(Press-News.org) Since the Industrial Revolution, over half of all the CO2 produced by burning fossil fuels has been absorbed by the ocean, making pH drop faster than any time in the last 650,000 years and resulting in ocean acidification. Recent studies have shown that this causes fish to lose their sense of smell, but a new study published today in Biology Letters shows that fish hearing is also compromised.
Working with Professor Philip Munday at James Cook University, lead author Dr Steve Simpson of the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Bristol reared larvae straight from hatching in different CO2 environments.
"We kept some of the baby clownfish in today's conditions, bubbling in air, and then had three other treatments where we added extra CO2 based on the predictions from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change for 2050 and 2100," Dr Simpson said.
After 17-20 days rearing, Dr Simpson monitored the response of his juvenile clownfish to the sounds of a predator-rich coral reef, consisting of noises produced by crustaceans and fish.
"We designed a totally new kind of experimental choice chamber that allowed us to play reef noise through an underwater speaker to fish in the lab, and watch how they responded," Dr Simpson continued. "Fish reared in today's conditions swam away from the predator noise, but those reared in the CO2 conditions of 2050 and 2100 showed no response."
This study demonstrates that ocean acidification not only affects external sensory systems, but also those inside the body of the fish. The ears of fish are buried deep in the back of their heads, suggesting lowered pH conditions may have a profound impact on the entire functioning of the sensory system.
The ability of fish to adapt to rapidly changing conditions is not known. Dr Simpson said: "What we have done here is to put today's fish in tomorrow's environment, and the effects are potentially devastating. What we don't know is whether, in the next few generations, fish can adapt and tolerate ocean acidification. This is a one-way experiment on a global scale, and predicting the outcomes and interactions is a major challenge for the scientific community."
### END
Ocean acidification leaves clownfish deaf to predators
2011-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCI researchers find link between environment and genetics in triggering MS
2011-06-01
Irvine, Calif. — Environmental and inherited risk factors associated with multiple sclerosis – previously poorly understood and not known to be connected – converge to alter a critical cellular function linked to the chronic neurologic disease, researchers with the UC Irvine Multiple Sclerosis Research Center have discovered.
The findings, which appear in the online, open-access journal Nature Communications, suggest that a unifying mechanism may be responsible for multiple sclerosis and point to therapies personalized according to genetic factors.
"MS results from ...
Steady relationships reduce amphetamine's rewarding effects
2011-06-01
Long-term relationships make the commonly abused drug amphetamine less appealing, according to a new animal study in the June 1 issue of The Journal of Neuroscience. The findings suggest that social bonds formed during adulthood lead to changes in the brain that may protect
against drug abuse.
Prairie voles are rodents that form lifelong bonds with mating partners. In the new study, researchers directed by Zuoxin Wang, PhD, of Florida State
University, found that male voles in established relationships displayed less interest ...
Association between biomarkers and disease often overstated, Stanford researcher finds
2011-06-01
STANFORD, Calif. — More than two dozen widely cited studies linking genes or other "biomarkers" to specific diseases vastly overstate the association, according to new research from an expert in scientific study design at the Stanford University School of Medicine. As a result, clinicians may be making decisions for their patients based on inaccurate conclusions not supported by other, larger studies.
The widely cited studies include one linking the BRCA1 mutation with colon cancer, another that links levels of C-reactive protein in the blood with cardiovascular disease ...
Nanoscale waveguide for future photonics
2011-06-01
The creation of a new quasiparticle called the "hybrid plasmon polariton" may throw open the doors to integrated photonic circuits and optical computing for the 21st century. Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have demonstrated the first true nanoscale waveguides for next generation on-chip optical communication systems.
"We have directly demonstrated the nanoscale waveguiding of light at visible and near infrared frequencies in a metal-insulator-semiconductor device featuring low loss and broadband ...
Mouse virus erroneously linked to chronic fatigue syndrome, UCSF collaborative study finds
2011-06-01
Two years ago, a widely publicized scientific report plucked an old mouse virus out of obscurity and held it up as a possible cause of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. According to a new study published today by a group of researchers in California, Wisconsin and Illinois, that report was wrong.
The mouse virus is not the culprit in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, said University of California, San Francisco Professor Jay A. Levy, MD, the senior author on the study, published this week by the journal Science.
"There is no evidence of this mouse virus in human blood," said Levy, ...
Noninvasive wireless near-infrared device provides reliable diagnosis of bladder dysfunction
2011-06-01
A cell phone-sized, wireless near-infrared device is as reliable as the current "gold standard" invasive tests in determining bladder disease, according to a study by researchers at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver Coastal Health and the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI).
The new physiologic information gathered through near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) could also advance treatment that tackles the root causes of urinary incontinence, says the research team.
Published in the current issue of the International Journal of Spectroscopy, the study is ...
Good guy or bad guy? Diagnosing stomach disease in pet reptiles
2011-06-01
Although known for over a century, cryptosporidiosis was believed to be an extremely rare condition and it only gained attention with the discovery that it can affect humans, especially immune-compromised individuals. It is caused by a single-cell parasite, one of a family known as cryptosporidia. Some cryptosporidia also infect reptiles, where after a sometimes lengthy incubation period they cause gastrointestinal problems even in otherwise healthy individuals. The condition is usually persistent and is presently impossible to cure. It is therefore important to minimize ...
Breaking the fracture cycle through effective and coordinated models of care
2011-06-01
A prior fracture at least doubles a patient's future fracture risk – yet numerous studies from across the world have found that healthcare systems fail to respond to the first fracture to prevent future fractures. Professor Cyrus Cooper, chair of the Committee of Scientific Advisors of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and director of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit, University of Southampton in the UK stated, "Studies from the UK, USA and Australia have reported that 45% or more of today's hip fracture patients have a prior fracture history. Healthcare ...
Scientists crack the spiders' web code
2011-06-01
Decorative white silk crosses are an ingenious tactic used by orb-weaving spiders to protect their webs from damage, a new study from the University of Melbourne has revealed.
The team, led by Dr Andre Walter and Professor Mark Elgar from the University of Melbourne's Department of Zoology, found that orb-weaving spiders respond to severe damage to their webs by building bigger silk crosses, but if the damage is mild they don't bother adding extra decoration.
Professor Mark Elgar said web damage is costly for spiders as a lot of nutritional resources are required to ...
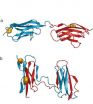
Similarities cause protein misfolding
2011-06-01
A large number of illnesses stem from misfolded proteins, molecules composed of amino acids. Researchers at the University of Zurich have now studied protein misfolding using a special spectroscopic technique. Misfolding, as they report in Nature, is more frequent if the sequence of the amino acids in the neighboring protein domains is very similar.
Proteins are the main molecular machines in our bodies. They perform a wide range of functions, from digesting and processing nutrients, converting energy and aiding cell structure to transmitting signals in cells and the ...