(Press-News.org) Older, sicker heart-transplant recipients are significantly more likely to be alive a year after their operations if they have their transplants at hospitals that do a large number of them annually new Johns Hopkins research suggests. These patients fare less well at low-volume centers, the research shows.
The findings, to be presented May 9 at the American Association of Thoracic Surgeons' annual meeting in Philadelphia, add more support to the notion that patients do better when treated at medical centers that handle a higher number of cases similar to theirs.
"There's growing evidence throughout medicine and surgery that the volume of cases done at a given medical center has an impact on outcomes," says George J. Arnaoutakis, M.D., a general surgery resident at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the study's leader. "Transplant teams more familiar with a procedure do a better job than those that only do a handful each year."
The researchers combed through United Network of Organ Sharing (UNOS) data from all of the heart transplants done in the United States between January 2000 and December 2009. Using that information, the researchers assigned each of the 17,211 patients a risk score, which took into account known risk factors for complications and/or death after heart transplant, including age, race, cause of heart failure, bilirubin and creatinine levels and whether they had been on life support. The higher the score, the greater risk of death one year after transplantation.
They also ranked the 141 hospitals where the transplants took place into low-, medium- and high-volume centers. Low-volume centers did fewer than six heart transplants a year, while high-volume centers performed more than 15 annually. Just 5.4 percent of heart transplants took place at low-volume centers over that period, while more than 67 percent were done at high-volume centers.
High-risk patients transplanted at low-volume centers had a 67 percent increased risk of death after one year compared with high-risk patients transplanted at high-volume centers. Severity of condition alone did not account for the difference, which diminished among low-risk patients.
"Patients at high risk of mortality should probably only be transplanted at high-volume centers," Arnaoutakis says.
Arnaoutakis cautions that the findings should not be seen as an indictment of the training and skill of surgeons at low-volume centers. Rather, he says, the systems and infrastructure of a center doing few heart transplants are most likely a bigger factor.
"There are certain processes that may be better performed at regional centers of excellence doing more of a certain procedure," he says. "People talk about it with airline pilots — only at 10,000 hours of flying are they considered expert at flying. The experience of a center can be discussed in similar terms."
Nurses at a high-volume center, for example, may be quicker to recognize complications and intervene earlier, he says. Operating room teams might be better prepared to handle a transplant that occurs in the middle of the night.
"The more you do it, the better you become at doing it," Arnaoutakis says.
INFORMATION:
Other Johns Hopkins researchers contributed to this study, including Timothy J. George, M.D.; Stuart D. Russell, M.D.; Ashish S. Shah, M.D.; John V. Conte, M.D.; and Eric S. Weiss, M.D., M.P.H.
For more information:
http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/transplant/Programs/heart/
END
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 9, 2011 – Unrealistic and uninformed media portrayals of weight not only can negatively influence individual behavior, but can impact how policymakers approach issues of weight and health. The result, according to experts from the Strategies to Overcome and Prevent (STOP) Obesity Alliance and the National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA), is a continued belief that these issues are largely a matter of personal responsibility and that little can or should be done in policy to address them.
Susan Dentzer, editor of Health Affairs, moderated a panel ...
Joe Altman, president of Altmans Winnebago, announced today that the Altman family has made the difficult decision to wind down their dealership operations beginning today, May 6, 2010.
In 1971, Altmans opened its doors in Baldwin Park, California and grew to become a trusted fixture within the RV industry.
"Our family has experienced 40 years of great and challenging times," notes Altman, "but current market conditions suggest it's time to end this chapter of our business."
Over the next month or so, Altmans will be liquidating the remaining ...
Los Angeles, CA (APRIL XX, 2011) Despite contrary belief, reducing unemployment in locations with active insurgencies does not decrease the rate of insurgent attacks against government and allied forces. Additionally, it was found that unemployment in these same locations also had no impact in reducing the deaths of civilians.
A new study released in the recent issue of the Journal of Conflict Resolution (published by SAGE) found that there is no correlation that aiding countries with high rates of unemployed young men leads to a decrease in political violence. Additionally, ...
New Haven, Conn. —Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in South Korea affect an estimated 2.64% of the population of school-age children, equivalent to 1 in 38 children, according to the first comprehensive study of autism prevalence using a total population sample. The study—conducted by Young-Shin Kim, M.D., of the Yale Child Study Center and her colleagues in the U.S., Korea and Canada—identifies children not yet diagnosed and has the potential to increase autism spectrum disorder prevalence estimates worldwide.
ASDs are complex neurobiological disorders that inhibit a ...
ASG Dine, a leading distributor of strategic risk management and employee benefits solutions for the restaurant and food service industries, has announced an exclusive partnership with Walmart to offer discounted prescription pharmaceuticals to our customers and corporate partners.
The program provides a company's employees with access to more than 300 different prescription pharmaceuticals for just $4/prescription with a 30-day supply, and only $10/prescription with a 90-day supply. Prescription drugs that are currently not included in the program will still maintain ...
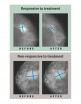
In the first large trial of its kind in the United States, researchers have shown that estrogen-lowering drugs can shrink tumors and reduce mastectomy rates for patients with stage 2 or 3 breast cancer.
Patients with these larger breast tumors have two options, says Matthew J. Ellis, MD, PhD, of Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and principal investigator of the trial conducted by the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group. "One option is to undergo mastectomy. The second is to receive medication before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor ...
215 Racing Inc. an American Based company, is proud to announce the exclusive rights to build the Lamborghini Indomable Concept created by Design 4 Motion. This design was created by Daniel Chinchilla under the Masters Program sponsored by Lamborghini. The design is a perfect fit for the first offering of 215 to the supercar market.
The car will be built by the Sub-company MOSTRO DI-POTENZA and will be renamed The SF22. This name comes from the design influence of the F22 fighter jet, and is incorporated in the car. SF stands for Street Fighter and only 50 of these cars ...
A new, promising marker for diagnosing prostate cancer has been discovered by Uppsala researchers with the aid of a unique method developed at the Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology. The study, being published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, PNAS, can lead to more reliable diagnoses and fewer unnecessary operations.
The PSA marker used for diagnosing prostate cancer today has been criticized for false positive responses, leading to unnecessary operations. There is therefore great interest in finding new and better ...
BOSTON – More than a third of Americans use some form of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) and that number continues to rise attributed mostly to increases in the use of mind-body therapies (MBT) like yoga, meditation and deep breathing exercises.
Prior research suggests that MBT, while used by millions of patients, is still on the fringe of mainstream medical care in America. New research suggests that attitudes are changing.
In a study from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Harvard Medical School, researchers found that one in 30 Americans ...
Scientists at Royal Holloway, University of London and the University of Leicester have discovered animals searching for food do not stick to a complicated pattern of movement as previously thought but tend to wander about randomly.
It was previously believed that when searching for food, animals move in very peculiar way called a Lévy flight where they move small distances most of the time, but occasionally move a very long distance.
This idea was based on studies in which many animals, like albatrosses or sharks, were tracked. However scientists have been analysing ...