(Press-News.org) (WASHINGTON) -- Researchers in the Materials Science and Technology division of the Naval Research Laboratory have recently demonstrated electrical injection, detection and precession of spin accumulation in silicon, the cornerstone material of modern device technology, at temperatures up to 225 degrees Celsius. These results provide the first demonstration that spin accumulation in Si is viable as a basis for practical devices which meet the operating temperatures specified for commercial (85˚C), industrial (100˚C) and military (125˚C) applications. This is a key enabling step for developing devices which rely on electron spin rather than electron charge, an approach known as semiconductor spintronics that is expected to provide devices with higher performance, lower power consumption and less heat dissipation. The complete findings of this study titled, "Electrical injection and detection of spin accumulation in silicon at 500K with magnetic metal / silicon dioxide contacts" are published in the 22 March 2011 issue of Nature Communications 2:245 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1256 (2011).
The electron possesses an internal angular momentum called the spin. The International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors has identified the electron's spin as a new state variable that should be explored as an alternative to the electron's charge for use beyond Moore's Law, a projection named after Intel co-founder Gordon E. Moore. Moore predicted in 1965 that the number of transistors per unit area in an integrated circuit would double approximately every two years as advances in fabrication technology enabled the devices to be made smaller. Although this approach has been remarkably successful, critical device dimensions now approach atomic length scales, so that further size scaling becomes untenable. "Researchers have been forced to look beyond the simple reduction of size to develop future generations of electronic devices," states NRL senior scientist Dr. Berry Jonker. "Electrical generation, manipulation and detection of significant spin polarization in silicon at temperatures that meet commercial and military requirements are essential to validate spin as an alternative to charge for a device technology beyond Moore's Law."
Using ferromagnetic metal / silicon dioxide contacts on silicon, NRL scientists Connie Li, Olaf van 't Erve and Jonker electrically generate and detect spin accumulation and precession in the silicon transport channel at temperatures up to 225˚C, and conclude that the spin information can be transported in the silicon over distances readily compatible with existing fabrication technology. They thus overcome a major obstacle in achieving control of the spin variable at temperatures required for practical applications in the most widely utilized semiconductor.
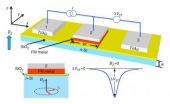
To make a semiconductor spintronic device, one needs contacts that can both generate a current of spin-polarized electrons (called a spin injector), and detect the spin polarization of the electrons (spin detector) in the semiconductor. Because the magnetic contact interface is likely to introduce additional scattering and spin relaxation mechanisms not present in the silicon bulk, the region of the semiconductor directly beneath the contact is expected to be a critical factor in the development of any future spin technology. The NRL scientists probe the spin environment directly under the magnetic metal / silicon dioxide contact using the three terminal geometry illustrated in the accompanying figure. Demonstration of spin precession and dephasing in a magnetic field transverse to the injected spin orientation, known as the Hanle effect, is conclusive evidence of spin accumulation, and enables a direct measure of the spin lifetime, a critical parameter for device operation. The NRL researchers observed Hanle precession of the electron spin accumulation in the silicon channel under the contact for biases corresponding to both spin injection and extraction, and determine the corresponding spin lifetimes.
Electronic states can form at the contact interface and introduce deleterious effects for both charge and spin transport. These undesirable states can serve as traps which prevent propagation of either charge or spin in the silicon channel. In bulk silicon, the spin lifetime is known to depend upon the carrier density, and generally decreases as the electron density increases.. "In this study we show that the spin lifetime determined from our measurements changes systematically as one changes carrier concentration of the particular silicon sample used," adds Jonker. "Our results were obtained for a number of different carrier densities and show this trend, thus making it very clear that we obtain spin injection and accumulation in the silicon itself rather than in interface defect states." The result of this research rules out spin accumulation in interface states and demonstrates spin injection, accumulation and precession in the silicon channel.
INFORMATION:
NRL scientists achieve high temperature milestone in silicon spintronics
2011-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pan American Metals of Miami Precious Metals Offer Investors Safe Haven from Inflation Fears in Medium to Long Term
2011-05-08
Pan American Metals of Miami (PAMOM), continues to provide opportunities for investment in the bullion markets. "Precious metals are tried and tested and provide investors with a safe alternative to low interest rates and decreasing currency values," says Bill Hionas, CEO of PAMOM.
PAMOM deals in four precious metals; silver, gold, platinum and palladium. The current market is showing dips in all precious metal prices, providing savvy investors with a perfect opportunity to buy.
"Long-term predictions remain optimistic for the precious metals market, ...
Worm discovery could help 1 billion people worldwide
2011-05-08
Scientists have discovered why some people may be protected from harmful parasitic worms naturally while others cannot in what could lead to new therapies for up to one billion people worldwide.
Parasitic worms are a major cause of mortality and morbidity affecting up to a billion people, particularly in the Third World, as well as domestic pets and livestock across the globe.
Now, University of Manchester researchers have, for the first time, identified a key component of mucus found in the guts of humans and animals that is toxic to worms.
"These parasitic worms ...
LateRooms.com - Enjoy Vatican Museums Under The Stars in Rome
2011-05-08
Anyone keen to see an age-old landmark from a different perspective should take advantage of the Vatican Museums Under The Stars experience in Rome.
As the name suggests, it allows people to visit the attraction after sunset, with the first session taking place on May 6th.
The activity, which sees the Vatican Museums staying open until 23:00 local time, is available every Friday from then on until October 28th 2011.
In a statement, director of the venue Antonio Paolucci remarked: "The Pope, as the bishop of Rome, wishes to offer the most beautiful works of ...
Can one model the social deficits of autism and schizophrenia in animals?
2011-05-08
Philadelphia, PA - 5 May 2011 - The use of animal models to study human disease is essential to help advance our understanding of disease and to develop new therapeutic treatments.
Social deficits are common in several psychiatric disorders, including autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia. Individuals with severe social dysfunction can experience significant difficulties with everyday functioning.
Oxytocin and vasopressin are hormones that play key roles in emotional and social behaviors and bonding. Oxytocin has been suggested as a treatment to improve social ...
LateRooms.com - Animal Collective to Play at Milan's Discoteca Alcatraz
2011-05-08
Experimental band Animal Collective are set to play a gig in Milan later this month, bringing their inimitable blend of folk and psychedelic noise to the city.
The group will take the stage on May 25th and no doubt play plenty of tunes from their most recent record Merriweather Pavilion, arguably their most critically and commercially successful album.
Animal Collective's live line-up is in a constant state of flux, but key members are Avey Tare, Deakin, Geologist and Panda Bear, who has received a lot of praise for his recent solo work.
The Baltimore group are ...
Families need to know more about feeding tubes for elderly dementia patients
2011-05-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Despite evidence that feeding tubes do not improve survival rates or quality of life for elderly patients with advanced dementia, their frequency of use varies widely across the states. A new survey of family members finds that discussions surrounding the decision to place feeding tubes surgically are often inadequate.
Advanced dementia is a terminal illness that often affects a patient's ability to eat. In prior research, Joan Teno, professor of community health at Brown University, has documented a striking variation in feeding ...
When the lungs come under pressure
2011-05-08
Patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension struggle with severe symptoms, which include shortness of breath, exhaustion and a lack of vitality. Moreover, the disease, which is more common in women, often claims the patient's life within a few years of its development. The currently available methods of treatment can slow down the progression of the disease and improve the symptoms; a cure, however, has thus far been unavailable. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research and Giessen University have now succeeded - for the first time in an animal ...
eQuoteMD Releases a Comprehensive Guide on What Doctors Need to Know When Purchasing Medical Malpractice Insurance
2011-05-08
As part of an ongoing commitment to empower physicians who purchase medical malpractice insurance, eQuoteMD.com is a releasing a comprehensive white paper delineating the most important topics and factors associated with a doctor's decisions when purchasing and maintaining medical malpractice insurance coverage. This exposition into the world of physician's liability coverage will serve to educate medical professionals who must make important decisions about this type of insurance in an effort to protect the practice's they have built.
This literary resource will assist ...
Reptile 'cousins' shed new light on end-Permian extinction
2011-05-08
An international team of researchers studied the parareptiles, a diverse group of bizarre-looking terrestrial vertebrates which varied in shape and size. Some were small, slender, agile and lizard-like creatures, while others attained the size of rhinos; many had knobbly ornaments, fringes, and bony spikes on their skulls.
The researchers found that, surprisingly, parareptiles were not hit much harder by the end-Permian extinction than at any other point in their 90 million-year history.
Furthermore, the group as a whole declined and diversified time and time again ...
Combination of ADHD and poor emotional control runs in families
2011-05-08
A subgroup of adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also exhibit excessive emotional reactions to everyday occurrences, and this combination of ADHD and emotional reactivity appears to run in families. A study from a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)-based research team finds that siblings of individuals with both ADHD and deficient emotional self-regulation (DESR) had a significantly greater risk of having both conditions than did siblings of those with ADHD alone. The study, which will appear in the American Journal of Psychiatry, has received ...