
"Neurons synchronize with different partners at different frequencies" says Dr. Dirk Jancke, Neuroscientist at the Ruhr-University in Bochum, Germany. A new imaging technique enabled to show that such functioning results in distinct activity patterns overlaid in primary visual cortex. These patterns individually signal motion direction, speed, and orientation of object contours within the same network at the same time. Together with colleagues at the University of Osnabrück, the Bochum scientists successfully visualized such brain multiplexing using a modern real-time optical imaging method that exploits a specific voltage-sensitive dye.
Imaging with voltage-sensitive dye: A method to capture real-time brain dynamics
The dye incorporates in the brain cells' membrane and changes fluorescence whenever these receive or send electrical signals. Hence, high resolution camera systems allow to simultaneously capture activities of millions of nerve cells across several square millimeters across the brain.
First-time visualization of grating pattern motion across the brain surface
As a stimulus the researchers used simple oriented gratings with alternating black-white stripes drifting at constant speed across a monitor screen. These stimuli have been used for more than 50 years in visual neuroscience and still are conventionally applied in medical diagnostics. However, brain activity that signals both the grating's orientation and its motion simultaneously has not been detected so far. Such signals could now be demonstrated for the first time. Note that further computational steps including sophisticated analysis were needed before those smallest brain activity signals became visible.
Cortical mapping of object orientation
Optical imaging became state-of-the-art since it allows fine grained resolution of cortical pattern activity, so-called maps, in which local groups of active nerve cells represent grating orientation. Thereby, a particular grating orientation activates different groups of nerve cells resulting in unique patchy patterns. Their specific map layout encodes actual stimulus orientation.
Transfer of motion information through overlaid activity waves
Jancke: "Our novel imaging method furthermore captures propagating activity waves across these orientation maps. Hence, we additionally observe gratings moving in real-time across the brain. In this way, motion direction and speed can be estimated independently from orientation maps, which enables resolving ambiguities occurring in visual scenes of everyday life." The emerging spatial-temporal patterns could then individually be received and interpreted by other brain areas. To give a picture: a radio gets a permanent stream of broadcasts simultaneously. In order to listen to a particular station one has to choose only the channel to tune. For example, a following brain area might preferentially compute an object's orientation while others process its movement direction or speed simultaneously. In the future, the scientists hope to discover more of the brains real-time action when similar tools are used with increasing stimulus complexity: Naturalistic images are experienced so effortlessly in everyday life. Still it remains an intriguing question how the brain handles such complex data gaining a stable percept every moment in time.
INFORMATION:
Title Listing
Onat S, Nortmann N, Rekauzke S, König P, Jancke D (2011). Independent encoding of grating motion across stationary feature maps in primary visual cortex visualized with voltage-sensitive dye imaging. Neuroimage 55: 1763-1770. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.004
NeuroImage: Multiplexing in the visual brain
RUB Scientists visualize for the first time simultaneous encoding of object orientation and its motion
2011-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Furniture, Electronics and Travel Savings with Latest DiscountVouchers.co.uk Weekly Deals
2011-03-25
New vouchers and deals introduced this week by popular voucher codes specialist DiscountVouchers.co.uk are able to save UK consumers money on leading brands right now. The latest weekly deals feature money off top name furniture plus also hotels, electrical and eating out to help consumers make the most of their budgets.
Available this week on the www.discountvouchers.co.uk website are deals which include -
- LoveFilm - EXCLUSIVE 30 Day Free Trial plus a GBP10 Amazon Voucher
- Movie buffs can enjoy this exclusive deal to save - DiscountVouchers.co.uk is home to ...
Sabrient Research Team Partners with Options Industry Veteran Stutland Volatility Group to Launch Stutland Volatility Funds
2011-03-25
Sabrient Systems and Stutland Volatility Group (SVG) announce the formation of Stutland Volatility Funds (SVF), an asset management firm offering a suite of long/short quant funds designed to deliver superior stock selection with enhanced risk management. SVF will benefit hedge funds, actively managed ETFs, mutual fund distributors and privately managed accounts for investors starting at $100,000.
"As U.S. markets approach 11 years of negative and near zero returns, simple buy-and-hold is no longer acceptable as a viable investment strategy," said SVG Managing Partner ...
Small code change, big effect
2011-03-25
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method which enables researchers to label any protein of their choice with any of a wide variety of previously available compounds, in living cells, by introducing a single reactive artificial amino acid. Published today in Angewandte Chemie, the new technique enables researchers to label even rare proteins very precisely for optical imaging and in the future likely also for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Carsten Schultz, Edward Lemke and colleagues tricked the ...
Case Western Reserve orthodontic researchers ask: Where's your retainer?
2011-03-25
Have you been wearing your retainer? It's a question countless parents ask of their children post-braces. Now Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine researchers are getting serious about the question.
"We found little written about the kinds of retainers prescribed and how compliant patients are in using them," said Case Western Reserve's Manish Valiathan, an assistant professor of orthodontics and a member of the American Board of Orthodontics. He notes that there is a dearth of information despite the devices being common in orthodontics practice.
Consequently ...
RakeTheRake's Poker World Exclusive - Victory for the Cereus Poker Network
2011-03-25
In a deal that is 99% complete and yet to be announced publicly, we can exclusively reveal that Victory Poker is due to leave the Cake Network to join The Cereus Poker Network imminently. Meanwhile Cake has news of its own: it is now owned by the PokerListings affiliate group.
Victory Poker, currently stable to pros such as Antonio Esfandiari, Lee Markholt, Paul Wasica and Andrew Robl to name but a few of the 20, only joined the Cake Network in the last quarter of 2010. But they are already on their way to greener pastures.
The Cereus network is currently only made ...
A diabetes drug, sitagliptin, also has a potential to prevent diabetes
2011-03-25
Diabetes type 2 is caused by insufficient levels of insulin to keep blood glucose under control. Excessive levels of another hormone, glucagon, can also contribute to diabetes type 2 by causing the liver to flood the body with stored glucose. Diabetes type 2 does not arise overnight, but slowly progresses for many years as a condition known as prediabetes. In prediabetes, blood sugar rises to excessive levels after a meal, but is normal or nearly normal after an overnight fast. Researchers are seeking ways to prevent prediabetes from progressing to diabetes. Besides diet ...
Johns Hopkins scientists link DNA 'end-caps' length to diabetes risk
2011-03-25
New evidence has emerged from studies in mice that short telomeres or "caps" at the ends of chromosomes may predispose people to age-related diabetes, according to Johns Hopkins scientists.
Telomeres are repetitive sequences of DNA that protect the ends of chromosomes, and they normally shorten with age, much like the caps that protect the end of shoelaces. As telomeres shorten, cells lose the ability to divide normally and eventually die. Telomere shortening has been linked to cancer, lung disease, and other age-related illnesses. Diabetes, also a disease of aging, ...
Drug-resistant pathogen found in large numbers in LA County
2011-03-25
Arlington, Va. (March 24, 2011) – Researchers with the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health have found high rates of the multi-drug resistant pathogen, carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) among the patient population in long-term acute care hospitals compared to general acute care hospitals across the county. These findings are particularly important because CRKP was thought to be contained to East Coast facilities and communities. These findings will be presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) ...
Cosmetic Dentist in Park Ridge Educates Patients Through Online Resources
2011-03-25
Leading Park Ridge dentist, Dr. Daniel Hogan invites patients to visit the practice's website for new educational resources, including the extensive patient library covering a wide array of topics related to the different phases of dentistry. Patients are encouraged to look through the topics whenever they have an interest or a concern that may arise about the function, appearance, comfort or health of the teeth.
Providing patients with the opportunity to learn more about various procedures and treatments creates a welcoming environment for this cosmetic dentist in ...
Researchers develop a halometer that tests alterations in night vision
2011-03-25
This press release is available in French and Spanish.
Researchers from the Department of Optics of the University of Granada, belonging to the Laboratorio de Ciencias de la Visión y Aplicaciones, have developed a programme for testing alterations in night vision, and the tool required to implement it, which has been named "halometer".
This instrument consists on a software named Software Halo v1.0, and a computer where the mouse is used as a response button, and a chin cup with a forehead holder to fix the observer's position. Software Halo v1.0 was initially ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
[Press-News.org] NeuroImage: Multiplexing in the visual brainRUB Scientists visualize for the first time simultaneous encoding of object orientation and its motion