(Press-News.org) The nature of the connective tissue surrounding lung cancer nests can help predict the aggressiveness of squamous cell carcinoma, according to research published in the September issue of the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC).
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the major cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide; its two major subtypes are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC). Although many reports have described the prognostic markers for adenocarcinoma, less research has been done into prognostic markers for SqCC.
In the study, researchers from Japan's National Cancer Center Hospital East and Keio University found that the prognosis for lung cancer patients with SqCC tumors surrounded by "fibrous stroma" was significantly worse than for patients whose SqCC cells were surrounded by "thin stroma."
Of the 220 patients whose tissue specimens were reviewed, 85 had fibrous stroma -- that is, stroma wider than some cancer nests and intermingled with plump fibroblast and/or collagen fibers -- and 135 had thin stroma, narrower than the cancer nest and composed of thin collagen-fiber lamellae or infiltrative lymphocytes. All had undergone a complete resection for a solitary lesion and were diagnosed as having a pathologic stage I disease. Patients who had received preoperative chemotherapy
or preoperative thoracic radiation were excluded.
The 5-year recurrence-free survival rate was 70% for patients with thin stroma and 50% for patients with fibrous stroma. The 5-year overall survival rate was 72.3% for thin stroma cases and 55.5% for those with fibrous stroma.
SqCC tumors surrounded by fibrous stroma showed reduced expression of E-cadherin and increased expression of laminin-5y2 and matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7), proteins that have been found to increase cell motility and invasiveness.
"Elucidating whether the peritumoral stroma of lung SqCC contributes to cancer progression would be meaningful for the development of treatment targeting the tumor microenvironment and tailored to the histological subtype," researchers wrote.
###
Supported, in part, by a Grant-in-Aid for Cancer Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and
Welfare of Japan and a Grant-in-Aid for the Third Term Comprehensive 10-year Strategy for Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan.
About the Journal of Thoracic Oncology:
The Journal of Thoracic Oncology (JTO) is the official monthly journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC). It is a valuable resource for medical specialists and scientists who focus on the detection, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer. It emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach, including original research (clinical trials and translational or basic research), reviews and opinion pieces.
To learn more about the JTO please visit http://journals.lww.com/jto/pages/default.aspx.
About the IASLC:
The Denver-based International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) is the only global organization dedicated to the study of lung cancer. Founded in 1972, the association's membership includes more than 3,500 lung cancer specialists in 80 countries.
IASLC members promote the study of etiology, epidemiology, prevention, diagnosis, treatment and all other aspects of lung cancer and thoracic malignancies. IASLC disseminates information about lung cancer to scientists, members of the medical community and the public, and uses all available means to eliminate lung cancer as a health threat for the individual patients and throughout the world. Membership is open to any physician, health professional or scientist interested in lung cancer.
To learn more about IASLC please visit http://iaslc.org/
Fibrous stroma associated with poor prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
2011-09-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wrong Site Surgeries a Troubling Problem for Patients in North Carolina
2011-09-02
Operating on the wrong side of a patient's body is a horrible mistake that should never happen. Unfortunately, it occurs more often than you think. Based on data submitted to the Joint Commission Center for Transforming Healthcare, wrong site surgeries and procedures occur nearly 40 times per week across the U.S.
The aftermath of wrong site and wrong side surgeries are devastating. In addition to the pain of additional surgery and a lifetime of disfigurement, these mistakes can leave lasting emotional scars. Victims of this type of error may have grounds for a surgery ...
Insect gut microbe with a molecular iron reservoir
2011-09-02
Microbes are omnipresent on earth. They are found as free-living microorganisms as well as in communities with other higher organisms. Thanks to modern biological techniques we are now able to address the complex communities and study the role of individual microorganisms and enzymes in more detail.
Microbacterium arborescens is a bacterium, which can be found in the guts of herbivorous caterpillars. The Department of Bioorganic Chemistry at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology studies interactions between insects and microorganisms which live in their digestive ...
Defense of Drug Possession and Drug Distribution Cases
2011-09-02
Under Virginia law prosecutors bear the burden to prove each and every element of a crime beyond a reasonable doubt. In short, that means they bear the burden of excluding every reasonable hypothesis of innocence.
In drug cases there are generally three prevailing defenses. Each defense is fact driven so although a defense may work in one case it may not actually work on all. The three prevailing defenses in drug cases are (1) search and seizure issues (2) possession issues and (3) whether the commonwealth can prove that the substance found is illegal.
All searches ...
Perception of facial expressions differs across cultures
2011-09-02
WASHINGTON — Facial expressions have been called the "universal language of emotion," but people from different cultures perceive happy, sad or angry facial expressions in unique ways, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
"By conducting this study, we hoped to show that people from different cultures think about facial expressions in different ways," said lead researcher Rachael E. Jack, PhD, of the University of Glasgow. "East Asians and Western Caucasians differ in terms of the features they think constitute an angry face ...
Missouri Lawmakers Consider Comprehensive Driver Texting Ban
2011-09-02
Distracted driving takes a horrible toll on innocent Missouri drivers every year. It does not matter whether the distraction comes from applying makeup, checking a map, talking to a passenger or changing a radio station; a moment's negligence, even at moderate speeds, is enough for a car or truck to miss a stop sign or veer into an opposing lane and cause a serious or fatal auto accident. Missouri personal injury attorneys are all too familiar with the horrific harm that such accidents can cause to injury victims and surviving family members.
Personal electronic devices ...
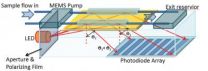
Faster diagnostics through cheap, ultra-portable blood testing
2011-09-02
WASHINGTON, Sept. 1—Blood tests are important diagnostic tools. They accurately tease-out vanishingly small concentrations of proteins and other molecules that help give a picture of overall health or signal the presence of specific diseases. Current testing procedures, however, are expensive and time-consuming, while sophisticated test equipment is bulky and difficult to transport.
Now, a team of researchers from the University of Toledo in Ohio has addressed all these drawbacks by developing a low-cost, portable technique that is able to quickly and reliably detect ...
Dangers on Missouri Highways: Unsecured Truck Loads
2011-09-02
It might seem like an accident that could only happen in a horror movie, but the reality of unsecured cargo is much more serious and more prevalent than most people assume. AAA reported that around 25,000 vehicle accidents and 80-90 deaths occur as a direct result of unsecured cargo per year. Unsecured cargo is essentially insufficient stability of the materials a trucker is transporting.
Typically, materials transported by 18-wheelers include steel coils, lumber, auto parts and various construction supplies, but the list can also extends to liquid or hazardous materials ...
Getting the Lead Out: Protecting Children From Dangerous Toys
2011-09-02
How do you protect your child's safety when there are 30,000 tons of potentially dangerous toys pouring into the United States from foreign countries every year? These boatloads of foreign toys account for 95 percent of the toys sold in the U.S. every year -- and many of them cause serious injuries to children.
Of course, American-made toys can cause children's injuries too. Regardless of their origin, toys should not put children at undue risk of injury.
Trouble in Toyland Report
That's why a leading consumer advocacy group, U.S. PIRG, tries to educate the public ...
Lung cancer ALK rearrangement may predict pemetrexed efficacy, study shows
2011-09-02
Patients with ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) responded significantly better to pemetrexed (brand name: Alimta) than patients whose cancer did not show ALK translocation, according to research published in the September issue of the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC).
Lung adenocarcinoma can display genetic mutations, including anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. Knowing whether the tumor displays ...
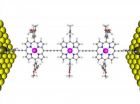
The quantum tunneling effect leads electron transport in porphyrins
2011-09-02
Porphyrins are organic molecules that appear in the central region of
macromolecules such as chlorophyll and hemoglobin, and have a metal atom
at their center that determines their specific function. The importance of these molecules
in the field of molecular electronics lies in their "ease of transfer
electrons from one region to another" explains the responsible of the work at the Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology Research Center (a joint research center of the CSIC, the University of Oviedo and the Government of the Principality of Asturias) Víctor Manuel García. ...