(Press-News.org) Researchers have discovered that a protein found in the walls of blood vessels plays a key role in maintaining healthy blood pressure; a discovery that could one day lead to new treatments for people with high blood pressure.
The research, funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and the British Heart Foundation (BHF), shows that malfunction of the protein – a potassium channel called Kv7.4 – contributes to the maintenance of high blood pressure. The discovery is published this evening (2100hrs, 11 July) in the journal Circulation.
Dr Iain Greenwood from St George's, University of London led the study. He said "High blood pressure is one of the most common diagnoses in the UK and one in three adults has it – that's around 16 million people. People with high blood pressure are at much greater risk of heart attack, heart failure, and kidney disease and it's the main risk factor for stroke.
"We are trying to understand how our bodies go about regulating our blood pressure under normal circumstances – the more we understand, the better we can get at spotting what is going wrong and intervening when someone has this common chronic health issue. This discovery is an important part of the puzzle and might one day lead to new treatments."
Dr Greenwood and his team have shown that Kv7.4 plays an essential role in maintaining the extent to which arteries are constricted or dilated. He said "We have to be able to change our blood pressure at the drop of a hat – quite literally! If you dropped your hat and bent over to pick it up, you body would automatically reduce your blood pressure to account for the position of your head relative to your heart and the effect of gravity and then when you stood up again, your body would adjust it back up.
"The muscles in the walls of your blood vessels play a role in adjusting blood pressure and if they need to increase it, they squeeze the blood vessels more tightly to literally put mechanical pressure on your blood."
The researchers examined rodents that had high blood pressure and discovered that in some cases the Kv7.4 channels weren't working properly. These channels allow the passage of potassium out of the muscle cells in our blood vessels and they have to be open and closed at the right times so that the muscles can contract or relax when we need them to. In the animals that had high blood pressure and malfunctioning Kv7.4 channels, the problem was that the channels were blocked. This caused an imbalance in the finely controlled chemical environment of the muscle cell.
"The problem is," continued Dr Greenwood, "if the Kv7.4 channels cannot function, the muscle cells overreact to the signals the body is giving to increase blood pressure. We think that in the animals we studied the redundant Kv7.4 channels contributed markedly to their high blood pressure."
Whilst it is extremely unlikely that most people with high blood pressure have defective Kv7.4 channels, the researchers hope that by understanding the key role they play in maintaining healthy blood pressure we can use this knowledge to develop new strategies for adjusting blood pressure using drug treatments in the future.
Professor Douglas Kell, Chief Executive, BBSRC said "If we are to have long, healthy lives, we need to understand how our bodies cope with the demands we place on them. Increasing our knowledge of the biology that underpins normal, healthy processes will pave the way for future strategies to prevent or treat health problems. Maintaining healthy blood pressure is an important part of keeping us all well and so this research could be of great benefit to many people in the future."
Professor Jeremy Pearson, Associate Medical Director at the British Heart Foundation, said "Physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the amount of salt and alcohol you consume, and increasing the amount of fruit and vegetables you eat can all play a part in lowering your risk of having high blood pressure. However, we still do not fully understand what causes the condition in most people - and current medicines to treat it are often not fully effective. Crucial research such as this could lead to new medical treatments for high blood pressure."
###
END
Philadelphia, PA, July 11, 2011 – In people with Parkinson's Disease (PD), the inability to make quick movements limits basic functioning in daily life. Movement can be improved by various cueing techniques, such as providing visual or auditory stimuli when movements are started. In a study scheduled for publication in the August issue of the Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, researchers report that virtual reality (VR) and physical reality exercises can be used to provide effective stimuli to increase movement speeds in PD patients.
Investigators from ...
A freeroll tournament requires no buy-in and anyone can play it for free. Because of the lack of deposit, playing freerolls is really a win-win situation as you can earn money without losing a single penny.
Such tournaments are excellent for novice poker players who are new to the game and these tournaments are good enough to improve a player's skills in a poker game. When playing free poker, there are certain approaches a player needs to learn in order to play the game strategically, and learning these can take some time. To get better, play freerolls and gain experience ...
Tampa, Fla. (July 11, 2011) – A team of researchers from Spain and Switzerland have developed a new model for studying the development of testicular germ cell tumors by transplanting embryonic stem cells into the seminiferous tubules in mouse models, resulting in the development of testicular germ cell tumors (TGCT) that mimic the early stages of TGCT development. The study, published in Cell Transplantation (20:5), is now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/.
"Over the last fifteen years, cell transplantation into seminiferous tubules ...
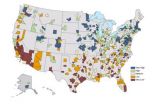
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Which U.S. metro region is most likely to come out of the next recession, natural disaster or other regional "shock" relatively unscathed? Rochester, Minn. A little more battered might be College Station-Bryan, Texas.
These two regions are ranked first and last, respectively, by a new online tool measuring more than 360 U.S. metros for their "regional resilience," or capacity to weather acute and chronic stresses ranging from gradual economic decline to rapid population gains to earthquakes and floods.
The Resilience Capacity Index (RCI), developed ...
Since 2008, Habitatter.com has been offering the highest quality in home decorating accessories, and Good Night Irene! has been with them since the beginning.
Good Night Irene! is a one-woman studio in beautiful Asheville, North Carolina who has been creating imaginative switch plates since 1992. Her designs reflect nature and all have texture to thrill your hands as well as your eyes. These light switch plates are made with polymer clay, a versatile and durable synthetic material, and cured directly onto plastic switch plates to ensure a perfect fit.
All good things ...
A difficult-to-treat form of childhood leukemia relies on changes in the structure of DNA – so-called epigenetic changes – to wreak genomic havoc within white blood cells, according to one of two studies conducted by a research team at Children's Hospital Boston and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. Together with collaborators from a biotechnology company, the same team also showed that a new drug that blocks these changes could deactivate cancer-promoting genes and halt the growth of this cancer.
These studies, reported in a pair of papers in the July 11, 2011 issue of Cancer ...
Tampa, Fla. (July. 11, 2011) – A study published in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (20:5) investigating optimal routes for transplanting neural stem/progenitor cells (NS/PCs) in animal models of spinal cord injury (SCI) has demonstrated that intralesional (IL) injection conferred benefits over intravenous injection (IV) and intrathecal (IT) injection. The study, by a team of Keio University (Japan) researchers, is now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/ .
"Spinal cord injury usually results in severe, paralytic damage ...
They may not dress like Justin Bieber or Selena Gomez, but parents are a whole lot like their teenagers when it comes to their behaviour on Facebook. That's the finding of a new study by University of Guelph researchers.
Parents are just as likely as their kids to disclose personal information on the social networking site, according to the research, which will be published in the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science and is available online now.
And (gasp!) mom and dad are just as susceptible to the need for popularity.
"Facebook is not just a phenomenon ...
Tampa, Fla. (July 11, 2011) – Two papers published in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (20:5), now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/, highlight the therapeutic potential of human Sertoli cells that are present in the testes and are also called "nurse" or "mother" cells because they nurture the developing sperm cells. Sertoli cells form the blood-testes barrier that separates the blood compartment of the testes from the compartment of the seminiferous tubules. Once differentiated to form the blood-testes barrier, Sertoli cells ...
WASHINGTON – Pets can serve as important sources of social and emotional support for "everyday people," not just individuals facing significant health challenges, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
And, the study found, pet owners were just as close to key people in their lives as to their animals, indicating no evidence that relationships with pets came at the expense of relationships with other people, or that people relied more on pets when their human social support was poorer.
Psychologists at Miami University and Saint ...