U of M researchers discover gene required to maintain male sex throughout life
Researchers find that loss of gene Dmrt1 leads to male cells becoming female
2011-07-22
(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (July 20, 2011) – University of Minnesota Medical School and College of Biological Sciences researchers have made a key discovery showing that male sex must be maintained throughout life.
The research team, led by Drs. David Zarkower and Vivian Bardwell of the U of M Department of Genetics, Cell Biology and Development, found that removing an important male development gene, called Dmrt1, causes male cells in mouse testis to become female cells.
The findings are published online today in Nature.
In mammals, sex chromosomes (XX in female, XY in male) determine the future sex of the animal during embryonic development by establishing whether the gonads will become testes or ovaries.
"Scientists have long assumed that once the sex determination decision is made in the embryo, it's final," Zarkower said. "We have now discovered that when Dmrt1 is lost in mouse testes – even in adults – many male cells become female cells and the testes show signs of becoming more like ovaries."
Previous research has shown that removing a gene, called Foxl2, in ovaries caused female cells to become male cells and the ovaries to become more like testes. According to Zarkower, the latest U of M research determines that the gonads of both sexes must actively maintain the original sex determination decision throughout the remainder of life.
For the genetic research community this new understanding is a breakthrough. The findings provide new insight into how to turn one cell type into another, a process known as reprogramming, and also show that throughout life, cells in the testis must be actively prevented from transforming into female cells normally found in the ovary.
"This work shows that sex determination in mammals can be surprisingly prone to change, and must be actively maintained throughout an organism's lifetime," said Dr. Susan Haynes, who oversees developmental biology grants at the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. "These new insights have important implications for our understanding of how to reprogram cells to take on different identities, and may shed light on the origin of some human sex reversal disorders."
The new findings may force the scientific community to reconsider how disorders involving human sex-reversal occur. Some of these disorders may not result from errors in the original sex determination decision in the embryo, but instead may result from failure to maintain that decision later in embryonic development. In addition, because DMRT1 has been associated with human gonadal cancers, the researchers hope their findings will provide another clue into how gonadal cancer develops.
INFORMATION:Drs. Clinton Matson and Mark Murphy of the Department of Genetics, Cell Biology and Development, and Dr. Aaron Sarver of the U of M Masonic Cancer Center were instrumental in performing these studies. The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-07-22
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A University at Buffalo-led research team has developed a mathematical framework that could one day form the basis of technologies that turn road vibrations, airport runway noise and other "junk" energy into useful power.
The concept all begins with a granular system comprising a chain of equal-sized particles -- spheres, for instance -- that touch one another.
In a paper in Physical Review E this June, UB theoretical physicist Surajit Sen and colleagues describe how altering the shape of grain-to-grain contact areas between the particles dramatically ...
2011-07-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Instead of calming fears, the death of Osama bin Laden actually led more Americans to feel threatened by Muslims living in the United States, according to a new nationwide survey.
In the weeks following the U.S. military campaign that killed bin Laden, the head of the terrorist organization Al Qaeda, American attitudes toward Muslim Americans took a significant negative shift, results showed.
Americans found Muslims living in the United States more threatening after bin Laden's death, positive perceptions of Muslims plummeted, and those surveyed were ...
2011-07-22
DURHAM, N.C. – Esses are everywhere.
From economic trends, population growth, the spread of cancer, or the adoption of new technology, certain patterns inevitably seem to emerge. A new technology, for example, begins with slow acceptance, followed by explosive growth, only to level off before "hitting the wall."
When plotted on graph, this pattern of growth takes the shape of an "S."
While this S-curve has long been recognized by economists and scientists, a Duke University professor believes that a theory he developed explains the reason for the prevalence of this ...
2011-07-22
Los Angeles, (July 2011) — Despite helping to push Hosni Mubarak and his regime from power, Egypt's liberals and pro-democracy activists are having trouble moving from revolution to politics, according to a recent article in the World Policy Journal (published by SAGE).
In this in-depth look at the Egyptian political landscape, the article's author, Jenna Krasjeki, examines various groups vying for influence and public support in the run-up to elections this fall. One common characteristic that Krasjeski notes is the lack of organization in the groups of young, liberal ...
2011-07-22
A simple cut to the skin unleashes a complex cascade of chemistry to stem the flow of blood. Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have used evolutionary clues to reveal how a key clotting protein assembles. The finding sheds new light on common bleeding disorders.
The long tube-shaped protein with a vital role in blood clotting is called von Willebrand Factor (VWF). Made in cells that form the inner lining of blood vessels, VWF circulates in the blood seeking out sites of injury. When it finds them, its helical tube unfurls to catch ...
2011-07-22
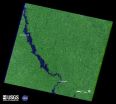
Flooding along the Missouri River continues as shown in recent Landsat satellite images of the Nebraska and Iowa border. Heavy rains and snowmelt have caused the river to remain above flood stage for an extended period.
A Landsat 5 image of the area from May 5, 2011 shows normal flow. In contrast, a Landsat 7 image from July 17 depicts flood conditions in the same location.
A national overview map of streamflow provided by U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) WaterWatch graphically portrays the immense geographic extent of flooding in the Missouri River basin.
Monitoring ...
2011-07-22
In the fight to improve global health, alleviate hunger, raise living standards and empower women in the developing world, chickens have an important role to play.
Jagdev Sharma, a researcher at the Center for Infectious Diseases and Vaccinology at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute has been investigating the advantages of a more productive species of chicken for villagers in rural Uganda. He reports his findings this week at the American Veterinary Medical Association Meeting in Saint Louis, Missouri.
The star of this developing story is a type of chicken ...
2011-07-22
Scientists of the CDF collaboration at the Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory announced the observation of a new particle, the neutral Xi-sub-b. This particle contains three quarks: a strange quark, an up quark and a bottom quark (s-u-b). While its existence was predicted by the Standard Model, the observation of the neutral Xi-sub-b is significant because it strengthens our understanding of how quarks form matter. Fermilab physicist Pat Lukens, a member of the CDF collaboration, presented the discovery at Fermilab on Wednesday, July 20.
The ...
2011-07-22
The GOES-13 satellite captured a triple-header in the tropics today when it captured three tropical cyclones in one image in the Northern Hemisphere.
A visible image taken from the GOES-13 satellite on July 20 at 14:45 UTC (10:45 a.m. EDT) and shows a consolidating low pressure area called System 99L in the eastern North Atlantic Ocean, Tropical Storm Bret several hundred miles east of South Carolina, and a large Hurricane Dora off the west coast of Mexico. The image was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
System ...
2011-07-22
Birds use their bills largely to forage and eat, and these behaviors strongly influence the shape and size of a bird's bill. But the bill can play an important role in regulating the bird's body temperature by acting as a radiator for excess heat. A team of scientists have found that because of this, high summer temperatures have been a strong influence in determining bill size in some birds, particularly species of sparrows that favor salt marshes. The team's findings are published in the scientific journal Ecography, July 20.
Scientists at the Smithsonian Migratory ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] U of M researchers discover gene required to maintain male sex throughout life
Researchers find that loss of gene Dmrt1 leads to male cells becoming female