(Press-News.org) A team of scientists from the University of Sheffield and Bangor University have used a computer climate model to study how freshwater entering the oceans at the end of the penultimate Ice Age 140,000 years ago affected the parts of the ocean currents that control climate.
A paper based on the research, co-authored by Professor Grant Bigg, Head of the University of Sheffield's Department of Geography, his PhD student Clare Green, and Dr Mattias Green, a Senior Research fellow at Bangor University's School of Ocean Sciences, is currently featured as an Editor's Highlight in top US journal, Paleoceanography. The study is the first of this kind for the time period.
The research found that freshwater entering the ocean from melting ice sheets can weaken the climate controlling part of the large-scale ocean circulation, with dramatic climate change as a consequence. During the period of the study, the experts noted that the global temperature dropped by up to two degrees over a few centuries, but changes were not uniform over the planet, and it took a long time for the climate to recover after the ice sheets had melted completely.
The team argues that it is not only the volume of freshwater being released from the melting ice sheet which is important but also the state of the freshwater: icebergs act to reduce the ocean circulation less than meltwater, but the effects of icebergs last for longer periods of time. The effect is similar to the difference between adding very cold water to a drink or adding an ice cube or two.
The study also shows that at the end of the more recent Ice Age 20,000 years ago, the ocean circulation was more sensitive to ice sheet collapses than during the earlier period.
Professor Grant Bigg, Head of the University of Sheffield's Department of Geography, said: "An important component of the work is that it shows that the impact of freshwater releases from past, or future, ice masses depends critically on the form - whether fresh water or icebergs - and the location of the release.
"The Arctic has been surrounded by extensive glaciations several times in the past and this study has shown that large-scale changes in such Arctic ice sheets could affect the climate in places far from the release site. Our work also suggests that the Pacific Ocean may have been more sensitive to major changes in past glaciations than previously realised. We plan to investigate this possibility more in the future."
Dr Mattias Green from Bangor University, added: "With meltwater- similar to adding water to your drink, the water spreads out quickly and has an immediate effect, but it is also absorbed quickly into the rest of the ocean. In a similar way to your ice cube, the icebergs drift along and melt more slowly. This means the immediate impact is weaker, but they are there for a longer time and distribute the water over a larger area.
"Our results lead us to conclude that a future ice sheet collapse, that might happen in Antarctica or Greenland, would have climatic consequences, but the exact impact needs to be evaluated in each case."
INFORMATION:
END
Vitamin D is important for optimal reproductive function in both animals and humans. It has long been known that serum vitamin D level is important for reproductive function in various animals, but now researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Copenhagen University Hospital have shown that this relationship can also be demonstrated in humans.
A new study conducted in 300 normal men showed a positive correlation between the percentage of motile sperm and serum vitamin D levels. The study was recently published in the scientific journal Human Reproduction, and showed ...
Groundbreaking research has shown a quantum atom has been tracked inside a living human cell and may lead to improvements in the testing and development of new drugs.
Professor Lloyd Hollenberg from the University of Melbourne's School of Physics who led the research said it is the first time a single atom encased in nanodiamond has been used as a sensor to explore the nanoscale environment inside a living human cell.
"It is exciting to see how the atom experiences the biological environment at the nanoscale," he said.
"This research paves the way towards a new class ...
Scientists have discovered an important enzyme molecule that may prevent fatal cardiac disorders associated with cardiac hypertrophy – the leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.
Cardiac hypertrophy is a disease of the heart muscle where a portion of the tissue is thickened without any obvious cause. It is commonly linked to high blood pressure (hypertension) and excessive exercises and results in a shrinking of the heart chamber and a reduction of its blood-pumping volume.
The condition is also associated with fatal cardiac disorders related to irregular ...
Research led by the University of Warwick's Centre for Competitive Advantage in the Global Economy has found that not only did the events of 9/11 produce an immediate shift in favour of the Republican party among new young US voters but that shift persisted into later years. The research shows that party strategists should focus on winning over voters when they are young.
The researchers Professor Sharun Mukand, from the University of Warwick, and Professor Ethan Kaplan, from Stockholm University and the University of Maryland, looked at whether the mere act of registering ...
For many patients with the hepatitis C virus (HCV), direct antiviral agents (DAA) offer a potential cure for the disease. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved two new DAAs, telaprevir and boceprevir, and with that clinicians must now decide who should be the first to receive this treatment. Discussion of this timely topic is now available in the June issue of Hepatology, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates up to 170,000 million ...
Scientists are reporting development and successful testing of a promising new way of using a troublesome byproduct of the global steel industry as raw materials for bricks that can be used in construction projects. Their study appears in ACS' Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
In the report, Ana Andrés and colleagues note that steel mills around the world produce vast quantities of waste dust each year — 8 million – 12 million tons in the United States, for instance, and 700,000 tons in the European Union countries. The dust often is converted into a rock-like ...
Female drink-drivers are more likely to be older, better-educated and divorced, widowed or separated, research has shown.
The study by academics at The University of Nottingham found that emotional factors and mental health problems were common triggers in alcohol-related offences committed by women.
And they also discovered that rehabilitation programmes that force women to face the consequences of their crime can intensify their feelings of guilt and shame, leading them to turn to alcohol and increasing the risk that they will re-offend.
In a paper to be published ...
In the first study of its kind on K-12 Christian education in North America, University of Notre Dame sociologist David Sikkink, in partnership with Cardus – a public policy think tank – found that while Protestant Christian school graduates show uncommon commitment to their families and churches, donate more money than graduates of other schools, and divorce less, they also have lower incomes, less education, and are less engaged in politics than their Catholic and non-religious private school peers.
The two-year study surveyed a representative sample of religious school ...
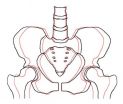
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – By the age of 20, most people have reached skeletal maturity and do not grow any taller. Until recently it was assumed that skeletal enlargement elsewhere in the body also stopped by age 20.
But a new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found evidence that, even though you're not getting taller anymore, the pelvis ("hipbones") does continue to widen as people advance in age from 20 years to 79 years.
"I think it's a fairly common human experience that people find themselves to be wider at the age of 40 or 60 ...
This press release is available in French.Montreal, May 25, 2011 – Birds do it. Bees do it. Fish, lobsters, frogs and lizards do it, too. But when it comes to securing a mate in the animal world, variety is literally the spice of life.
A group of scientists from Simon Fraser University, Concordia University and Dalhousie University has found flexibility in mating rituals is the key to reproductive success when males outnumber females.
The research team pored through hundreds of investigations on mating trends in mammals, insects, fish, crustaceans, amphibians and reptiles. ...