(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Despite evidence that feeding tubes do not improve survival rates or quality of life for elderly patients with advanced dementia, their frequency of use varies widely across the states. A new survey of family members finds that discussions surrounding the decision to place feeding tubes surgically are often inadequate.
Advanced dementia is a terminal illness that often affects a patient's ability to eat. In prior research, Joan Teno, professor of community health at Brown University, has documented a striking variation in feeding tube insertion rates.
To gain insight into the decision process and how it is informed by doctors, Teno and colleagues led a five-state survey regarding feeding tube insertion with family members of elderly patients who had advanced dementia. The results, published online in advance by the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, will appear in the May 13 print issue.
"Our results suggest that in these states with a high rate of feeding tube insertion we need to improve decision making so that the decision to insert a feeding tube is based on a process that elicits and respects patient's wishes," said Teno, the paper's lead author.
Among the study's key findings:
13.7 percent of family members who said their family member received a feeding tube stated that medical providers inserted the tube without discussing it first;
11.2 percent said they felt pressured by the physician to put in a feeding tube;
38.2 percent believed that that physician was strongly in favor of feeding tube insertion;
41.6 percent of the time the discussion regarding feeding tube insertion lasted less than 15 minutes;
39.3 percent did not discuss the risks of feeding tubes.
The study sample size was 486 people in five states, mostly sons and daughters who were either the persons named in an advance directive or were the person identified as the surrogate decision maker for a patient with advanced dementia. Teno led a group of researchers from Brown, the Hebrew Senior Life Institute for Aging Research in Massachusetts, and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in asking people to describe the communication they had with physicians surrounding whether to insert a feeding tube for their loved ones.
The five states were selected because they had especially high (Texas, Alabama, and Florida) or very low (Massachusetts and Minnesota) rates of intubation. Extrapolating the survey group to the entire population of the five states, much like public opinion polls do, the figures would represent 9,652 cases of elderly patients with eating problems while dying from advanced dementia.
Some satisfaction
Despite research studies that question the value of feeding tubes, 32.9 percent of people in the survey said the feeding tube did improve quality of life for their loved ones. That was more than the 23.4 percent who said they regretted using a tube.
Teno cautioned against becoming complacent about the level of satisfaction family members recall, especially after dialogues that sometimes lack all elements necessary for fully informed consent.
"I watch people who make decisions that are really difficult," she said. "To continue on they have to make peace with their decisions."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Teno, authors from Brown were Sylvia Kuo, Pedro Gozalo, Julie Lima, and Vincent Mor; the author from Hebrew Senior Life was Susan Mitchell; the author from UT Southwestern was Ramona Rhodes.
The work was funded by the National Institute on Aging.
END
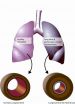
Patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension struggle with severe symptoms, which include shortness of breath, exhaustion and a lack of vitality. Moreover, the disease, which is more common in women, often claims the patient's life within a few years of its development. The currently available methods of treatment can slow down the progression of the disease and improve the symptoms; a cure, however, has thus far been unavailable. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research and Giessen University have now succeeded - for the first time in an animal ...
As part of an ongoing commitment to empower physicians who purchase medical malpractice insurance, eQuoteMD.com is a releasing a comprehensive white paper delineating the most important topics and factors associated with a doctor's decisions when purchasing and maintaining medical malpractice insurance coverage. This exposition into the world of physician's liability coverage will serve to educate medical professionals who must make important decisions about this type of insurance in an effort to protect the practice's they have built.
This literary resource will assist ...
An international team of researchers studied the parareptiles, a diverse group of bizarre-looking terrestrial vertebrates which varied in shape and size. Some were small, slender, agile and lizard-like creatures, while others attained the size of rhinos; many had knobbly ornaments, fringes, and bony spikes on their skulls.
The researchers found that, surprisingly, parareptiles were not hit much harder by the end-Permian extinction than at any other point in their 90 million-year history.
Furthermore, the group as a whole declined and diversified time and time again ...
A subgroup of adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also exhibit excessive emotional reactions to everyday occurrences, and this combination of ADHD and emotional reactivity appears to run in families. A study from a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)-based research team finds that siblings of individuals with both ADHD and deficient emotional self-regulation (DESR) had a significantly greater risk of having both conditions than did siblings of those with ADHD alone. The study, which will appear in the American Journal of Psychiatry, has received ...
Familiar blueberries and their lesser-known wild relatives are safeguarded by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and curators at America's official blueberry genebank. The plants, collected from throughout the United States and more than two dozen foreign countries, are growing at the USDA Agricultural Research Service National Clonal Germplasm Repository in Corvallis, Ore.
The blueberries are maintained as outdoor plants, potted greenhouse and screenhouse specimens, tissue culture plantlets, or as seeds, according to research leader Kim E. Hummer.
The ...
This release is available in French.
Montreal May 5, 2011 – Children whose mother or father is affected by bipolar disorder may need to keep their stress levels in check. A new international study, led by Concordia University, suggests the stress hormone cortisol is a key player in the mood disorder. The findings published in Psychological Medicine, are the first to show that cortisol is elevated more readily in these children in response to the stressors of normal everyday life.
"Previous research has shown that children of parents with bipolar disorder are four times ...
WASHINGTON -- How can some people respond to a question without answering the question, yet satisfy their listeners? This skill of "artful dodging" and how to better detect it are explored in an article published by the American Psychological Association.
People typically judge a speaker with the goal of forming an opinion of the speaker, which can make them susceptible to dodges, according to the study published online in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. Limited attention capacity is another reason people fall for dodges, said the authors, citing a previous ...
A Swedish research team partly consisting of researchers from Uppsala University followed a group of prostate cancer patients in the Nordic region for 15 years. The study found, among other things, that surgery reduces the risk that men with prostate cancer (even those with low-risk tumours) will die within 15 years. The results were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers followed Swedish, Finnish and Icelandic prostate cancer patients. Radical prostatectomy (surgical removal of the prostate gland) was performed on 347 randomly chosen ...
Researchers from the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology at the University of Vienna and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences used a quantum mechanical system in the laboratory to simulate complex many-body systems. This experiment, which is published in Nature Physics, promises future quantum simulators enormous potential insights into unknown quantum phenomena.
Already the behavior of relatively small quantum systems cannot be calculated because quantum states contain much more information than their ...
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, after isolating normal stem cells that form the developing placenta, have given them the same properties of stem cells associated with an aggressive type of breast cancer.
The scientific first opens the door for developing novel targeted therapies aimed at triple negative breast cancer. Known also as TNBC, this is a highly recurrent tumor that spreads aggressively beyond its original site in the breast and carries a poor prognosis for patients who have it.
The study ...