(Press-News.org) New research from North Carolina State University will help medical examiners and others identify human remains of those killed during the recent earthquake in Chile, as well as the bodies of the "disappeared" who were killed during the Pinochet administration.
"We have developed population-specific identification criteria for the Chilean population, which will help us determine the stature and biological sex of skeletal remains," says Dr. Ann Ross, an associate professor of sociology and anthropology at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the research.
"My vision for this work is to help identify the remains of victims of political violence that occurred under the Pinochet regime," says Ross, whose mother is Chilean. "This will also help in contemporary body identification efforts in Chile. For example, in the event of a mass fatality – such as the February earthquake in Chile – this will help authorities identify recovered remains."
For the past decade, forensic researchers – such as Ross – have been developing population-specific identification criteria that account for variations in height, build and other characteristics that can be critical when attempting to identify human remains. "This is important," Ross explains, "because populations vary. Identifying characteristics such as height and sex can be significantly different from population to population."
For this study, the researchers evaluated remains from a 20th century Chilean cemetery in order to accurately characterize Chilean skeletal features. They were then able to develop stature criteria that can help researchers arrive at an accurate height for an individual based on an analysis of his or her long bones, including the femur and tibia.
The researchers were able to develop criteria to determine a body's biological sex based on measurements of the articulation of the upper arm bone (the humerus) and the femur.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "New identification criteria for the Chilean population: Estimation of sex and stature," was co-authored by Maria Jose Manneschi of the Universidad de Chile. The paper will be published in a forthcoming issue of Forensic Science International. The research was made possible by support from NC State.
Research will help ID bodies left behind by Chilean earthquake, Pinochet regime
2010-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hybrids as city runabouts, natural gas fueled cars for the country
2010-09-14
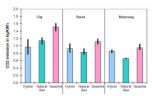
Hybrid cars and those fuelled by natural gas produce significantly less carbon dioxide (CO2) than equivalent vehicles running on gasoline. In the course of a study undertaken on behalf of the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN), the results of which were recently published, Empa has investigated the CO2 emission behavior of current hybrid cars. A comparison with gasoline and natural gas fuelled vehicles concludes that hybrid vehicles are the cleanest during inner-city driving whilst natural gas fuelled cars do best on the motorway. When driven in rural areas, ...
From chemical engineering to the catwalk
2010-09-14
Seamless fabric that can be sprayed on to skin and other surfaces to make clothes, medical bandages and even upholstery will be demonstrated this Thursday, in advance of the Science in Style spray-on fashion show next week at Imperial College London.
Dr Manel Torres is a Spanish fashion designer and academic visitor at Imperial, where he has collaborated with Paul Luckham, Professor of Particle Technology from the Department of Chemical Engineering, to create a seamless material called Fabrican Spray-on fabric that can be sprayed directly onto the body, using aerosol ...
Fla. med student study reveals disparity of skin cancer knowledge -- Ben-Gurion U. study
2010-09-14
MIAMI -- September 14, 2010 --There is a significant disparity between knowledge and attitudes on the dangers of skin cancer among male and female medical students in Florida according to a new study by a joint team of researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. The study was published in the American Medical Association's Archives of Dermatology.
While their overall knowledge was judged to be satisfactory there was a significant difference between male and female students' knowledge survey scores: 93.1 percent ...
Researchers build 'artificial ovary' to develop oocytes into mature human eggs
2010-09-14
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Researchers at Brown University and Women & Infants Hospital have invented the first artificial human ovary, an advance that provides a potentially powerful new means for conducting fertility research and could also yield infertility treatments for cancer patients. The team has already used the lab-grown organ to mature human eggs.
"An ovary is composed of three main cell types, and this is the first time that anyone has created a 3-D tissue structure with triple cell line," said Sandra Carson, professor of obstetrics and gynecology ...
VCU study: Team uncovers possible risk gene for schizophrenia
2010-09-14
RICHMOND, Va. (Sept. 14, 2010) – An international team of researchers has identified a risk gene for schizophrenia, including a potentially causative mutation, using genome-wide association data-mining techniques and independent replications.
The results of the research, led by Xiangning Chen, Ph.D., associate professor of psychiatry and human and molecular genetics in Virginia Commonwealth University's School of Medicine and the Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, and Kenneth S. Kendler, M.D., professor of psychiatry and human and molecular genetics ...
Long-term stenting of aortic coarctation yields 77 percent success rate
2010-09-14
Researchers from the Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium (CCISC) who evaluated the intermediate and long-term results of stent implantation for aortic coarctation found that cumulative intermediate success was 86%, and cumulative long-term success was 77%. Results of this study appear in the October issue of Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions.
Coarctation, or narrowing, of the aorta, restricts blood flow to the lower extremities ...
Chandra finds evidence for stellar cannibalism
2010-09-14
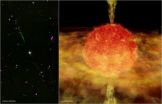
Evidence that a star has recently engulfed a companion star or a giant planet has been found using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. The likely existence of such a "cannibal" star provides new insight into how stars and the planets around them may interact as they age.
The star in question, known as BP Piscium (BP Psc), appears to be a more evolved version of our Sun, but with a dusty and gaseous disk surrounding it. A pair of jets several light years long blasting out of the system in opposite directions has also been seen in optical data. While the disk and jets ...
Molecule identified that increases survival of stomach cancer patients
2010-09-14
"The high presence of microRNA 451 enhances the response to treatment with chemo-radiotherapy and increases the survival of patients with stomach cancer", explained Dr. Jesús García-Foncillas, chief researcher of the Pharmacogenomics Laboratory at the Applied Medical Research Centre (CIMA) and Director of Oncology at the University Hospital of Navarra. This was one of the results presented at the IV Congress of the Spanish Society for Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomic, recently held at CIMA.
Pharmacogenetics studies the genetic bases determining the response of an ...
New current meter provides answers for lobster industry, oyster farmers, scientists
2010-09-14
NARRAGANSETT, R.I. – September 14, 2010 – When a federal fisheries scientist sought to learn how ocean currents affect the catch rate of lobsters, he turned to a University of Rhode Island oceanographer who had developed an innovative and inexpensive meter for measuring currents near the bottom of bays, rivers and other shallow waters.
So did aquaculture farmers in Rhode Island looking to identify the best site for farming oysters, Cape Cod officials interested in understanding tidal fluctuations in Waquoit Bay, and students at Cohasset (Mass.) High School studying circulation ...
Why 'scientific consensus' fails to persuade
2010-09-14
Suppose a close friend who is trying to figure out the facts about climate change asks whether you think a scientist who has written a book on the topic is a knowledgeable and trustworthy expert. You see from the dust jacket that the author received a Ph.D. in a pertinent field from a major university, is on the faculty at another one, and is a member of the National Academy of Sciences. Would you advise your friend that the scientist seems like an "expert"?
If you are like most people, the answer is likely to be, "it depends." What it depends on, a recent study found, ...