(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Newspaper endorsements for presidential candidates can influence voting decisions, according to newly published research co-authored by Brown University economist Brian Knight. The paper, co-authored by Chun Fang Chiang, demonstrates that voters are more likely to support the recommended candidate following a newspaper's endorsement, but any degree of influence depends on the credibility of the paper's pick. The findings are published in The Review of Economic Studies.
The researchers take into account that newspapers are potentially biased in favor of one of the candidates and found that voters rationally account for the credibility of any endorsement. Endorsements for the Democratic candidate from left-leaning newspapers are less influential than endorsements from neutral or right-leaning newspapers and likewise for endorsements from papers sympathetic to Republican candidates. Knight said these results "suggest that voters are sophisticated and attempt to filter out any bias in media coverage of politics."
To estimate the influence of newspaper endorsements, the researchers used individual-level data on voting intentions and newspaper readership in the months leading up to the 2000 and 2004 elections. They measured endorsement credibility based on the ideological leanings of newspapers, ownership, and reader preferences.
To provide a sense of the magnitude of endorsement effects, Knight and Chiang feature a data table that shows the estimated influence in the top 20 newspapers during the 2000 presidential campaign. They show the least credible endorsements were for Al Gore from The New York Times and for George W. Bush from the Dallas Morning News, which convinced less than 1 percent of their readers to switch allegiance to the endorsed candidate. By contrast, the endorsement with the largest effects came from the Chicago Sun Times and the Denver Post, both of which had surprising endorsements. The Chicago Sun Times was predicted to endorse Gore with a probability of 58 percent, but instead endorsed Bush, while the Denver Post endorsed Gore even though it was only predicted to do so by a probability of only 35 percent. Both "surprising" endorsements convinced about 3 percent of readers to switch allegiances, according to the findings. Knight and Chiang also found that endorsements are more influential among moderate voters.
###
Chiang conducted this research as a graduate student at Brown and is currently assistant professor of economics at National Taiwan University.
Endorsements matter but voters are wise to media bias
2011-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Elusive prey
2011-08-01
WORCESTER, Mass. – Escape responses are some of the most studied behaviors by neurobiologists who want to understand how the brain processes sensory information. The ability to evade predators plays a vital role in the process of natural selection. Animals explore their environment to find food, find mates and locate new habitats, and have developed distinct escape responses to avoid predators, thereby increasing their chances for survival. Yet there are few examples that illustrate a complete understanding of the basic biological mechanisms of behavior with its ecological ...
Geographic analysis offers new insight into coral disease spread
2011-08-01
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — In the last 30 years, more than 90 percent of the reef-building coral responsible for maintaining major marine habitats and providing a natural barrier against hurricanes in the Caribbean has disappeared because of a disease of unknown origin.
Now a University of Florida geographer and his colleagues applied Geographic Information Systems, known as GIS — as well as software previously used to examine human illness — to show where clusters of diseased coral exist. Their findings, published this month in the journal PLoS One, may help scientists derive ...
NASA identifies the areas of Tropical Storm Muifa's strength
2011-08-01
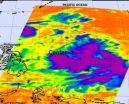
The strongest thunderstorms that make up tropical storm Muifa are on the storm's eastern and southern sides, according to infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite. The northern side is being weakened by a nearby weather system.
Tropical Storm Muifa is moving through the western North Pacific Ocean, and had strengthened during the early morning hours of July 28. On July 27, it was tropical depression 11W and winds have since increased to 40 knots (46 mph/74 kmh).
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Muifa the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument ...
NASA eyes Tropical Storm Nock-Ten's heavy rains for Hainan Island and Vietnam
2011-08-01
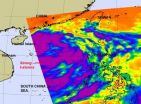
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows bands of strong thunderstorms wrapping around the center of Tropical Storm Nock-Ten as it makes its way through the South China Sea and two landfalls on Hainan Island and in Vietnam.
Bands of strong thunderstorms that make up tropical storm Nock-ten were visible in an infrared image captured on July 28 by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. The colder the cloud tops, the higher the thunderstorms and the stronger they are, and cloud top temperatures over a large ...
NASA measures wildfire pollution pour over Niagara Falls
2011-08-01
Water isn't the only thing pouring over Niagara Falls. Pollution from fires in Ontario, Canada is also making the one thousand mile trip, while being measured by NASA's Aqua satellite.
One instrument that flies aboard two of NASA's satellites has provided two views of the pollution from the fires in Ontario. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS instrument, flies onboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. MODIS has provided a visible look at the smoke and pollution that has spread over Niagara Falls and east to Nova Scotia.
As of July 20, the Canadian ...
Cash Advances US Provides Fast Cash Loans Online With No Credit Check
2011-08-01
Less-than-perfect credit score can wipe off any opportunity to get some cash you need at the moment as most of the lenders consider people with bad credit history as high-risk borrowers. However, Cash Advances US offers particular cash loans with no credit check which are available online. The service was actually designed specially for consumers with damaged credit report who often face troubles applying for some extra money.
It's fast and simple to take out online payday advance loans performed by the company as the application process is held totally on the Internet. ...
Using a 'systems biology' approach to look under the hood of an aggressive form of breast cancer
2011-08-01
SEATTLE – Using a "systems biology" approach – which focuses on understanding the complex relationships between biological systems – to look under the hood of an aggressive form of breast cancer, researchers for the first time have identified a set of proteins in the blood that change in abundance long before the cancer is clinically detectable. The findings, by co-authors Christopher Kemp, Ph.D., and Samir Hanash, M.D., Ph.D., members of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center's Human Biology and Public Health Sciences divisions, respectively, are published online ahead ...
SOHO watches a comet fading away
2011-08-01
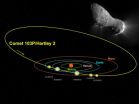
On Nov. 4, 2010, NASA's EPOXI spacecraft came within 450 miles of Comet Hartley 2, a small comet not even a mile in diameter, which takes about six and a half years to orbit the sun. Designated officially as 103P/Hartley 2, the comet thus became the fifth for which scientists have collected close-up images.
But the comet was also observed from another spacecraft: the Solar and Heliospheric Observer (SOHO), better known for its observations of the sun. Together, the two returned data about what appears to be an irregular comet, belching chunks of ice and losing water at ...
Fresh Produce Clothing's Summer-Fall Collections Feature Unique Pieces of Wearable Works of Art
2011-08-01
Fresh Produce customers can make an artful statement when they wear the eclectic prints featured in its latest collections of effortless and spirited looks. The inspired prints are available in a variety of new styles and fabrications from cool cotton voile to comfy cotton jersey and versatile rayon-lycra.
This summer's standout print is the Blue Tahitian Flower. Fresh Produce women adore this romantic watercolor-inspired motif. Its look and feel is "pure summer" with beautiful tropical flowers captured in soft, watery hues and translated to new chic tunics, ...
An unexpected clue to thermopower efficiency
2011-08-01
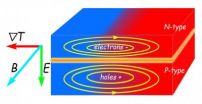
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and their colleagues have discovered a new relation among electric and magnetic fields and differences in temperature, which may lead to more efficient thermoelectric devices that convert heat into electricity or electricity into heat.
"In the search for new sources of energy, thermopower – the ability to convert temperature differences directly into electricity without wasteful intervening steps – is tremendously promising," says Junqiao Wu of Berkeley Lab's Materials ...