(Press-News.org) Monday, 18 July, 2011 (Rome, Italy) -- A special press conference at the 6th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention (IAS 2011) will today feature a panel consisting of researchers from the CDC TDF2 study, the Partners PrEP Study and the HPTN 052 study. They will be joined by Anthony Fauci, Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Gottfried Hirnschall, Director of the HIV Department of the World Health Organization (WHO) and Elly Katabira, IAS 2011 International Chair and President of the International AIDS Society (IAS). The IAS 2011 conference opened yesterday, Sunday 17 July and runs until Wednesday 20 July and is being attended by over 5000 researchers, clinicians and community leaders.
In light of announcements this past week about new data on PrEP effectiveness, both the HPTN 052 abstract session (16.30, SR1) and press conference have been expanded to include presentations on the Partners PrEP Study and the CDC's TDF2 study, both of which were released on 13 July in the US. The presentation on the CDC study was originally scheduled for a late breaker session at IAS 2011 on Wednesday 20 July.
"Treatment is prevention and these three studies provide the proof," said Katabira.
"The XI International AIDS Conference in Vancouver in 1996 is remembered as the conference that heralded the arrival of combination antiretroviral treatment. The IAS 2011 Conference will be remembered as the beginning of the treatment as prevention revolution."
"These studies mark a turning point in HIV science and in HIV prevention," said Stefano Vella, IAS 2011 Local Co-Chair and Research Director at the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS). "The urgent challenge now is to implement treatment as prevention in the developing world."
Press conference line up:
Chair: Stefano Vella: IAS 2011 Local Co-Chair and Research Director at the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS)
Myron Cohen: HPTN 052 Protocol Chair and Associate Vice Chancellor for Global Health and Director of the Institute of Global Health and Infectious Diseases at the University of North Carolina
About the HPTN 052 study:
The HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) 052 study found that men and women, who were already infected with HIV, had a reduced risk of transmitting the virus to their uninfected sexual partners by 96% through early initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy (cART). HPTN 052 also found that early initiation of cART benefits the HIV-infected individual.
HPTN 052 was designed to evaluate whether early versus delayed use of cART by HIV-infected individuals would reduce transmission of HIV to their uninfected partners and benefit the HIV-infected individuals as well. During the course of the study, 39 participants who had been HIV-uninfected at the start of the study became infected with HIV. Of those, 29 were linked transmissions, where the virus from the originally-infected partner was confirmed by genetic analysis to be the source of infection in the newly infected sexual partner. Only one of the 29 infections occurred in the early cART arm. Based on the latest analyses, this one transmission most likely occurred close to the time the couple enrolled in the study and before HIV viral replication could have been suppressed by cART in the infected participant.
The new analyses also provide more insight as to how early initiation of cART benefits the HIV-infected person. Individuals who were put on early cART maintained higher absolute CD4 counts than those in the delayed arm, who received treatment when their CD4 counts fell below 250 cells/mm³ or an AIDS-related event occurred. Early cART was also associated with a 41% reduction in HIV-related illnesses or death, a direct benefit for the HIV-infected partner. The reliable suppression of HIV among HIV-infected people in the early treatment arm suggests potential impact on adherence when the infected individual is informed that their cART may also benefit their partner.
Michael C.Thigpen: Principal study investigator and epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), USA
About the TDF2 study:
The CDC TDF2 study was a randomized, placebo-controlled trial examining the safety and efficacy of a once-daily tablet containing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine (TDF/FTC, known by the brand name Truvada) for reducing the risk of HIV acquisition among heterosexual men and women at two sites in Botswana. In addition to study medication, all participants received a comprehensive package of HIV prevention services. The study provides strong evidence that a daily oral dose of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection can reduce HIV acquisition among uninfected individuals exposed to the virus through heterosexual sex. The study, conducted in partnership with the Botswana Ministry of Health, found TDF/FTC reduced the risk of acquiring HIV infection by roughly 63 percent overall in the study population (95% CI, 21.5 to 83.4; p= 0.0133) ,and by 78 percent among trial participants believed to be taking study medications (95% CI 41.2 to 93.6, p=0.0053). Adherence (as measured by pill count) was high, both among those receiving TDF/FTC and those receiving placebo (84.1 percent and 83.7 percent, respectively). Reported sexual risk behavior was similar between the two study arms. Consistent with other PrEP studies, preliminary analyses did not identify any significant safety concerns associated with daily use of TDF/FTC.
Jared Baeten: Co-leader of the Partners PrEP Study and epidemiologist at the University of Washington, USA
About the Partners PrEP Study:
This is a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of daily oral tenofovir and emtricitabine/tenofovir for the prevention of HIV-1 acquisition among HIV-1 seronegative partners in heterosexual HIV-1 serodiscordant partnerships. The study is funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The University of Washington coordinated the trial, in collaboration with investigators at nine sites in Kenya and Uganda. The study enrolled 4758 HIV-1 serodiscordant couples; HIV-1 uninfected partners were randomly assigned in equal numbers to one of three study groups: one group received tenofovir, one emtricitabine/tenofovir, and one matching placebo. All study participants received a comprehensive package of HIV-1 prevention services. On 10 July 2011, the Partners PrEP Study independent Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) recommended, after review of the study data, that the study results be publically reported and the placebo arm be discontinued, because of definitive demonstration of HIV-1 protection from pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in the study population. Tenofovir reduced HIV-1 risk by 62% (95% CI 34 to 78, p=0.0003), emtricitabine/tenofovir by 73% (95% CI 49 to 85, p< 0.0001). Efficacy for tenofovir and emtricitabine/tenofovir were not statistically different. 62% of HIV negative participants were male, 38% were female: both PrEP medications reduced HIV-1 risk in men and women. Adherence to the daily PrEP medication was very high – more than 97% of dispensed doses of the study medications were taken. More than 95% of participants were retained in study follow-up. Safety parameters were comparable across the three study groups.
Anthony Fauci: Director, NIAID, USA
Fauci will remark on the implications for prevention research. He will talk about the collective importance of these studies in finding new HIV prevention methods and the optimism that these combinations when viewed in total will help to end the HIV/AIDS epidemic.
Gottfried Hirnschall: Head of the HIV Department at the WHO, Switzerland
Over the past year, WHO has been developing recommendations for couples HIV testing and counseling. More than half of all people living with HIV do not know their infection status, and therefore, may transmit HIV unknowingly. By partners testing together and mutually disclosing their test results, couples can learn about their options for HIV prevention and treatment.
The findings of the three cited studies above will be reflected in WHO guidelines for couples HIV testing and counseling and also to develop broader guidance on the strategic use of antiretrovirals for treatment and prevention of HIV.
Elly Katabira: International Chair IAS 2011 and IAS President
Katabira will talk about the implications of the three cited studies for HIV professionals
###
Online Coverage of IAS 2011 at www.ias2011.org
The online Programme-at-a-Glance, available through the website, includes links to abstracts, as well as session slides with audio and speeches (all abstract findings are embargoed until date and time of delivery at the conference). Additional online programming is provided by IAS 2011's two official online partners: Clinical Care Options and NAM. Reporters and others can also follow key developments on the IAS 2011 blog at http://blog.ias2011.org or on Twitter at www.twitter.com/ias2011.
About the IAS 2011 Organizers
IAS: The International AIDS Society (IAS) is the world's leading independent association of HIV professionals, with over 16,000 members from more than 196 countries working at all levels of the global response to AIDS. Our members include researchers from all disciplines, clinicians, public health and community practitioners on the frontlines of the epidemic, as well as policy and programme planners. The IAS is the custodian of the biennial International AIDS Conference and lead organizer of the IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention, which is currently being held in Rome, Italy.
www.iasociety.org | www.facebook.com/iasociety | Follow us on Twitter @iasociety
ISS: The Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS) is the leading technical and scientific body of the Italian National Health Service. Its activities include research, clinical trials, and control and training in public health. It also serves as a major national clearing-house for technical and scientific information on public health issues. Among other things, the Institute conducts scientific research in a wide variety of fields, from cutting-edge molecular and genetic research, to population-based studies of risk factors for disease and disability, to Global Health research.
Further information:
In Rome:
Onsite Media Centre Landline No. +39 068 0241 756
International media:
Lindsey Rodger
lindsey.rodger@iasociety.org
Michael Kessler
mkessler@ya.com
+39 348 686 8417
Italian media:
Andrea Tomasini
tomasini39@hotmail.com
+39 329 263 4619
Antiretroviral treatment is HIV prevention: The proof is here
2011-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
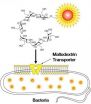
New contrast agents detect bacterial infections with high sensitivity and specificity
2011-07-19
A new family of contrast agents that sneak into bacteria disguised as glucose food can detect bacterial infections in animals with high sensitivity and specificity. These agents -- called maltodextrin-based imaging probes -- can also distinguish a bacterial infection from other inflammatory conditions.
"These contrast agents fill the need for probes that can accurately image small numbers of bacteria in vivo and distinguish infections from other pathologies like cancer," said Niren Murthy, an associate professor in the Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering ...
Adult day care services provide much-needed break to family caregivers
2011-07-19
Adult day care services significantly reduce the stress levels of family caregivers of older adults with dementia, according to a team of Penn State and Virginia Tech researchers.
"Family members who care for dementia patients are susceptible to experiencing high levels of stress," said Steven Zarit, professor and head, department of human development and family studies, Penn State. "One way of alleviating that stress is through the use of an adult day care center, which allows them a predictable break from caregiving responsibilities."
Not only do caregivers benefit ...
EARTH: Great Lakes geologic sunken treasure
2011-07-19
Alexandria, VA - Shipwreck enthusiasts find a bounty of nautical relics preserved in the chilly depths of the Great Lakes. But only within the last decade have explorers and scientists begun to reveal the secrets of a much different - and much more ancient - sunken treasure in Lake Huron: sinkholes.
As EARTH explores in its August feature "Great Lakes Geologic Sunken Treasure," researchers have recently begun exploring several mysterious sinkholes in Lake Huron. These pockets of water teem with microbial life similar to that found around deep ocean hydrothermal vents ...
Esophageal cancer risk higher in medically treated GERD patients with fewest symptoms
2011-07-19
PITTSBURGH, July 18 – Medically treated patients with mild or no symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are at higher risk for developing esophageal cancer than those with severe GERD symptoms, according to a University of Pittsburgh study published in the current issue of Archives of Surgery.
Many patients who develop adenocarcinoma, a common form of esophageal cancer, are unaware that they have Barrett's esophagus – a change in the cells lining the esophagus often due to repeated stomach acid exposure. In some cases, Barrett's esophagus develops into esophageal ...
GOES-13 movie catches Tropical Storm Bret form and intensify
2011-07-19
VIDEO:
GOES-13 satellite imagery in 15 minute intervals from July 16 at 7:31 a.m. EDT until July 18 at 7:31 a.m. EDT shows Bret developing from a low pressure area in...
Click here for more information.
The GOES-13 satellite that monitors weather over the eastern U.S. recorded a movie of the birth and strengthening of the Atlantic Ocean season's second tropical storm. Tropical Storm Bret was born in the northwestern Bahamas and continues to strengthen.
The Geostationary ...
Steps needed to ensure that home medical devices are easy-to-use and caregivers are well-trained
2011-07-19
WASHINGTON – A new report from the National Research Council recommends steps the Food and Drug Administration and other agencies and professional associations can take to ensure that the medical devices and health information technology used in home health care are easy and safe for laypeople to use and that caregivers, whether formal or informal, are well-trained.
For many reasons -- including the rising cost of health care, the aging of the U.S. population, and patients' desire to remain in their homes -- health care is increasingly moving from formal medical facilities ...
Researchers identify how a gene linked to both Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes works
2011-07-19
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have identified how a gene for a protein that can cause Type 2 diabetes, also possibly kills nerve cells in the brain, thereby contributing to Alzheimer's disease.
The gene, called SorCS1, controls the generation of amyloid-beta (Abeta) in the brain. Abeta plays a key role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. The researchers previously linked SorCS1 to Alzheimer's disease and identified where the molecules lived in the cell, but not how they control Abeta. The new data were presented today at the Alzheimer's Association's ...
MIT: The tallest tree in the land
2011-07-19
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- The next time you're outdoors, see if you can spot the tallest tree. If you're in the desert Southwest, this may be an easy task — trees there are few and far between, and tend to hunch low to the ground to conserve resources. In the temperate Northeast, dense forests make the exercise a bit more difficult. And in the rainy Northwest, the towering stands of sequoias often reach higher than the eye can estimate.
Knowing how tall trees can grow in any given region can give ecologists a wealth of information, from the potential density of a forest and ...
Face value
2011-07-19
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- The looks of political candidates are a key factor influencing voters, a phenomenon identified by a number of scholars in recent years. Now, a new study by MIT political scientists adds to this body of research by detailing which types of citizens are most influenced by candidate appearances, and why: The tendency is most prevalent among low-information voters who watch a lot of television.
Using data from the 2006 U.S. Senate and governors' races, the study shows that for every 10-point increase in the advantage a candidate has when rated by voters ...
John Theurer Cancer Center researchers shared 14 leading edge studies at recent ASCO meeting
2011-07-19
HACKENSACK, N.J. (July 18, 2011) — Researchers from the John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center presented results from 14 cancer-related studies during the recently concluded American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, which took place June 3 – 7, 2011 in Chicago. The studies examined new cancer treatments, ways to predict the best treatment outcomes, and patient quality of life issues.
"ASCO is a great venue for sharing best practices and learning about new treatment approaches – we are proud to help contribute by presenting ...