(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. – A growing body of evidence suggests that antioxidants may have significant value in addressing infertility issues in both women and men, including erectile dysfunction, and researchers say that large, specific clinical studies are merited to determine how much they could help.
A new analysis, published online in the journal Pharmacological Research, noted that previous studies on the potential for antioxidants to help address this serious and growing problem have been inconclusive, but that other data indicates nutritional therapies may have significant potential.
The researchers also observed that infertility problems are often an early indicator of other degenerative disease issues such as atherosclerosis, high blood pressure and congestive heart failure. The same approaches that may help treat infertility could also be of value to head off those problems, they said.
The findings were made by Tory Hagen, in the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University, and Francesco Visioli, lead author of the study at the Madrid Institute for Advanced Studies in Spain.
"If oxidative stress is an underlying factor causing infertility, which we think the evidence points to, we should be able to do something about it," said Hagen, the Jamieson Chair of Healthspan Research in the Linus Pauling Institute. "This might help prevent other critical health problems as well, at an early stage when nutritional therapies often work best."
The results from early research have been equivocal, Hagen said, but that may be because they were too small or did not focus on antioxidants. Laboratory and in-vitro studies have been very promising, especially with some newer antioxidants such as lipoic acid that have received much less attention.
"The jury is still out on this," Hagen said. "But the problem is huge, and the data from laboratory studies is very robust, it all fits. There is evidence this might work, and the potential benefits could be enormous."
The researchers from Oregon and Spain point, in particular, to inadequate production of nitric oxide, an agent that relaxes and dilates blood vessels. This is often caused, in turn, by free radicals that destroy nitric oxide and reduce its function. Antioxidants can help control free radicals. Some existing medical treatments for erectile dysfunction work, in part, by increasing production of nitric oxide.
Aging, which is often associated with erectile dysfunction problems, is also a time when nitric oxide synthesis begins to falter. And infertility problems in general are increasing, scientists say, as more people delay having children until older ages.
"Infertility is multifactorial and we still don't know the precise nature of this phenomenon," Visioli said.
If new approaches were developed successfully, the researchers said, they might help treat erectile dysfunction in men, egg implantation and endometriosis in women, and reduce the often serious and sometimes fatal condition of pre-eclampsia in pregnancy. The quality and health of semen and eggs might be improved.
As many as 50 percent of conceptions fail and about 20 percent of clinical pregnancies end in miscarriage, the researchers noted in their report. Both male and female reproductive dysfunction is believed to contribute to this high level of reproductive failure, they said, but few real causes have been identified.
"Some people and physicians are already using antioxidants to help with fertility problems, but we don't have the real scientific evidence yet to prove its efficacy," Hagen said. "It's time to change that."
Some commonly used antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, could help, Hagen said. But others, such as lipoic acid, are a little more cutting-edge and set up a biological chain reaction that has a more sustained impact on vasomotor function and health.
Polyphenols, the phytochemicals that often give vegetables their intense color and are also found in chocolate and tea, are also of considerable interest. But many claims are being made and products marketed, the researchers said, before the appropriate science is completed – actions that have actually delayed doing the proper studies.
"There's a large market of plant-based supplements that requires hard data," Visioli said. "Most claims are not backed by scientific evidence and human trials. We still need to obtain proof of efficacy before people invest money and hope in preparations of doubtful efficacy."
###
Editor's Note: The study this story is based on is available in ScholarsArchive@OSU: http://bit.ly/nNir7E
END
The human brain is the most complex of all organs, containing billions of neurons with their corresponding projections, all woven together in a highly complex, three-dimensional web. To date, mapping this vast network posed a practically insurmountable challenge to scientists. Now, however, a research team from the Heidelberg-based Max Planck Institute for Medical Research has developed a method for tackling the mammoth task. Using two new computer programs, KNOSSOS and RESCOP, a group of over 70 students mapped a network of more than 100 neurons – and they did so faster ...
DERMagic Skin Care for Animals (www.DERMagic.com) today announced its popular and recently introduced Organic Skin Rescue Shampoo Bar has won 1st Place in the Pet Product News International "2011 Retailer's Top Pick" Awards in the Grooming Products category. Created by the editors at Pet Product News International to identify new products retailers would most like to see on their store shelves, the 2011 Retailers' Top Picks Awards presented product in 14 categories and asked pet specialty retailers to vote for their favorite three within each category.
"We ...
BELLINZONA (Switzerland) – July 28, 2011 – A paper published today in the scientific research journal Science, describes a novel, proprietary monoclonal antibody (FI6) discovered in a collaboration between Humabs BioMed SA, the Institute for Research in Biomedicine ("IRB") and the UK Medical Research Council (MRC). FI6 is the first neutralizing antibody that targets all 16 hemagglutinin subtypes of influenza A and represents an important development in the treatment of severe cases of flu, and in finding a universal flu vaccine. The paper also discusses Humabs' high throughput ...
New Rochelle, NY, July 28, 2011—Avian influenza virus is a threat to the commercial chicken industry and, with its recent rapid spread across China, has also shown the ability for transmission from chickens to humans and other mammals. In an article in Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Chinese researchers report that oral chicken interferon-alpha may significantly reduce influenza virus levels when given either preventively or therapeutically. The article is available free online at www.liebertpub.com/jir
Chickens ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Newspaper endorsements for presidential candidates can influence voting decisions, according to newly published research co-authored by Brown University economist Brian Knight. The paper, co-authored by Chun Fang Chiang, demonstrates that voters are more likely to support the recommended candidate following a newspaper's endorsement, but any degree of influence depends on the credibility of the paper's pick. The findings are published in The Review of Economic Studies.
The researchers take into account that newspapers are potentially ...
WORCESTER, Mass. – Escape responses are some of the most studied behaviors by neurobiologists who want to understand how the brain processes sensory information. The ability to evade predators plays a vital role in the process of natural selection. Animals explore their environment to find food, find mates and locate new habitats, and have developed distinct escape responses to avoid predators, thereby increasing their chances for survival. Yet there are few examples that illustrate a complete understanding of the basic biological mechanisms of behavior with its ecological ...
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — In the last 30 years, more than 90 percent of the reef-building coral responsible for maintaining major marine habitats and providing a natural barrier against hurricanes in the Caribbean has disappeared because of a disease of unknown origin.
Now a University of Florida geographer and his colleagues applied Geographic Information Systems, known as GIS — as well as software previously used to examine human illness — to show where clusters of diseased coral exist. Their findings, published this month in the journal PLoS One, may help scientists derive ...
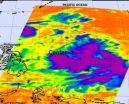
The strongest thunderstorms that make up tropical storm Muifa are on the storm's eastern and southern sides, according to infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite. The northern side is being weakened by a nearby weather system.
Tropical Storm Muifa is moving through the western North Pacific Ocean, and had strengthened during the early morning hours of July 28. On July 27, it was tropical depression 11W and winds have since increased to 40 knots (46 mph/74 kmh).
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Muifa the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument ...
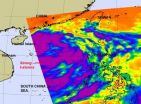
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows bands of strong thunderstorms wrapping around the center of Tropical Storm Nock-Ten as it makes its way through the South China Sea and two landfalls on Hainan Island and in Vietnam.
Bands of strong thunderstorms that make up tropical storm Nock-ten were visible in an infrared image captured on July 28 by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. The colder the cloud tops, the higher the thunderstorms and the stronger they are, and cloud top temperatures over a large ...
Water isn't the only thing pouring over Niagara Falls. Pollution from fires in Ontario, Canada is also making the one thousand mile trip, while being measured by NASA's Aqua satellite.
One instrument that flies aboard two of NASA's satellites has provided two views of the pollution from the fires in Ontario. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS instrument, flies onboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. MODIS has provided a visible look at the smoke and pollution that has spread over Niagara Falls and east to Nova Scotia.
As of July 20, the Canadian ...