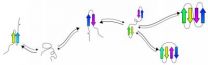
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from Columbia Engineering, the Italian National Research Council, Princeton University, University of Missouri, and University of Nijmegen (Netherlands) has developed an artificial semiconductor structure that has superimposed a pattern created by advanced fabrication methods that are precise at the nanometer scale. The pattern is similar to the honeycomb lattice that occurs in graphene. The device, called "artificial graphene" (AG), simulates quantum behavior of strongly interacting electrons. The research team sees the AG-device as a first step towards the realization of an innovative class of solid-state quantum simulators to explore fundamental quantum physics.
The research is reported in the June 3rd, 2011, issue of Science (http://www.sciencemag.org.ezproxy.cul.columbia.edu/content/332/6034/1176.full.pdf). The work is co-authored by Vittorio Pellegrini and Marco Polini of the NEST Laboratory of Istituto Nanoscienze-Cnr and Scuola Normale Superiore of Pisa; and by Aron Pinczuk, Applied Physics Professor at The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science and Physics Professor at the School of Arts and Sciences, Columbia University; along with researchers from the Universities of Nijmegen, Missouri, and Princeton.
In order to study quantum phenomena that are difficult to be directly observed, scientists use artificial ad-hoc designed systems — quantum simulators — that can be controlled and manipulated in the laboratory. Researchers have only just begun to develop quantum simulators using different technologies. The AG-device is the first quantum simulator to be based on a semiconductor material that is designed with the goal of uncovering quantum behavior of electrons.
Phenomena such as high-temperature superconductivity, ferromagnetism, and exotic states of matter such as quantum Hall liquids and spin liquids originate from mutual interactions among many electrons. Exact calculations of the behavior of these complex systems are an impossible task even for the more sophisticated and powerful computers. Quantum simulators help bypass the problem by replacing the "uncomputable" quantum system with a controllable artificial one that is able to emulate the dynamics of the original system.
"Quantum simulators based on novel artificial semiconductor structures are at the crossroads of quantum science and innovative technologies," says Aron Pinczuk, Applied Physics Professor at The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science and Physics Professor at the School of Arts and Sciences, Columbia University. "While the frontiers of quantum physics are being explored with giant accelerators, in this branch of condensed matter science we employ advanced methods that expand the state-of-the-art in growth and processing of semiconductors. We could describe our work on quantum simulators as 'probing quantum weirdness in a nano-nut-shell.'"
The simulator developed by the researchers consists of a honeycomb lattice realized on the surface of a Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) heterostructure using advanced nanofabrication methods. The artificial honeycomb lattice structure replicates that of graphene, a material in which electrons behave in a peculiar way because of the crystal-lattice geometry. With the ability to modify key parameters such as the lattice constant of the artificial lattice, the researchers are in the position to explore different regimes of electron-electron interactions in graphene-like systems.
Vittorio Pellegrini and Marco Polini from NEST Laboratory of Istituto Nanoscienze-Cnr and Scuola Normale Superiore note that the AG-device has been tested with a "first run" trial that generated an unexpected peculiar quantum state. "The early data we collected are quite promising and show the great potential our device has," they say. "The next step in this research is a fine-tuning of the AG-device". The researchers are excited about the potential of creating venues for the uncovering of novel quantum states that could, eventually, lead to new device concepts and eventually to an array of applications, for instance, in advanced information processing or in cryptography.
Pinczuk added that they hope next to achieve new breakthroughs through the creation of smaller nanofabricated structures reaching limits in which individual units in patterns have lengths of five nanometers. "This is a state-of-the-art that should open access to physics and materials science that has not yet been explored!"
###
Research at two of the U.S. universities has been supported by grants from the National Science Foundation.
NEST Cnr Nano and Scuola Normale Superiore
NEST is an interdisciplinary research and training centre that addresses scientific issues at the nanoscale. The "National Enterprise for nanoScience and nanoTechnology" (NEST) comprises the Istituto Nanoscienze (CnrNano) and the laboratories of Scuola Normale Superiore (SNS). The Istituto Nanoscienze is a recently founded institute of the National Research Council (Cnr) devoted to frontier research in nanoscience and nanotechnology. Interests range from fundamental science to emerging technologies as well as applied projects of direct industrial and societal interest. SNS is a center of excellence of the Italian University system. It was founded by Napoleon in 1810 as a branch of the École Normale Supérieure in Paris. The greatest resource of the Scuola Normale is the quality of its students.
http://www.nano.cnr.it/
Columbia Engineering
Columbia University's Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science, founded in 1864, offers programs in nine departments to both undergraduate and graduate students. With facilities specifically designed and equipped to meet the laboratory and research needs of faculty and students, Columbia Engineering is home to NSF- and NIH-funded centers in genomic science, molecular nanostructures, materials science, and energy, as well as one of the world's leading programs in financial engineering. These interdisciplinary centers are leading the way in their respective fields while individual groups of engineers and scientists collaborate to solve some of society's more vexing challenges. http://www.engineering.columbia.edu/
Innovative device for quantum simulations
2011-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dolphins use double sonar
2011-06-08
Dolphins and porpoises use echolocation for hunting and orientation. By sending out high-frequency sound, known as ultrasound, dolphins can use the echoes to determine what type of object the sound beam has hit.
Researchers from Sweden and the US have now discovered that dolphins can generate two sound beam projections simultaneously.
"The beam projections have different frequencies and can be sent in different directions. The advantage is probably that the dolphin can locate the object more precisely", says Josefin Starkhammar, a newly examined doctor in Electrical ...
Will the eel survive its management?
2011-06-08
The European eel is on the way to disappearing for good. The species is critically endangered, and there are strong scientific arguments for suspending all fishing. Despite this situation, Swedish eel fishery is allowed to continue. Analysis of the eel management plan by the Swedish Institute for the Marine Environment identifies clear shortcomings. It is unlikely that Sweden will meet the target that has been set for silver eels capable of migrating back to the Sargasso Sea so that they can contribute to regeneration.
The recruitment of new annual cohorts of European ...
First of its kind study conducted by BUSM finds women as resilient to combat stress as men
2011-06-08
(Boston) - In what is believed to be the first published study on the topic, researchers affiliated with the Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) believe female military service-members from Operation Enduring Freedom OEF)/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF) may be as resilient to combat-related stress as men. These findings currently appear on-line in the Journal of Abnormal Psychology.
Though the literature suggests that women may be more vulnerable to the effects of trauma exposure, most available studies on combat trauma have relied on samples in which women's combat ...
Red-light cameras critical to public safety, MU traffic researcher finds
2011-06-08
COLUMBIA, Mo. — As automated traffic monitoring systems such as red light cameras keep a law enforcement "eye" on the streets across the country, many drivers accuse city governments of installing the monitors as a way to generate revenue. New research from the University of Missouri says the safety benefits of automated traffic monitoring systems far outweigh the potential for abuse.
"A red light camera is not a panacea for traffic problems; it is a very effective tool for safe and efficient transportation," said Carlos Sun, an associate professor of civil engineering ...
Protein folding made easy
2011-06-08
Protein folding has nothing to do with laundry. It is, in fact, one of the central questions in biochemistry. Protein folding is the continual and universal process whereby the long, coiled strings of amino acids that make up proteins in all living things fold into more complex three-dimensional structures. By understanding how proteins fold, and what structures they are likely to assume in their final form, researchers are then able to move closer to predicting their function.
This is important because incorrectly folded proteins in humans result in such devastating ...
Paved surfaces can foster build-up of polluted air
2011-06-08
BOULDER—New research focusing on the Houston area suggests that widespread urban development alters wind patterns in a way that can make it easier for pollutants to build up during warm summer weather instead of being blown out to sea.
The international study, led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), could have implications for the air quality of fast-growing coastal cities in the United States and other midlatitude regions overseas. The reason: the proliferation of strip malls, subdivisions, and other paved areas may interfere with breezes needed to ...
The heat is on for sodium-manganese oxide rechargeable batteries
2011-06-08
RICHLAND, Wash. -- By adding the right amount of heat, researchers have developed a method that improves the electrical capacity and recharging lifetime of sodium ion rechargeable batteries, which could be a cheaper alternative for large-scale uses such as storing energy on the electrical grid.
To connect solar and wind energy sources to the electrical grid, grid managers require batteries that can store large amounts of energy created at the source. Lithium ion rechargeable batteries -- common in consumer electronics and electric vehicles -- perform well, but are too ...
Glaciations may have larger influence on biodiversity than current climate
2011-06-08
An investigation by the Spanish Scientifc Council (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, CSIC) reveals that the large impacts occurred during the last ice age maintain their effects on the current distribution of dung beetles of the scarab family (Scarabaeidae). The presence of these beetles in Europe seems to be more influenced by the climate of that glaciation than by the present one.
The study, published yesterday in the journal Ecology Letters, analyzed the species richness and the structure of their communities throughout the different regions of the European ...
Your attention please: 'Rewarding' objects can't be ignored
2011-06-08
The world is a dazzling array of people, objects, sounds, smells and events: far too much for us to fully experience at any moment. So our attention may automatically be snagged by something startling, such as a slamming door, or we may deliberately focus on something that is important to us right then, such as locating our child among the happily screaming hordes on the school playground. We also know that people are hard-wired to seek out and pay attention to things that are rewarding, such as food when we are hungry, or water when we are thirsty.
So what happens ...
Chicago Plastic Surgeon Makes Appearance on Popular Show, The Doctors
2011-06-08
Dr. Kotis, a Chicago plastic surgeon, made an appearance on the popular daytime television show The Doctors. He and the show's host, Dr. Drew Ordon, scrubbed in to demonstrate a cutting-edge procedure that can end the pain and limitations caused by rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
In the May 24th airing of The Doctors take on Chicago, Dr. Kotis performed a surgery to replace a thumb joint which has been worn down on a woman due to a terrible car accident. The damaged joint caused the bones in the thumb to rub together causing severe rheumatoid as well as osteoarthritis. ...