(Press-News.org) Scientists have for the first time estimated the physical footprint of human activities on the deep seafloor of the North East Atlantic. The findings published in the journal PLoS ONE reveal that the area disturbed by bottom trawling commercial fishing fleets exceeds the combined physical footprint of other major human activities considered.
The deep seafloor covers approximately 60% of Earth's surface, but only a tiny fraction of it has been studied to date. Yet as technology advances and resources from relatively shallow marine environments are depleted, human impacts on the deep seafloor are likely to increase.
"Information on the location and spatial extent of human activities affecting the deep-sea environment is crucial for conservation of seafloor ecosystems and for governance and sustainable management of the world's oceans," said Angela Benn of the National Oceanography Centre, who led the new study.
The researchers focused on the OSPAR maritime area of the North East Atlantic, where human activities are particularly intense. The area covers over eleven million square kilometres, about 75 percent of which is deeper than 200 metres, and includes important fishing grounds such as those of Hatton and Rockall.
Using available data for the year 2005, they mapped and estimated the spatial extent of intentional human activities occurring directly on the seafloor as well as structures and artefacts present on the seafloor resulting from past activities.
They looked exclusively at the physical footprint rather than the consequential ecological effects of disturbance, contamination and pollution, which are harder to ascertain. One difficulty that they faced was that of accessing data on human activities that was accurate, up to date and comprehensive, and in a suitable format for analysis.
"Some governments, public organisations and private companies were far more forthcoming with information than others," explained Benn. "Significant improvements are needed in data collection and availability, and this requirement needs to be built into international conventions and treaties with a legal framework in place to ensure informed environmental management."
Despite difficulties and various uncertainties, the researchers' assessment suggests that, although now banned, previously dumped radioactive waste, munitions and chemical weapons together have the lowest physical footprint of the human activities considered, although they do not consider potential dispersal after leakage.
Non-fisheries marine scientific research also has a relatively small footprint, whereas those of fisheries marine scientific research, telecommunication cables and the oil and gas industry are moderate. However, even on the lowest estimates, the spatial extent of bottom trawling is at least ten times that for the other activities assessed, with a physical footprint greater than that of all the others combined.
The study estimated the total area of physical imprint in 2005 to be around 28,000 km2. However many human activities in the deep sea are concentrated in certain areas, particularly in shallower depths between 200 m and 1500 m, and in particular habitats which become disproportionally impacted. The OSPAR area comprises many different habitats each with different and diverse ecosystems. The percentage impact in each of these habitats would provide important information but unfortunately there is virtually no detailed seabed mapping to provide this information.
As demands drive human activities ever deeper the imprint will become more widespread. "Consequently," argues Benn, "there needs to be a much greater understanding of the relative impacts of human activities on the deep seafloor, and in particular how these activities affect seafloor ecosystems and biodiversity."
INFORMATION:
Human impacts on the deep seafloor
2010-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Global fisheries research finds promise and peril
2010-09-14
Global fisheries, a vital source of food and revenue throughout the world, contribute between US$225-$240 billion per year to the worldwide economy, according to four new studies released today. Researchers also concluded that healthier fisheries could have prevented malnourishment in nearly 20 million people in poorer countries.
This first comprehensive, peer-reviewed estimate of the global economic contribution of fisheries was published online today in four papers as part of a special issue of the Journal of Bioeconomics.
This research, conducted by the University ...
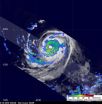
GOES-13 sees system 92L looking more like a tropical depression
2010-09-14
GOES-13 captured a look at System 92L this morning as it continues moving through the central Caribbean, and it's looking more and more like a tropical depression.
As the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite called GOES-13 satellite keeps relaying data to NOAA (who manages the satellite) and the NASA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., the images created by the NASA GOES Project reveal that System 92L appears to be taking on the appearance of a tropical depression. In the imagery captured today, Sept. 14 at 1340 UTC (9:40 ...
Neuralstem stem cells survive and differentiate into neurons in rats with stroke
2010-09-14
ROCKVILLE, Maryland, September 14, 2010 – Neuralstem, Inc. (NYSE Amex: CUR) announced that its spinal cord stem cells survived in rat brains affected by stroke and differentiated predominantly into neurons. The transplanted animals showed significant improvement in some motor skill and strength measurements. The study entitled, "Intracerebral Implantation of Adherent Human Neural Stem Cells To Reverse Motor Deficits in Chronic Stroke Rats," was presented earlier today by senior study author, Dr. Shinn-Zong Lin, M.D., Ph.D., at the Stem Cells USA & Regenerative Medicine ...
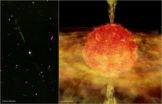
Enigmatic star devours companion; possibly pregnant with second-generation planets
2010-09-14
An astronomer may have caught a cannibalistic star in the act of devouring a companion and making a second generation of exoplanets from the resulting orbiting disk.
Using data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, Joel Kastner, professor at Rochester Institute of Technology, has found evidence that a variable star in the constellation of Pisces, BP Piscium, is not the young star it appears to be, but is more likely a one billion-year-old red giant that has gobbled up a star or planet in its vicinity.
The star's extreme properties have puzzled astronomers since Kastner ...
International Fertility Societies call for harmonization of cross-border reproductive care standards
2010-09-14
"The IFFS's 'Surveillance 2010' report, compiled by Professor Ian Cooke and published on 14 September 2010, illustrates this for over 100 countries. The survey highlights how widely assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are being used and how different cultures are regulating services in different ways. In most countries there is no state or insurance support, so these services are costly and frequently beyond the reach of many families. In some countries access to donor gametes is denied or supply is limited.
To address the safety of patients that seek treatment abroad, ...
September/October 2010 Annals of Family Medicine tip sheet
2010-09-14
Low Adherence with Regular Fecal Occult Blood Test Screening Among Insured Patients
In a large U.S. health plan, nearly one-half of patients who initiated biennial fecal occult blood test (FOBT) screening did not adhere to subsequent colorectal screening in the ensuing 2-year period, compromising the effectiveness of the screening endeavor which hinges on regular screening. Analyzing data on 11,110 patients enrolled in a Washington State health plan who completed an FOBT during the baseline period (2000-2001), researchers found 47 percent received no colorectal screening ...
Farm management choice can benefit fungi key to healthy ecosystems
2010-09-14
Farming practices have a significant impact on the diversity of beneficial microbial fungi known to play important roles in crop productivity, soil recovery and maintenance of healthy ecosystems, according to new research published today (14 September 2010) in the journal Environmental Microbiology. The conclusions could have important implications for the way humans manage the agricultural landscape and tackle food security issues.
The study was led by Dr Christopher van der Gast at the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH), UK and Dr Gary Bending from the University ...
Childhood cancer survivors show sustained benefit from common ADHD medication
2010-09-14
A medicine widely used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also provides long-term relief from the attention and behavior changes that affect many childhood cancer survivors, according to a multicenter trial led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators.
Researchers reported that one year after starting the drug methylphenidate, young cancer survivors scored better on tests of sustained attention and other measures of attention, social skills and behavior than did a similar group of unmedicated survivors. While taking methylphenidate, ...
Igor now a Category 4 hurricane with icy cloud tops and heavy rainfall
2010-09-14
NASA Satellites have noticed two distinct features in Igor that both indicate how powerful he has become, icy cold, high cloud tops and very heavy rainfall. NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites have provided that insight to forecasters who are predicting Igor's next move as a powerful Category 4 Hurricane.
Last week, Igor was a tropical storm who faded into a tropical depression. The National Hurricane Center had forecast that over the weekend Igor would approach more favorable conditions (low wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures) causing it to strengthen into a hurricane ...
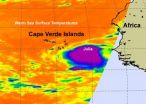
NASA sees Tropical Storm Julia born with strong thunderstorms and heavy rainfall
2010-09-14
Tropical Depression 12 was born in the far eastern Atlantic Ocean yesterday, Sept. 12 and two NASA satellites saw factors that indicated she would later strengthen into Tropical Storm Julia. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed strong convection in its center that powered the storm into tropical storm status by 11 p.m. EDT. NASA's TRMM satellite indicated very heavy rainfall from that strong area of convection.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite gives scientists and meteorologists clues about how a tropical ...